ASTM E1409-97
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determination of Oxygen in Titanium and Titanium Alloys by the Inert Gas Fusion Technique
Standard Test Method for Determination of Oxygen in Titanium and Titanium Alloys by the Inert Gas Fusion Technique
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of oxygen in titanium and titanium alloys in concentrations from 0.04 and 0.3%.
1.2 The values stated in both inch-pound and SI units are to be regarded separately as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific precautionary statements are given in Note 2.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: E 1409 – 97
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Oxygen in Titanium and Titanium Alloys by
the Inert Gas Fusion Technique
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E 1409; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method covers the determination of oxygen in
titanium and titanium alloys in concentrations from 0.04 and
0.3 %.
1.2 The values stated in both inch-pound and SI units are to
be regarded separately as the standard. The values given in
parentheses are for information only.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific precau-
tionary statements are given in Note 2.
2. Referenced Documents
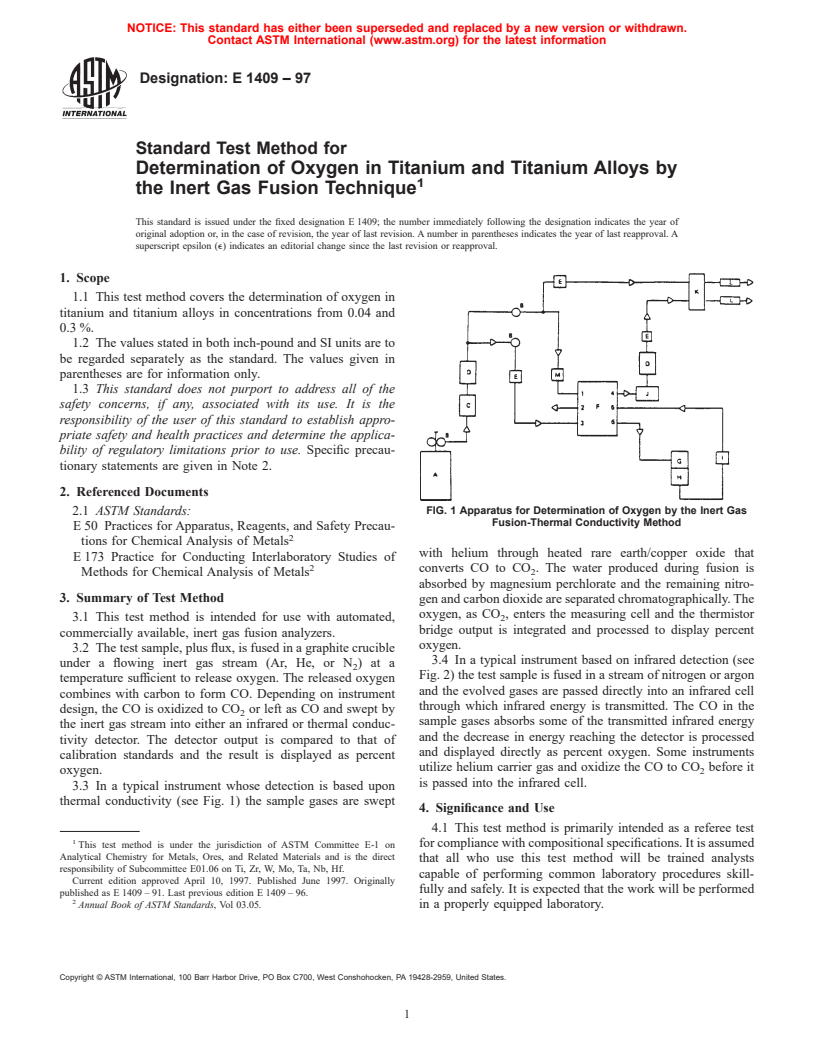
FIG. 1 Apparatus for Determination of Oxygen by the Inert Gas
2.1 ASTM Standards:
Fusion-Thermal Conductivity Method
E 50 Practices for Apparatus, Reagents, and Safety Precau-
tions for Chemical Analysis of Metals
with helium through heated rare earth/copper oxide that
E 173 Practice for Conducting Interlaboratory Studies of
converts CO to CO . The water produced during fusion is
Methods for Chemical Analysis of Metals
absorbed by magnesium perchlorate and the remaining nitro-
3. Summary of Test Method
gen and carbon dioxide are separated chromatographically. The
oxygen, as CO , enters the measuring cell and the thermistor
3.1 This test method is intended for use with automated, 2
bridge output is integrated and processed to display percent
commercially available, inert gas fusion analyzers.
oxygen.
3.2 The test sample, plus flux, is fused in a graphite crucible
3.4 In a typical instrument based on infrared detection (see
under a flowing inert gas stream (Ar, He, or N)ata
Fig. 2) the test sample is fused in a stream of nitrogen or argon
temperature sufficient to release oxygen. The released oxygen
and the evolved gases are passed directly into an infrared cell
combines with carbon to form CO. Depending on instrument
through which infrared energy is transmitted. The CO in the
design, the CO is oxidized to CO or left as CO and swept by
sample gases absorbs some of the transmitted infrared energy
the inert gas stream into either an infrared or thermal conduc-
and the decrease in energy reaching the detector is processed
tivity detector. The detector output is compared to that of
and displayed directly as percent oxygen. Some instruments
calibration standards and the result is displayed as percent
utilize helium carrier gas and oxidize the CO to CO before it
oxygen. 2
is passed into the infrared cell.
3.3 In a typical instrument whose detection is based upon
thermal conductivity (see Fig. 1) the sample gases are swept
4. Significance and Use
4.1 This test method is primarily intended as a referee test
for compliance with compositional specifications. It is assumed
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E-1 on
Analytical Chemistry for Metals, Ores, and Related Materials and is the direct
that all who use this test method will be trained analysts
responsibility of Subcommittee E01.06 on Ti, Zr, W, Mo, Ta, Nb, Hf.
capable of performing common laboratory procedures skill-
Current edition approved April 10, 1997. Published June 1997. Originally
fully and safely. It is expected that the work will be performed
published as E 1409 – 91. Last previous edition E 1409 – 96.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 03.05. in a properly equipped laboratory.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
E1409–97
7.3 Inert Gas—Use the purity and type (Ar, N ,orHe)
specified by the instrument manufacturer.
7.4 Magnesium Perchlorate, Anhydrous —Used in the in-
strument to absorb water. Use the purity specified by the
instrument manufacturer.
7.5 Nickel Flux Cleaning Solution—Prepare a fresh solution
of nickel cleaning solution by combining 75 mL of acetic acid,
25 mL of HNO and 2 mL of HCl.
7.6 Rare Earth/Copper Oxide—Reagent used in some in-
struments to oxidize CO to CO for thermal conductivity
detection. Use the purity specified by the instrument manufac-
turer.
7.7 Sodium Hydroxide on Clay —Reagent used in some
instruments to absorb CO . Use a purity specified by the
instrument manufacturer.
7.8 Titanium Sample Pickle Solution—Prepare a fresh solu-
FIG. 2 Apparatus for Determination of Oxygen by the Inert Gas
tion of 3 parts 30 % H O and 1 part 48 % HF. HNO may be
2 2 3
Fusion-Infrared Absorption Method
substituted for 30 % H O (see Notes 2 and 3).
2 2
NOTE 2—Warning: HF causes serious burns that may not be immedi-
5. Interferences
ately painful; refer to the paragraph about HF in the Safety Precautions
Section of Practices E 50.
5.1 The elements usually present in titanium and its alloys
do not interfere but there is some evidence to suggest that low NOTE 3—In 1996, alternative sample preparation procedures were
investigated by two laboratories, both active members of subcommittee
purity flux can cause some adsorption of the released oxygen.
E01.06, which has jurisdiction over E1409. The first alternative allows
direct substitution of nitric acid for hydrogen peroxide when preparing
6. Apparatus
titanium pickle solution and subsequent etching of the test specimen as
6.1 Instrument—The general features of the instruments are
specified in 10.2. The second entails removing surfaces of the sample
shown in Figs. 1 and 2.
specimen by filing with a file, thus eliminating the need to use any
6.2 Graphite Crucibles—The crucibles must be made of leaching procedure. The results of the interlaboratory study comparing
these two preparation techniques is summarized in Table 1.
high-purity graphite and be of the dimensions recommended by
the instrument manufacturer.
8. Preparation of Apparatus
6.3 Flux—Wire baskets must be made of high-purity nickel
and the dimensions must meet the requirements of the auto- 8.1 Assemble the apparatus as recommended by the manu-
matic sample drop, if present, on the instrument. (See Note 1.) facturer. Make the required power, gas, and water connections.
Turn on the instrument and allow sufficient time to stabilize the
NOTE 1—In some instruments, nitrogen and oxygen are run sequen-
equipment.
tially and platinum is the required flux for nitrogen. High-purity platinum
8.2 Change the chemical traps and filters as required. Test
can be substituted for nickel in the same ratio of flux to sample.
the furnace and analyzer to ensure the absence of leaks. Make
6.4 Tweezers—Six inches (152 millimetres), solvent and
a minimum of two test runs using a sample as directed in 12.3
acid-resistant plastic (used during the sample preparation
and 12.4 to condition the newly changed filters before attempt-
process).
ing to calibrate the system or to determine the value of the
blank.
7. Reagents
7.1 Acetone—Residue after evaporation must be<
0.0005 %.
7.2 Graphite Powder—High-purity graphite powder speci-
Known commercially as Anhydrone.
fied by the instrument manufacturer. Known commercially as Ascarite II.
TABLE 1 Results of Interlaboratory Study
Lab Sample ID Sample Desc. Filed, % Oxygen HF-HNO Etched, % Oxygen
Comparison of Filed versus HF-HNO Etched Sample Prep Procedures
Lab 1 030 Ti-5A1-2.5Sn 0.160 0.164
Lab 2 0.161 6 0.002, n = 3 0.165 6 0.003, n = 3
Lab 1 035 CP-Ti 0.163 0.163
Lab 2 0.154 6 0.001, n = 3 0.156 6 0.001, n = 3
Lab 1 040 Ti-6A1-4V 0.164 0.160
Lab 2 0.156 6 0.003, n = 3 0.155 6 0.002, n = 3
Comparison of HF-H O Etched versus HF-HNO Etched Sample Prep Procedures
2 2 3
HF-H O Etched, % Oxygen HF-HNO Etched, % Oxygen
2 2 3
Lab 2 CP-Ti 0.1412 6 0.0025, n = 10 0.1422 6 0.0016, n = 10
Ti-6A1-4V 0.1425 6 0.0026, n = 10 0.1418 6 0.0021, n = 10
E1409–97
9. Flux Preparation indicated. Using the last three analyses, adjust the instrument
signal to provide a reading within the range of the certified
9.1 Immerse the flux in nickel flux cleaning solution (see
value of the standard. (Outgassing is accomplished automati-
7.5) for 50 to 60 s, then rinse in running water for 2 to 3 min.
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.