ASTM E1226-10
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Explosibility of Dust Clouds
Standard Test Method for Explosibility of Dust Clouds
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
This test method provides a procedure for performing laboratory tests to evaluate deflagration parameters of dusts.
The data developed by this test method may be used for the purpose of sizing deflagration vents in conjunction with the nomographs published in NFPA 68, ISO 6184/1, or VDI 3673.
The values obtained by this testing technique are specific to the sample tested and the method used and are not to be considered intrinsic material constants.
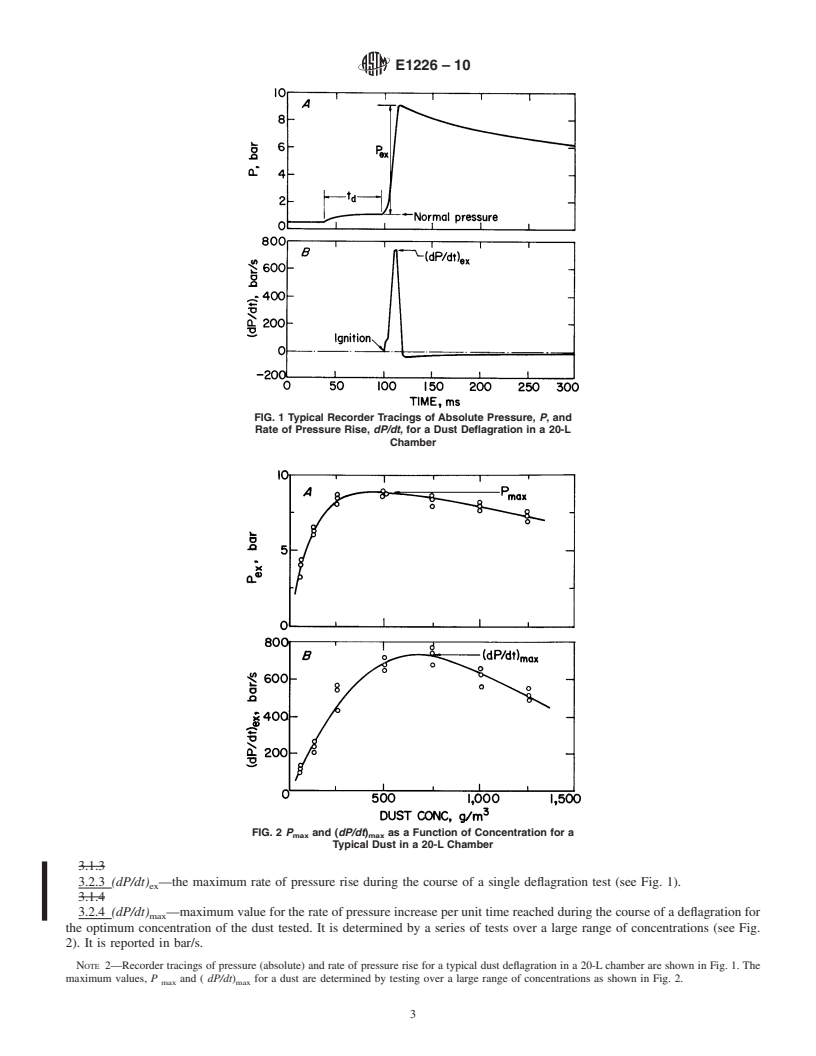
For hard-to-ignite dusts with low KSt-values, a very strong ignitor may overdrive a 20-L chamber, as discussed in E1515 and Ref 2. If a dust has measurable (nonzero) Pmax- and KSt-values with a 5000 or 10 000-J ignitor but not with a 2500-J ignitor in a 20-L chamber, this may be an overdriven system. In this case, it is recommended that the dust be tested with a 10 000-J ignitor in a larger chamber such as a 1-m3 chamber to determine if it is actually explosible.
SCOPE
1.1 Purpose. The purpose of this test method is to provide standard test methods for characterizing the “explosibility” of dust clouds in two ways, first by determining if a dust is “explosible,” meaning a cloud of dust dispersed in air is capable of propagating a deflagration; or, if explosible, determining the degree of “explosibility,” meaning the potential explosion hazard of a dust cloud as characterized by the dust explosibility parameters, maximum explosion pressure, Pmax ; maximum rate of pressure rise, (dP/dt)max; and explosibility index, KSt.
1.2 Limitations. Results obtained by the application of the methods of this standard pertain only to certain combustion characteristics of dispersed dust clouds. No inference should be drawn from such results relating to the combustion characteristics of dusts in other forms or conditions (e.g., ignition temperature or spark ignition energy of dust clouds, ignition properties of dust layers on hot surfaces, ignition of bulk dust in heated environments, etc.)
1.3 Use. It is intended that results obtained by application of this test be used as elements of an explosion risk assessment that takes into account other pertinent risk factors; and in the specification of explosion prevention systems (see, for example NFPA 68, NFPA 69, and NFPA 654) when used in conjunction with approved or recognized design methods by those skilled in the art.
Note 1—Historically, the evaluation of the deflagration parameters of maximum pressure and maximum rate of pressure rise has been done using a 1.2-L Hartmann Apparatus. Test Method E789, which describes this method, has been withdrawn. The use of data obtained from the test method in the design of explosion protection systems is not recommended.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: E1226 – 10
Standard Test Method for
1
Explosibility of Dust Clouds
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E1226; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (ϵ) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
INTRODUCTION
Particulate solids of combustible materials present a significant risk of dust explosion if suspended
in air and subjected to an ignition source. The methods of this standard can be used to determine if
adisperseddustcloudis“explosible”and,ifso,towhatdegreeitisexplosible,i.e.its“explosibility.”
Knowledge that a dust may be explosible if dispersed as a dust cloud is important in the conduct of
a process hazard safety review. Contained herein is a screening test procedure for the purpose of
determining whether a dust sample is explosible.
If a dust is explosible, the explosibility parameters, maximum explosion pressure, P ; maximum
max
rate of pressure rise, (dP/dt) ; and explosibility index, K , are useful in the design of explosion
max St
prevention and control measures as described in national (NFPA) and international (ISO, CEN and
others) explosion protection standards.
1. Scope NFPA68,NFPA69,andNFPA654)whenusedinconjunction
with approved or recognized design methods by those skilled
1.1 Purpose. The purpose of this test method is to provide
in the art.
standard test methods for characterizing the “explosibility” of
dust clouds in two ways, first by determining if a dust is
NOTE 1—Historically, the evaluation of the deflagration parameters of
“explosible,” meaning a cloud of dust dispersed in air is
maximum pressure and maximum rate of pressure rise has been done
using a 1.2-L Hartmann Apparatus. Test Method E789, which describes
capable of propagating a deflagration; or, if explosible, deter-
this method, has been withdrawn. The use of data obtained from the test
mining the degree of “explosibility,” meaning the potential
methodinthedesignofexplosionprotectionsystemsisnotrecommended.
explosion hazard of a dust cloud as characterized by the dust
explosibility parameters, maximum explosion pressure, P ; 1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
max
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
maximum rate of pressure rise, (dP/dt) ; and explosibility
max
index, K . standard.
St
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
1.2 Limitations. Results obtained by the application of the
methods of this standard pertain only to certain combustion safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
characteristicsofdisperseddustclouds.Noinferenceshouldbe
drawn from such results relating to the combustion character- priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
istics of dusts in other forms or conditions (e.g., ignition
temperature or spark ignition energy of dust clouds, ignition
2. Referenced Documents
properties of dust layers on hot surfaces, ignition of bulk dust
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
in heated environments, etc.)
D3173 Test Method for Moisture in theAnalysis Sample of
1.3 Use.Itisintendedthatresultsobtainedbyapplicationof
Coal and Coke
this test be used as elements of an explosion risk assessment
D3175 Test Method for Volatile Matter in the Analysis
that takes into account other pertinent risk factors; and in the
Sample of Coal and Coke
specificationofexplosionpreventionsystems(see,forexample
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee E27 on Hazard
Potential of Chemicals and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E27.05 on
2
Explosibility and Ignitability of Dust Clouds. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved Jan. 1, 2010. Published March 2010. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
approved in 1988. Last previous edition approved in 2009 as E1226–09. DOI: Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
10.1520/E1226-10. the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E1226 – 10
E789 TestMethodforDustExplosionsina1.2-LitreClosed 3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3
Cylindrical Vessel 3.2.1 P —the maximum explosion pressure (above the
ex
E1445 TerminologyRelatingtoHazardPotentialofChemi- pressureinthevesselatthetimeofignition)reachedduringthe
cals course of a single deflagration test (see Fig. 1).
E1515 TestMethodforMinimu
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:E1226–09 Designation: E1226 – 10
Standard Test Method for
Pressure and Rate of Pressure Rise for Combustible
1
DustsExplosibility of Dust Clouds
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E1226; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
INTRODUCTION
The primary objective for the laboratory determination of the dust deflagration index, K , the
St
maximum pressure, P
Particulate solids of combustible materials present a significant risk of dust explosion if suspended
in air and subjected to an ignition source. The methods of this standard can be used to determine if
adisperseddustcloudis“explosible”and,ifso,towhatdegreeitisexplosible,i.e.its“explosibility.”
Knowledge that a dust may be explosible if dispersed as a dust cloud is important in the conduct of
a process hazard safety review. Contained herein is a screening test procedure for the purpose of
determining whether a dust sample is explosible.
If a dust is explosible, the explosibility parameters, maximum explosion pressure, P , and the
max
maximumrateofpressurerise,(dP/dt) ,istheuseofthesevaluesfor
; maximum rate of pressure rise, (dP/dt)
max
the design of protection systems. These parameters provide a measure of the potential severity of a
deflagration of a combustible dust-air mixture.These parameters are a function of many factors, such
as the turbulence, concentration, and homogeneity of the dust-air mixture; the type, energy, and
locationoftheignitionsource;thegeometryofthetestvessel;theparticlesizedistributionofthedust;
and the initial temperature and pressure of the tested mixture. Therefore, it is necessary to develop a
standard laboratory test method, the data from which can be referenced against data from large-scale
testing. For information on the sizing of deflagration vents, see NFPA 68.
This test method describes procedures for explosibility testing of dusts in laboratory chambers that
have volumes of 20 Lor greater. It is the purpose of this test method to provide information that can
be used to predict the effects of an industrial scale deflagration of a dust-air mixture without requiring
large-scale tests. ; and explosibility index, K , are useful in the design of explosion prevention and
St
control measures as described in national (NFPA) and international (ISO, CEN and others) explosion
protection standards.
1. Scope
1.1This test method is designed to determine the deflagration parameters of a combustible dust-air mixture within a
near-spherical closed vessel of 20 L or greater volume. The parameters measured are the maximum pressure and the maximum
rate of pressure rise.
1.2Dataobtainedfromthistestmethodprovidearelativemeasureofdeflagrationcharacteristics.Thedatahavealsobeenshown
to be applicable to the design of protective measures, such as deflagration venting (1).
1.3This test method should be used to measure and describe the properties of materials in response to heat and flame under
controlled laboratory conditions and should not be used to describe or appraise the fire hazard or fire risk of materials, products,
orassembliesunderactualfireconditions.However,resultsofthistestmaybeusedaselementsofafireriskassessmentthattakes
into account all of the factors that are pertinent to an assessment of the fire hazard of a particular end use.
1.1 Purpose. The purpose of this test method is to provide standard test methods for characterizing the “explosibility” of dust
cloudsintwoways,firstbydeterminingifadustis“explosible,”meaningacloudofdustdispersedinairiscapableofpropagating
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E27 on Hazard Potential of Chemicals and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E27.05 on
Explosibility and Ignitability of Dust Clouds.
´1
Current edition approved Nov. 15, 2009. Published January 2010. Originally approved in 1988. Last previous edition approved in 2005 as E1226–05 . DOI:
10.1520/E1226-09.
Current edition approved Jan. 1, 2010. Published March 2010. Originally approved in 1988. Last previous edition approved in 2009 as E1226–09. DOI:
10.1520/E1226-09.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E1226 – 10
a deflagration; or, if explosible, determining the deg
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.