ASTM A193/A193M-14a
(Specification)Standard Specification for Alloy-Steel and Stainless Steel Bolting for High Temperature or High Pressure Service and Other Special Purpose Applications
Standard Specification for Alloy-Steel and Stainless Steel Bolting for High Temperature or High Pressure Service and Other Special Purpose Applications
ABSTRACT
This specification covers alloy steel and stainless steel bolting material for pressure vessels, valves, flanges, and fittings for high temperature or high pressure service, or other special purpose applications. Ferritic steels shall be properly heat treated as best suits the high temperature characteristics of each grade. Immediately after rolling or forging, the bolting material shall be allowed to cool to a temperature below the cooling transformation range. The chemical composition requirements for each alloy are presented in details. The steel shall not contain an unspecified element for ordered grade to the extent that the steel conforms to the requirements of another grade for which that element is a specified element. The tensile property and hardness property requirements are discussed, the tensile property requirement is highlighted by a full size fasteners, wedge tensile testing.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification2 covers alloy and stainless steel bolting for pressure vessels, valves, flanges, and fittings for high temperature or high pressure service, or other special purpose applications. See Specification A962/A962M for the definition of bolting. Bars and wire shall be hot-wrought and may be further processed by centerless grinding or by cold drawing. Austenitic stainless steel may be carbide solution treated or carbide solution treated and strain-hardened. When strain hardened austenitic steel is ordered, the purchaser should take special care to ensure that Appendix X1 is thoroughly understood.
1.2 Several grades are covered, including ferritic steels and austenitic stainless steels designated B5, B8, and so forth. Selection will depend upon design, service conditions, mechanical properties, and high temperature characteristics.
1.3 The following referenced general requirements are indispensable for application of this specification: Specification A962/A962M.
Note 1: The committee formulating this specification has included several steel types that have been rather extensively used for the present purpose. Other compositions will be considered for inclusion by the committee from time to time as the need becomes apparent.
Note 2: For grades of alloy-steel bolting suitable for use at the lower range of high temperature applications, reference should be made to Specification A354.
Note 3: For grades of alloy-steel bolting suitable for use in low temperature applications, reference should be made to Specification A320/A320M.
1.4 Nuts for use with bolting are covered in Section 13.
1.5 Supplementary Requirements are provided for use at the option of the purchaser. The supplementary requirements shall apply only when specified in the purchase order or contract.
1.6 This specification is expressed in both inch-pound units and in SI units; however, unless the purchase order or contract specifies the applicable M specification designation (SI units), the inch-pound units shall apply.
1.7 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the text, the SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:A193/A193M −14a
StandardSpecification for
Alloy-Steel and Stainless Steel Bolting for High Temperature
or High Pressure Service and Other Special Purpose
Applications
This standard is issued under the fixed designationA193/A193M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope* 1.5 Supplementary Requirements are provided for use at the
option of the purchaser. The supplementary requirements shall
1.1 This specification covers alloy and stainless steel bolt-
apply only when specified in the purchase order or contract.
ing for pressure vessels, valves, flanges, and fittings for high
1.6 This specification is expressed in both inch-pound units
temperature or high pressure service, or other special purpose
and in SI units; however, unless the purchase order or contract
applications. See Specification A962/A962M for the definition
specifies the applicable M specification designation (SI units),
of bolting. Bars and wire shall be hot-wrought and may be
the inch-pound units shall apply.
further processed by centerless grinding or by cold drawing.
Austenitic stainless steel may be carbide solution treated or
1.7 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units
carbide solution treated and strain-hardened. When strain
are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the text, the
hardened austenitic steel is ordered, the purchaser should take
SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each
special care to ensure that Appendix X1 is thoroughly under-
system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system
stood.
shall be used independently of the other. Combining values
from the two systems may result in non-conformance with the
1.2 Several grades are covered, including ferritic steels and
standard.
austenitic stainless steels designated B5, B8, and so forth.
Selection will depend upon design, service conditions, me-
2. Referenced Documents
chanical properties, and high temperature characteristics.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
1.3 The following referenced general requirements are in-
A153/A153M Specification for Zinc Coating (Hot-Dip) on
dispensable for application of this specification: Specification
Iron and Steel Hardware
A962/A962M.
A194/A194M Specification for Carbon andAlloy Steel Nuts
NOTE 1—The committee formulating this specification has included
for Bolts for High Pressure or High Temperature Service,
several steel types that have been rather extensively used for the present
or Both
purpose. Other compositions will be considered for inclusion by the
A320/A320M Specification for Alloy-Steel and Stainless
committee from time to time as the need becomes apparent.
Steel Bolting for Low-Temperature Service
NOTE 2—For grades of alloy-steel bolting suitable for use at the lower
A354 Specification for Quenched and TemperedAlloy Steel
range of high temperature applications, reference should be made to
Specification A354.
Bolts, Studs, and Other Externally Threaded Fasteners
NOTE 3—For grades of alloy-steel bolting suitable for use in low
A788/A788M Specification for Steel Forgings, General Re-
temperature applications, reference should be made to Specification
quirements
A320/A320M.
A962/A962M Specification for Common Requirements for
1.4 Nuts for use with bolting are covered in Section 13.
Bolting Intended for Use at Any Temperature from Cryo-
genic to the Creep Range
B633 Specification for Electrodeposited Coatings of Zinc on
Iron and Steel
This specification is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee A01 on Steel,
B695 Specification for Coatings of Zinc Mechanically De-
Stainless Steel and Related Alloysand is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
A01.22 on Steel Forgings andWrought Fittings for PipingApplications and Bolting
posited on Iron and Steel
Materials for Piping and Special Purpose Applications.
Current edition approved Nov. 15, 2014. Published December 2014. Originally
approved in 1936. Last previous edition approved in 2014 as A193/A193M–14. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
DOI: 10.1520/A0193_A0193M-14A. contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
For ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code applications, see related Specifi- Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
cation SA-193 in Section II of that Code. the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
A193/A193M−14a
B696 Specification for Coatings of Cadmium Mechanically 3. General Requirements and Ordering Information
Deposited
3.1 The inquiry and orders shall include the following, as
B766 Specification for Electrodeposited Coatings of Cad-
required, to describe the desired material adequately:
mium
3.1.1 Heat-treated condition (that is carbide solution treated
E18 Test Methods for Rockwell Hardness of Metallic Ma-
(Class 1), carbide solution treated after finishing (Class 1A),
terials
and carbide solution treated and strain-hardened (Classes 2, 2B
E21 TestMethodsforElevatedTemperatureTensionTestsof
and 2C), for the austenitic stainless steels; Classes 1B and 1C
Metallic Materials
apply to the carbide solution-treated nitrogen-bearing stainless
E112 Test Methods for Determining Average Grain Size
steels; Class 1D applies to material carbide solution treated by
E139 Test Methods for Conducting Creep, Creep-Rupture,
cooling rapidly from the rolling temperature),
and Stress-Rupture Tests of Metallic Materials
3.1.2 Description of items required (that is, bars, bolts,
E150 Recommended Practice for Conducting Creep and
screws, or studs),
Creep-Rupture Tension Tests of Metallic Materials Under
3.1.3 Nuts, if required by purchaser, in accordance with
Conditions of Rapid Heating and ShortTimes(Withdrawn
4 13.1,
1984)
3.1.4 Supplementary requirements, if any, and
E151 Recommended Practice for Tension Tests of Metallic
3.1.5 Special requirements, in accordance with 6.1.5.1,
Materials at Elevated Temperatures with Rapid Heating
6.2.6, 8.1, and 13.1.
and Conventional or Rapid Strain Rates (Withdrawn
1984)
3.2 Coatings—Coatings are prohibited unless specified by
E292 Test Methods for Conducting Time-for-Rupture Notch
thepurchaser(SeeSupplementaryRequirementsS13andS14).
Tension Tests of Materials
When coated fasteners are ordered the purchaser should take
E328 Test Methods for Stress Relaxation for Materials and
special care to ensure that Appendix X2 is thoroughly under-
Structures
stood.
E566 PracticeforElectromagnetic(EddyCurrent)Sortingof
Ferrous Metals
4. Common Requirements
E709 Guide for Magnetic Particle Testing
4.1 Bolting supplied to this specification shall conform to
F606 Test Methods for Determining the Mechanical Proper-
the requirements of Specification A962/A962M. These re-
ties of Externally and Internally Threaded Fasteners,
quirements include test methods, finish, thread dimensions,
Washers, Direct Tension Indicators, and Rivets
macroetch (alloy steels only), marking, certification, optional
F1940 Test Method for Process Control Verification to
supplementary requirements, and others. Failure to comply
Prevent Hydrogen Embrittlement in Plated or Coated
with the requirements of Specification A962/A962M consti-
Fasteners
tutes nonconformance with this specification. In case of con-
F1941 Specification for Electrodeposited Coatings on
flict between this specification and Specification A962/
Threaded Fasteners (Unified Inch Screw Threads (UN/
A962M, this specification shall prevail.
UNR))
F2329 Specification for Zinc Coating, Hot-Dip, Require-
5. Manufacture (Process)
ments for Application to Carbon and Alloy Steel Bolts,
Screws, Washers, Nuts, and Special Threaded Fasteners
5.1 Melting—See Specification A962/A962M for require-
2.2 ASME Standards:
ments.
B18.2.1 Square and Hex Bolts and Screws
5.2 Quality—See Specification A962/A962M for require-
B18.2.3.3M Metric Heavy Hex Screws
ments.
B18.3 Hexagon Socket and Spline Socket Screws
B18.3.1M Metric Socket Head Cap Screws
6. Heat Treatment
2.3 AIAG Standard:
AIAG B-5 02.00 Primary Metals Identification TagApplica- 6.1 Ferritic Steels:
tion Standard 6.1.1 Ferriticsteelsshallbeallowedtocooltoatemperature
below the cooling transformation range immediately after
rollingorforging.Materialsshallthenbeuniformlyreheatedto
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
the proper temperature to refine the grain (a group thus
www.astm.org.
Available from American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), ASME
reheated being known as a quenching charge), quenched in a
International Headquarters, Two Park Ave., New York, NY 10016-5990, http://
liquid medium under substantially uniform conditions for each
www.asme.org.
6 quenching charge, and tempered. The minimum tempering
Available fromAutomotive IndustryAction Group (AIAG), 26200 Lahser Rd.,
temperature shall be as specified in Tables 2 and 3.
Suite 200, Southfield, MI 48033, http://www.aiag.org.
A193/A193M−14a
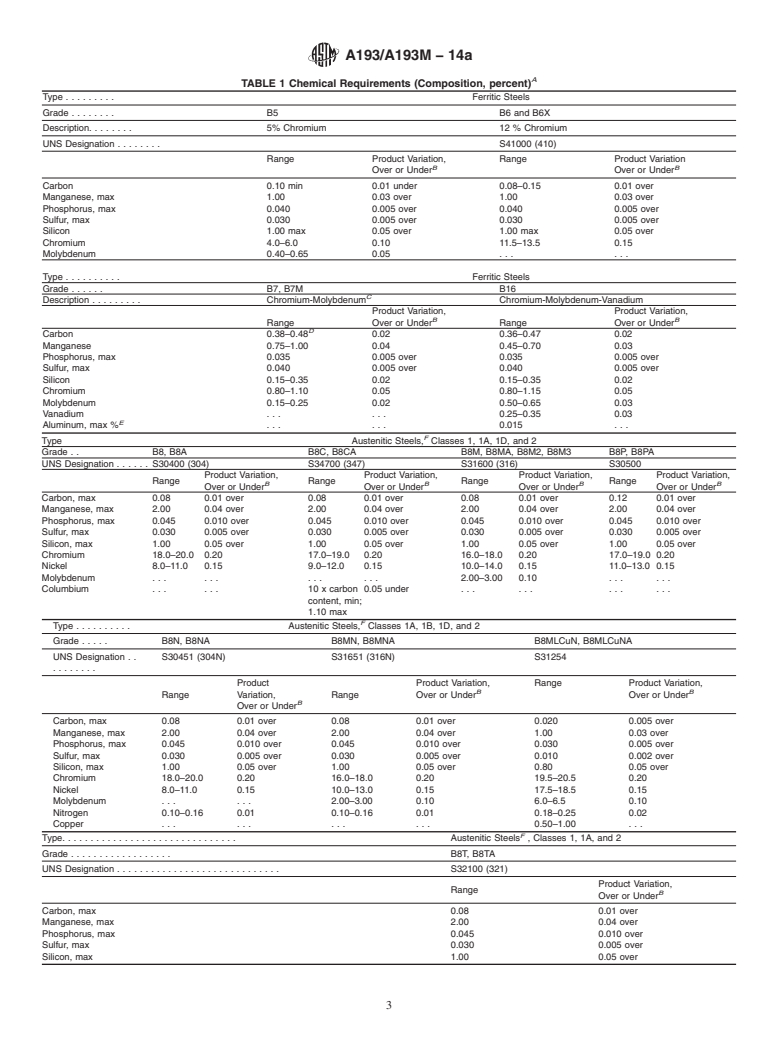
A
TABLE 1 Chemical Requirements (Composition, percent)
Type . Ferritic Steels
Grade . B5 B6 and B6X
Description. 5% Chromium 12%Chromium
UNS Designation . S41000 (410)
Range Product Variation, Range Product Variation
B B
Over or Under Over or Under
Carbon 0.10 min 0.01 under 0.08–0.15 0.01 over
Manganese, max 1.00 0.03 over 1.00 0.03 over
Phosphorus, max 0.040 0.005 over 0.040 0.005 over
Sulfur, max 0.030 0.005 over 0.030 0.005 over
Silicon 1.00 max 0.05 over 1.00 max 0.05 over
Chromium 4.0–6.0 0.10 11.5–13.5 0.15
Molybdenum 0.40–0.65 0.05 . . . . . .
Type . Ferritic Steels
Grade . B7, B7M B16
C
Description . Chromium-Molybdenum Chromium-Molybdenum-Vanadium
Product Variation, Product Variation,
B B
Range Over or Under Range Over or Under
D
Carbon 0.38–0.48 0.02 0.36–0.47 0.02
Manganese 0.75–1.00 0.04 0.45–0.70 0.03
Phosphorus, max 0.035 0.005 over 0.035 0.005 over
Sulfur, max 0.040 0.005 over 0.040 0.005 over
Silicon 0.15–0.35 0.02 0.15–0.35 0.02
Chromium 0.80–1.10 0.05 0.80–1.15 0.05
Molybdenum 0.15–0.25 0.02 0.50–0.65 0.03
Vanadium . . . . . . 0.25–0.35 0.03
E
Aluminum, max % . . 0.015 .
F
Type Austenitic Steels, Classes 1, 1A, 1D, and 2
Grade . . B8, B8A B8C, B8CA B8M, B8MA, B8M2, B8M3 B8P, B8PA
UNS Designation . S30400 (304) S34700 (347) S31600 (316) S30500
Product Variation, Product Variation, Product Variation, Product Variation,
Range Range Range Range
B B B B
Over or Under Over or Under Over or Under Over or Under
Carbon, max 0.08 0.01 over 0.08 0.01 over 0.08 0.01 over 0.12 0.01 over
Manganese, max 2.00 0.04 over 2.00 0.04 over 2.00 0.04 over 2.00 0.04 over
Phosphorus, max 0.045 0.010 over 0.045 0.010 over 0.045 0.010 over 0.045 0.010 over
Sulfur, max 0.030 0.005 over 0.030 0.005 over 0.030 0.005 over 0.030 0.005 over
Silicon, max 1.00 0.05 over 1.00 0.05 over 1.00 0.05 over 1.00 0.05 over
Chromium 18.0–20.0 0.20 17.0–19.0 0.20 16.0–18.0 0.20 17.0–19.0 0.20
Nickel 8.0–11.0 0.15 9.0–12.0 0.15 10.0–14.0 0.15 11.0–13.0 0.15
Molybdenum . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.00–3.00 0.10 . . . . . .
Columbium . . . . . . 10 x carbon 0.05 under . . . . . . . . . . . .
content, min;
1.10 max
F
Type . Austenitic Steels, Classes 1A, 1B, 1D, and 2
Grade . B8N, B8NA B8MN, B8MNA B8MLCuN, B8MLCuNA
UNS Designation . . S30451 (304N) S31651 (316N) S31254
........
Product Product Variation, Range Product Variation,
B B
Range Variation, Range Over or Under Over or Under
B
Over or Under
Carbon, max 0.08 0.01 over 0.08 0.01 over 0.020 0.005 over
Manganese, max 2.00 0.04 over 2.00 0.04 over 1.00 0.03 over
Phosphorus, max 0.045 0.010 over 0.045 0.010 over 0.030 0.005 over
Sulfur, max 0.030 0.005 over 0.030 0.005 over 0.010 0.002 over
Silicon, max 1.00 0.05 over 1.00 0.05 over 0.80 0.05 over
Chromium 18.0–20.0 0.20 16.0–18.0 0.20 19.5–20.5 0.20
Nickel 8.0–11.0 0.15 10.0–13.0 0.15 17.5–18.5 0.15
Molybdenum . . . . . . 2.00–3.00 0.10 6.0–6.5 0.10
Nitrogen 0.10–0.16 0.01 0.10–0.16 0.01 0.18–0.25 0.02
Copper . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.50–1.00 . . .
F
Type. Austenitic Steels , Classes 1, 1A, and 2
Grade . B8T,B8TA
UNS Designation . S32100 (321)
Product Variation,
Range
B
Over or Under
Carbon, max 0.08 0.01 over
Manganese, max 2.00 0.04 over
Phosphorus, max 0.045 0.010 over
Sulfur, max 0.030 0.005 over
Silicon, max 1.00 0.05 over
A193/A193M−14a
TABLE1 Continued
F
Type. Austenitic Steels , Classes 1, 1A, and 2
Grade . B8T,B8TA
UNS Designation . S32100 (321)
Product Variation,
Range
B
Over or Under
Chromium 17.0–19.0 0.20
Nickel 9.0–12.0 0.15
Titanium 5 x (C + N) min, 0.70 max 0.05 under
Nitrogen 0.10 max . . .
F
Type Austenitic Steels , Classes 1C and 1D
Grade B8R, B8RA B8S, B8SA
UNS Designation S20910 S21800
Product Variation, Product Variation,
Range Range
B B
Over or Under Over or Under
Carbon, max 0.06 0.01 over 0.10 0.01 over
Manganese 4.0–6.0 0.05 7.0–9.0 0.06
Phosphorus, max 0.045 0.005 over 0.060 0.005 over
Sulfur, max 0.030 0.005 over 0.030 0.005 over
Silicon 1.00 max 0.05 over 3.5–4.5 0.15
Chromium 20.5–23.5 0.25 16.0–18.0 0.20
Nickel 11.5–13.5 0.15 8.0–9.0 0.10
Molybdenum 1.50–3.00 0.10 . . . . . .
Nitrogen 0.20–0.40 0.02 0.08–0.18 0.01
Columbium + tantalum 0.10–0.30 0.05 . . . . . .
Vanadium 0.10–0.30 0.02 . . . . . .
F
Type Austenitic Steels , Classes 1, 1A and 1D
Grade B8LN, B8LNA B8MLN, B8MLNA
UNS Designation S30453 S31653
Product Variation, Product Variation,
Range Range
B B
Over or Under Over or Under
Carbon, max 0.030 0.005 over 0.030 0.005 over
Manganese 2.00 0.04 over 2.00 0.04 over
Phosphorus, max 0.045 0.010 over 0.045 0.010 over
Sulfur, max 0.030 0.005 over 0.030 0.005 over
Silicon 1.00 0.05 over 1.00 0.05 over
Chromium 18.0–20.0 0.20 16.0–18.0 0.20
Nickel 8.0–11.0 0.15 10.0–13.0 0.15
Molybdenum . . . . . . 2.00–3.00 0.10
Nitrogen 0.10–0.16 0.01 0.10–0.16 0.01
F
Type Austenitic Steels , Classes 1, 1A and 1D
Grade B8CLN, B8CLNA B8ML4CuN, B8ML4CuNA
UNS Designation S34751 (347LN) S31730
Product Variation, Product Variation
Range Range
B B
Over or Under Over or Under
Carbon, max 0.005–0.020 0.002 under, 0.030 0.005 over
0.005 over
Manganese, max 2.00 0.04 over 2.00 0.04 over
Phosphorus, max 0.0
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: A193/A193M − 14 A193/A193M − 14a
Standard Specification for
Alloy-Steel and Stainless Steel Bolting for High Temperature
or High Pressure Service and Other Special Purpose
Applications
This standard is issued under the fixed designation A193/A193M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope*
1.1 This specification covers alloy and stainless steel bolting for pressure vessels, valves, flanges, and fittings for high
temperature or high pressure service, or other special purpose applications. See Specification A962/A962M for the definition of
bolting. Bars and wire shall be hot-wrought and may be further processed by centerless grinding or by cold drawing. Austenitic
stainless steel may be carbide solution treated or carbide solution treated and strain-hardened. When strain hardened austenitic steel
is ordered, the purchaser should take special care to ensure that Appendix X1 is thoroughly understood.
1.2 Several grades are covered, including ferritic steels and austenitic stainless steels designated B5, B8, and so forth. Selection
will depend upon design, service conditions, mechanical properties, and high temperature characteristics.
1.3 The following referenced general requirements are indispensable for application of this specification: Specification
A962/A962M.
NOTE 1—The committee formulating this specification has included several steel types that have been rather extensively used for the present purpose.
Other compositions will be considered for inclusion by the committee from time to time as the need becomes apparent.
NOTE 2—For grades of alloy-steel bolting suitable for use at the lower range of high temperature applications, reference should be made to Specification
A354.
NOTE 3—For grades of alloy-steel bolting suitable for use in low temperature applications, reference should be made to Specification A320/A320M.
1.4 Nuts for use with bolting are covered in Section 13.
1.5 Supplementary Requirements are provided for use at the option of the purchaser. The supplementary requirements shall
apply only when specified in the purchase order or contract.
1.6 This specification is expressed in both inch-pound units and in SI units; however, unless the purchase order or contract
specifies the applicable M specification designation (SI units), the inch-pound units shall apply.
1.7 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the text, the SI units
are shown in brackets. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used
independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
A153/A153M Specification for Zinc Coating (Hot-Dip) on Iron and Steel Hardware
A194/A194M Specification for Carbon and Alloy Steel Nuts for Bolts for High Pressure or High Temperature Service, or Both
A320/A320M Specification for Alloy-Steel and Stainless Steel Bolting for Low-Temperature Service
A354 Specification for Quenched and Tempered Alloy Steel Bolts, Studs, and Other Externally Threaded Fasteners
A788/A788M Specification for Steel Forgings, General Requirements
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee A01 on Steel, Stainless Steel and Related Alloysand is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee A01.22
on Steel Forgings and Wrought Fittings for Piping Applications and Bolting Materials for Piping and Special Purpose Applications.
Current edition approved June 1, 2014Nov. 15, 2014. Published June 2014December 2014. Originally approved in 1936. Last previous edition approved in 20122014 as
A193/A193M–12b.–14. DOI: 10.1520/A0193_A0193M-14.10.1520/A0193_A0193M-14A.
For ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code applications, see related Specification SA-193 in Section II of that Code.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
A193/A193M − 14a
A962/A962M Specification for Common Requirements for Bolting Intended for Use at Any Temperature from Cryogenic to the
Creep Range
B633 Specification for Electrodeposited Coatings of Zinc on Iron and Steel
B695 Specification for Coatings of Zinc Mechanically Deposited on Iron and Steel
B696 Specification for Coatings of Cadmium Mechanically Deposited
B766 Specification for Electrodeposited Coatings of Cadmium
E18 Test Methods for Rockwell Hardness of Metallic Materials
E21 Test Methods for Elevated Temperature Tension Tests of Metallic Materials
E112 Test Methods for Determining Average Grain Size
E139 Test Methods for Conducting Creep, Creep-Rupture, and Stress-Rupture Tests of Metallic Materials
E150 Recommended Practice for Conducting Creep and Creep-Rupture Tension Tests of Metallic Materials Under Conditions
of Rapid Heating and Short Times (Withdrawn 1984)
E151 Recommended Practice for Tension Tests of Metallic Materials at Elevated Temperatures with Rapid Heating and
Conventional or Rapid Strain Rates (Withdrawn 1984)
E292 Test Methods for Conducting Time-for-Rupture Notch Tension Tests of Materials
E328 Test Methods for Stress Relaxation for Materials and Structures
E566 Practice for Electromagnetic (Eddy Current) Sorting of Ferrous Metals
E709 Guide for Magnetic Particle Testing
F606 Test Methods for Determining the Mechanical Properties of Externally and Internally Threaded Fasteners, Washers, Direct
Tension Indicators, and Rivets
F1940 Test Method for Process Control Verification to Prevent Hydrogen Embrittlement in Plated or Coated Fasteners
F1941 Specification for Electrodeposited Coatings on Threaded Fasteners (Unified Inch Screw Threads (UN/UNR))
F2329 Specification for Zinc Coating, Hot-Dip, Requirements for Application to Carbon and Alloy Steel Bolts, Screws, Washers,
Nuts, and Special Threaded Fasteners
2.2 ASME Standards:
B18.2.1 Square and Hex Bolts and Screws
B18.2.3.3M Metric Heavy Hex Screws
B18.3 Hexagon Socket and Spline Socket Screws
B18.3.1M Metric Socket Head Cap Screws
2.3 AIAG Standard:
AIAG B-5 02.00 Primary Metals Identification Tag Application Standard
3. General Requirements and Ordering Information
3.1 The inquiry and orders shall include the following, as required, to describe the desired material adequately:
3.1.1 Heat-treated condition (that is carbide solution treated (Class 1), carbide solution treated after finishing (Class 1A), and
carbide solution treated and strain-hardened (Classes 2, 2B and 2C), for the austenitic stainless steels; Classes 1B and 1C apply
to the carbide solution-treated nitrogen-bearing stainless steels; Class 1D applies to material carbide solution treated by cooling
rapidly from the rolling temperature),
3.1.2 Description of items required (that is, bars, bolts, screws, or studs),
3.1.3 Nuts, if required by purchaser, in accordance with 13.1,
3.1.4 Supplementary requirements, if any, and
3.1.5 Special requirements, in accordance with 6.1.5.1, 6.2.6, 8.1, and 13.1.
3.2 Coatings—Coatings are prohibited unless specified by the purchaser (See Supplementary Requirements S13 and S14).
When coated fasteners are ordered the purchaser should take special care to ensure that Appendix X2 is thoroughly understood.
4. Common Requirements
4.1 Bolting supplied to this specification shall conform to the requirements of Specification A962/A962M. These requirements
include test methods, finish, thread dimensions, macroetch (alloy steels only), marking, certification, optional supplementary
requirements, and others. Failure to comply with the requirements of Specification A962/A962M constitutes nonconformance with
this specification. In case of conflict between this specification and Specification A962/A962M, this specification shall prevail.
5. Manufacture (Process)
5.1 Melting—See Specification A962/A962M for requirements.
5.2 Quality—See Specification A962/A962M for requirements.
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on www.astm.org.
Available from American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), ASME International Headquarters, Two Park Ave., New York, NY 10016-5990, http://
www.asme.org.
Available from Automotive Industry Action Group (AIAG), 26200 Lahser Rd., Suite 200, Southfield, MI 48033, http://www.aiag.org.
A193/A193M − 14a
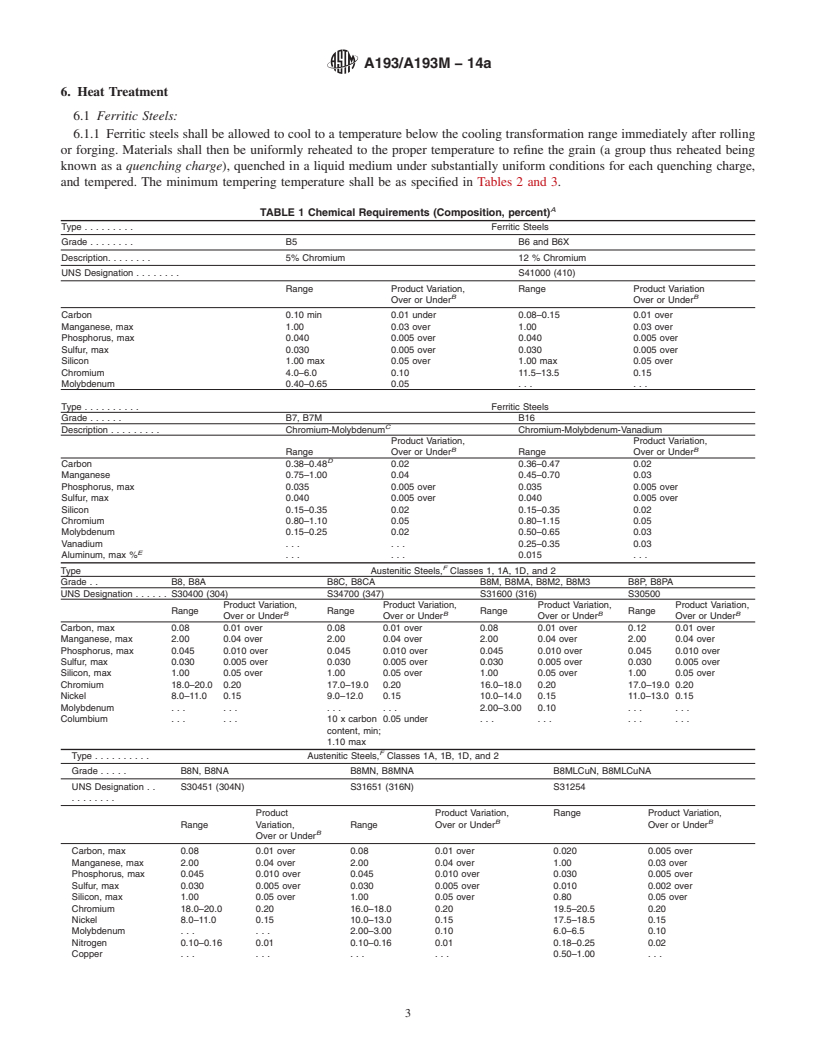
6. Heat Treatment
6.1 Ferritic Steels:
6.1.1 Ferritic steels shall be allowed to cool to a temperature below the cooling transformation range immediately after rolling
or forging. Materials shall then be uniformly reheated to the proper temperature to refine the grain (a group thus reheated being
known as a quenching charge), quenched in a liquid medium under substantially uniform conditions for each quenching charge,
and tempered. The minimum tempering temperature shall be as specified in Tables 2 and 3.
A
TABLE 1 Chemical Requirements (Composition, percent)
Type . . . . . . . . . Ferritic Steels
Grade . . . . . . . . B5 B6 and B6X
Description. . . . . . . . 5% Chromium 12 % Chromium
UNS Designation . . . . . . . . S41000 (410)
Range Product Variation, Range Product Variation
B B
Over or Under Over or Under
Carbon 0.10 min 0.01 under 0.08–0.15 0.01 over
Manganese, max 1.00 0.03 over 1.00 0.03 over
Phosphorus, max 0.040 0.005 over 0.040 0.005 over
Sulfur, max 0.030 0.005 over 0.030 0.005 over
Silicon 1.00 max 0.05 over 1.00 max 0.05 over
Chromium 4.0–6.0 0.10 11.5–13.5 0.15
Molybdenum 0.40–0.65 0.05 . . . . . .
Type . . . . . . . . . . Ferritic Steels
Grade . . . . . . B7, B7M B16
C
Description . . . . . . . . . Chromium-Molybdenum Chromium-Molybdenum-Vanadium
Product Variation, Product Variation,
B B
Range Over or Under Range Over or Under
D
Carbon 0.38–0.48 0.02 0.36–0.47 0.02
Manganese 0.75–1.00 0.04 0.45–0.70 0.03
Phosphorus, max 0.035 0.005 over 0.035 0.005 over
Sulfur, max 0.040 0.005 over 0.040 0.005 over
Silicon 0.15–0.35 0.02 0.15–0.35 0.02
Chromium 0.80–1.10 0.05 0.80–1.15 0.05
Molybdenum 0.15–0.25 0.02 0.50–0.65 0.03
Vanadium . . . . . . 0.25–0.35 0.03
E
Aluminum, max % . . . . . . 0.015 . . .
F
Type Austenitic Steels, Classes 1, 1A, 1D, and 2
Grade . . B8, B8A B8C, B8CA B8M, B8MA, B8M2, B8M3 B8P, B8PA
UNS Designation . . . . . . S30400 (304) S34700 (347) S31600 (316) S30500
Product Variation, Product Variation, Product Variation, Product Variation,
Range Range Range Range
B B B B
Over or Under Over or Under Over or Under Over or Under
Carbon, max 0.08 0.01 over 0.08 0.01 over 0.08 0.01 over 0.12 0.01 over
Manganese, max 2.00 0.04 over 2.00 0.04 over 2.00 0.04 over 2.00 0.04 over
Phosphorus, max 0.045 0.010 over 0.045 0.010 over 0.045 0.010 over 0.045 0.010 over
Sulfur, max 0.030 0.005 over 0.030 0.005 over 0.030 0.005 over 0.030 0.005 over
Silicon, max 1.00 0.05 over 1.00 0.05 over 1.00 0.05 over 1.00 0.05 over
Chromium 18.0–20.0 0.20 17.0–19.0 0.20 16.0–18.0 0.20 17.0–19.0 0.20
Nickel 8.0–11.0 0.15 9.0–12.0 0.15 10.0–14.0 0.15 11.0–13.0 0.15
Molybdenum . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.00–3.00 0.10 . . . . . .
Columbium . . . . . . 10 x carbon 0.05 under . . . . . . . . . . . .
content, min;
1.10 max
F
Type . . . . . . . . . . Austenitic Steels, Classes 1A, 1B, 1D, and 2
Grade . . . . . B8N, B8NA B8MN, B8MNA B8MLCuN, B8MLCuNA
UNS Designation . . S30451 (304N) S31651 (316N) S31254
. . . . . . . .
Product Product Variation, Range Product Variation,
B B
Range Variation, Range Over or Under Over or Under
B
Over or Under
Carbon, max 0.08 0.01 over 0.08 0.01 over 0.020 0.005 over
Manganese, max 2.00 0.04 over 2.00 0.04 over 1.00 0.03 over
Phosphorus, max 0.045 0.010 over 0.045 0.010 over 0.030 0.005 over
Sulfur, max 0.030 0.005 over 0.030 0.005 over 0.010 0.002 over
Silicon, max 1.00 0.05 over 1.00 0.05 over 0.80 0.05 over
Chromium 18.0–20.0 0.20 16.0–18.0 0.20 19.5–20.5 0.20
Nickel 8.0–11.0 0.15 10.0–13.0 0.15 17.5–18.5 0.15
Molybdenum . . . . . . 2.00–3.00 0.10 6.0–6.5 0.10
Nitrogen 0.10–0.16 0.01 0.10–0.16 0.01 0.18–0.25 0.02
Copper . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.50–1.00 . . .
A193/A193M − 14a
TABLE 1 Continued
F
Type. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Austenitic Steels , Classes 1, 1A, and 2
Grade . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . B8T, B8TA
UNS Designation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . S32100 (321)
Product Variation,
Range
B
Over or Under
Carbon, max 0.08 0.01 over
Manganese, max 2.00 0.04 over
Phosphorus, max 0.045 0.010 over
Sulfur, max 0.030 0.005 over
Silicon, max 1.00 0.05 over
Chromium 17.0–19.0 0.20
Nickel 9.0–12.0 0.15
Titanium 5 x (C + N) min, 0.70 max 0.05 under
Nitrogen 0.10 max . . .
F
Type Austenitic Steels , Classes 1C and 1D
Grade B8R, B8RA B8S, B8SA
UNS Designation S20910 S21800
Product Variation, Product Variation,
Range Range
B B
Over or Under Over or Under
Carbon, max 0.06 0.01 over 0.10 0.01 over
Manganese 4.0–6.0 0.05 7.0–9.0 0.06
Phosphorus, max 0.045 0.005 over 0.060 0.005 over
Sulfur, max 0.030 0.005 over 0.030 0.005 over
Silicon 1.00 max 0.05 over 3.5–4.5 0.15
Chromium 20.5–23.5 0.25 16.0–18.0 0.20
Nickel 11.5–13.5 0.15 8.0–9.0 0.10
Molybdenum 1.50–3.00 0.10 . . . . . .
Nitrogen 0.20–0.40 0.02 0.08–0.18 0.01
Columbium + tantalum 0.10–0.30 0.05 . . . . . .
Vanadium 0.10–0.30 0.02 . . . . . .
F
Type Austenitic Steels , Classes 1, 1A and 1D
Grade B8LN, B8LNA B8MLN, B8MLNA
UNS Designation S30453 S31653
Product Variation, Product Variation,
Range Range
B B
Over or Under Over or Under
Carbon, max 0.030 0.005 over 0.030 0.005 over
Manganese 2.00 0.04 over 2.00 0.04 over
Phosphorus, max 0.045 0.010 over 0.045 0.010 over
Sulfur, max 0.030 0.005 over 0.030 0.005 over
Silicon 1.00 0.05 over 1.00 0.05 over
Chromium 18.0–20.0 0.20 16.0–18.0 0.20
Nickel 8.0–11.0 0.15 10.0–13.0 0.15
Molybdenum . . . . . . 2.00–3.00 0.10
Nitrogen 0.10–0.16 0.01 0.10–0.16 0.01
F
Type Austenitic Ste
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.