ASTM D5383-16(2021)
(Practice)Standard Practice for Visual Determination of the Lightfastness of Art Materials by Artists and Art Technologists
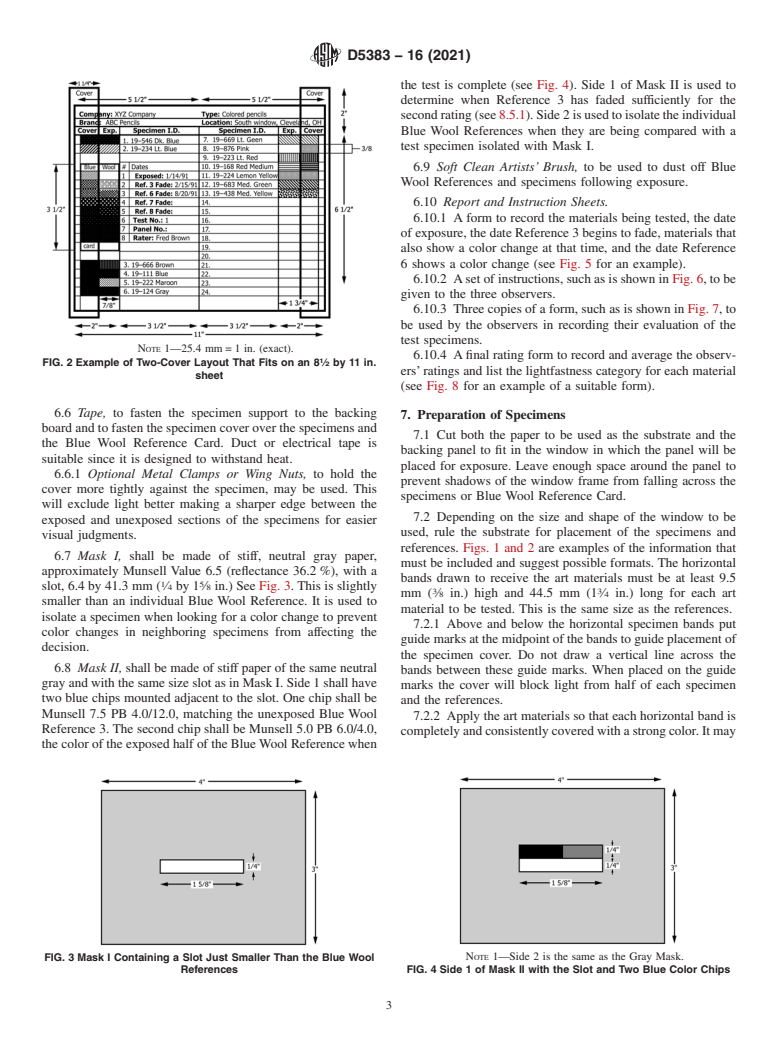
Standard Practice for Visual Determination of the Lightfastness of Art Materials by Artists and Art Technologists
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 Artists have available to them a wide variety of art materials such as markers, colored pencils, pastels, colored inks and airbrush colors. Many of these materials are manufactured for temporary artwork and may contain pigments and dyes that fade in a relatively short time. Product labels and manufacturers’ literature do not always supply the information necessary to distinguish products that are stable to light from those that are not. This practice makes it possible to check the general lightfastness of coloring materials to be used in works of art; however, Test Methods D4303 must be used if color measuring instruments and appropriate lightfastness testing apparatus are available. This practice may also be used to evaluate other types of colored materials for lightfastness.
SCOPE
1.1 This practice covers a method for exposing specimens of colored art materials indoors to sunlight coming through a closed window. A card containing eight Blue Wool References2 is exposed simultaneously. Blue Wool References2 3, 6, and 7, are used as controls in determining when to remove test specimens from exposure and rate them. Test specimens are rated by assigning each specimen the number of the Blue Wool Reference that shows the same amount of color change.
1.2 This practice may be used to indicate art materials that will change color within a few months or years in normal indoor exposure and those that will remain unchanged for a period of years. It is not rigorous enough to verify that materials will remain unchanged for more than fifty years in a home or office environment. A major consideration in developing this method was to keep it simple and short enough to be preformed without instrumentation in a comparatively short length of time.
1.3 This practice shall be used to evaluate the lightfastness of art materials only when it is not feasible to use Test Methods D4303.
1.4 This practice is not suitable for evaluating materials with a high oil content such as artists' oil, resin oil or alkyd paints.
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.7 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D5383 − 16 (Reapproved 2021)
Standard Practice for
Visual Determination of the Lightfastness of Art Materials by
Artists and Art Technologists
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D5383; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 1.7 This international standard was developed in accor-
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
1.1 This practice covers a method for exposing specimens
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
of colored art materials indoors to sunlight coming through a
2 Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
closedwindow.AcardcontainingeightBlueWoolReferences
2 mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
is exposed simultaneously. Blue Wool References 3, 6, and 7,
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
are used as controls in determining when to remove test
specimens from exposure and rate them. Test specimens are
2. Referenced Documents
rated by assigning each specimen the number of the BlueWool
Reference that shows the same amount of color change. 2.1 ASTM Standards:
D4303 Test Methods for Lightfastness of Colorants Used in
1.2 This practice may be used to indicate art materials that
Artists’ Materials
will change color within a few months or years in normal
E284 Terminology of Appearance
indoor exposure and those that will remain unchanged for a
period of years. It is not rigorous enough to verify that 2.2 Other Standards:
materials will remain unchanged for more than fifty years in a
ISO/R 105-B Textiles Tests for Colour Fastness Part B:
home or office environment. A major consideration in devel- Colour Fastness to Light and Weathering
oping this method was to keep it simple and short enough to be
BritishStandard 1006 GroupBMethodsforColourFastness
preformed without instrumentation in a comparatively short of Textiles and Leathers
length of time.
3. Terminology
1.3 This practice shall be used to evaluate the lightfastness
ofartmaterialsonlywhenitisnotfeasibletouseTestMethods
3.1 The definitions included in Terminology E284 are ap-
D4303. plicable to this practice.
1.4 This practice is not suitable for evaluating materials
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
with a high oil content such as artists’ oil, resin oil or alkyd 3.2.1 bloom, n—a cloudy exudation on the surface of
paints.
colored pencil due to wax migration.
3.2.2 fugitive color, n—colorant that changes color in a few
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information days or weeks, or that bleaches white in less than 18 months,
when exposed behind glass to sunlight.
only.
3.2.3 glazing, n—the transparent glass or plastic sheet
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the
placed in front of a picture when it is framed.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
3.2.4 substrate, n—the white, pH neutral (pH 6 to 8) paper
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
or board on which the art materials are applied.
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D01 on Paint and contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Related Coatings, Materials, and Applications and is the direct responsibility of Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Subcommittee D01.57 on Artist Paints and Related Materials. the ASTM website.
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2021. Published November 2021. Originally International Organization for Standardization, ISO/R 105-B is available from
approved in 1993. Last previous edition approved in 2016 as D5383 – 16. DOI: the American National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St., 4th Floor, New
10.1520/D5383-16R21. York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
2 5
The Blue Wool Reference Card is available from Talas, Division Technical British Standard 1006 can be obtained from British Standards Institute (BSI),
Library Service, 213 W. 35th St. New York, NY 10001-1992. 389 Chiswick High Rd., London W4 4AL, U.K., http://www.bsi-global.com.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
D5383 − 16 (2021)
4. Summary of Practice 6.2 Substrate, of white paper or museum board. To avoid
substrate discoloration during the testing procedure, the sub-
4.1 ThispracticeusesascontrolsthreeoftheeightISOBlue
strateshallbe100%cotton,pHneutral,buffered,uncoated,and
Wool References developed for use with ISO/R 105-B and
without optical brighteners. It is desirable for the surface of the
British Standard 1006 Group B.
substrate to be similar to that customarily used with the
4.2 Specimens are made from the colored materials to be
materials being tested; however, it must be possible to com-
tested and attached to a backing panel along with a card
pletely cover the substrate with an even coat of the colors.
containing the eight Blue Wool References.
Rough watercolor paper is not suitable.
4.3 OnehalfofeachcoloredspecimenandoftheBlueWool
6.3 Blue Wool Reference Card, contains bands of the eight
Referencearecovered,shieldingthathalfofthespecimensand
BlueWool References glued to a card 44.5 by 127 mm (1 ⁄4 by
references from light. The test specimens and references are
5 in.). Each Blue Wool Reference from 1 to 8 takes approxi-
exposed to sunlight through a closed window.
mately twice as long to fade as the reference immediately
preceding it. The card must be kept in complete darkness until
4.4 When BlueWool Reference 3 shows a color change, the
colored specimens are examined visually and any that also time for the test. It should be wrapped in an opaque covering
show a color change are noted. The cover is replaced and and stored in a drawer at normal room temperature.
exposure continued until the exposed and unexposed halves of
6.4 Colored Art Materials, to be tested.
Reference 3 reach a specified contrast and Reference 6 also
6.5 Specimen Cover, made from stiff material such as heavy
shows a color change. Three observers rate each specimen by
gagealuminum;stainlesssteel;stiff,opaqueplastic;orwooden
assigning it the number of the BlueWool Reference that shows
strips. The cover shall be at least 32-mm (1 ⁄4-in.) wide and as
a similar color change. The three numbers assigned to a
long as the backing panel. It is used to protect one half of each
specimenareaveragedandthisaveragedeterminesinwhichof
art material specimen and one half of the BlueWool Reference
four broad lightfastness categories the specimen belongs.
Card from light (see Figs. 1 and 2). The side of the cover that
4.5 If it is necessary to determine which materials have
touches the art material specimens should be chemically inert
excellent lightfastness, continue exposure until Reference 7
to prevent interaction with, or migration of substances onto the
shows a color change. Remove the panel from exposure and
test specimens.
examine only the specimens that had not changed color at the
time Reference 6 faded. Those specimens that still show no
color change are placed in the fifth and highest lightfastness
category.
NOTE 1—Depending on the test location, the time of year, and the
number of cloudy days, it will take from a few days to two months of
exposure in a window facing south to reveal fugitive materials that will
either bleach white or radically change color in a few years when
displayed in a normal home environment. It will take from 4 to 18 months
of exposure to determine materials that will show, under normal room
conditions, various degrees of color change, and those that will remain
unchanged, for a long period of time.
5. Significance and Use
5.1 Artists have available to them a wide variety of art
materials such as markers, colored pencils, pastels, colored
inks and airbrush colors. Many of these materials are manu-
factured for temporary artwork and may contain pigments and
dyes that fade in a relatively short time. Product labels and
manufacturers’literature do not always supply the information
necessary to distinguish products that are stable to light from
those that are not. This practice makes it possible to check the
general lightfastness of coloring materials to be used in works
of art; however, Test Methods D4303 must be used if color
measuring instruments and appropriate lightfastness testing
apparatus are available. This practice may also be used to
evaluate other types of colored materials for lightfastness.
6. Materials
6.1 Backing Panel, that is resistant to warping when placed
on its edge and exposed to light and heat passing through
window glass. Foam board, corrugated plastic board, alumi-
numcompositematerial(ACM),particleboard,hardboard,and
NOTE 1—25.4 mm = 1 in. (exact).
plywood are suitable. FIG. 1 Suggested Layout for Lightfastness Test Panel
D5383 − 16 (2021)
the test is complete (see Fig. 4). Side 1 of Mask II is used to
determine when Reference 3 has faded sufficiently for the
secondrating(see8.5.1).Side2isusedtoisolatetheindividual
Blue Wool References when they are being compared with a
test specimen isolated with Mask I.
6.9 Soft Clean Artists’ Brush, to be used to dust off Blue
Wool References and specimens following exposure.
6.10 Report and Instruction Sheets.
6.10.1 A form to record the materials being tested, the date
of exposure, the date Reference 3 begins to fade, materials that
also show a color change at that time, and the date Reference
6 shows a color change (see Fig. 5 for an example).
6.10.2 Aset of instructions, such as is shown in Fig. 6,tobe
given to the three observers.
6.10.3 Three copies of a form, such as is shown in Fig. 7,to
be used by the observers in recording their evaluation of the
test specimens.
NOTE 1—25.4 mm = 1 in. (exact).
6.10.4 Afinal rating form to record and average the observ-
FIG. 2 Example of Two-Cover Layout That Fits on an 8 ⁄2 by 11 in.
ers’ratings and list the lightfastness category for each material
sheet
(see Fig. 8 for an example of a suitable form).
6.6 Tape, to fasten the specimen support to the backing
7. Preparation of Specimens
board and to fasten the specimen cover over the specimens and
7.1 Cut both the paper to be used as the substrate and the
the Blue Wool Reference Card. Duct or electrical tape is
backing panel to fit in the window in which the panel will be
suitable since it is designed to withstand heat.
placed for exposure. Leave enough space around the panel to
6.6.1 Optional Metal Clamps or Wing Nuts, to hold the
prevent shadows of the window frame from falling across the
cover more tightly against the specimen, may be used. This
specimens or Blue Wool Reference Card.
will exclude light better making a sharper edge between the
7.2 Depending on the size and shape of the window to be
exposed and unexposed sections of the specimens for easier
used, rule the substrate for placement of the specimens and
visual judgments.
references. Figs. 1 and 2 are examples of the information that
6.7 Mask I, shall be made of stiff, neutral gray paper,
must be included and suggest possible formats. The horizontal
approximately Munsell Value 6.5 (reflectance 36.2 %), with a
bands drawn to receive the art materials must be at least 9.5
1 5
slot, 6.4 by 41.3 mm ( ⁄4 by 1 ⁄8 in.) See Fig. 3. This is slightly
3 3
mm ( ⁄8 in.) high and 44.5 mm (1 ⁄4 in.) long for each art
smaller than an individual Blue Wool Reference. It is used to
material to be tested. This is the same size as the references.
isolate a specimen when looking for a color change to prevent
7.2.1 Above and below the horizontal specimen bands put
color changes in neighboring specimens from affecting the
guide marks at the midpoint of the bands to guide placement of
decision.
the specimen cover. Do not draw a vertical line across the
6.8 Mask II, shall be made of stiff paper of the same neutral
bands between these guide marks. When placed on the guide
gray and with the same size slot as in Mask I. Side 1 shall have
marks the cover will block light from half of each specimen
two blue chips mounted adjacent to the slot. One chip shall be
and the references.
Munsell 7.5 PB 4.0/12.0, matching the unexposed Blue Wool
7.2.2 Apply the art materials so that each horizontal band is
Reference 3. The second chip shall be Munsell 5.0 PB 6.0/4.0,
completelyandconsistentlycoveredwithastrongcolor.Itmay
the color of the exposed half of the BlueWool Reference when
NOTE 1—Side 2 is the same as the Gray Mask.
FIG. 3 Mask I Containing a Slot Just Smaller Than the Blue Wool
References FIG. 4 Side 1 of Mask II with the Slot and Two Blue Color Chips
D5383 − 16 (2021)
FIG. 6 An Example of an Instruction Sheet to be Furnished to the
Observers Who Will Rate the Specimens
FIG. 5 Example of Technician’s Record Sheet
7.3.3 A separate Blue Wool Reference Card shall be used
with each set of test specimens exposed in a different window.
7.4 Attach the specimen support to the backing board with
be necessary to use more than one coat of a watercolor or ink the tape.
to produce a color in which small amounts of fading can be
7.5 Line the specimen cover up with the guide marks and
detected visually.
fasten it tightly over the specimens and Blue Wool Reference
7.2.3 At the top of the substrate enter the type of material,
Cardwithsuitabletape,clampsorwingnuts.Tapemayhaveto
name of the manufacturer, and product line. Record the date
be replaced during the exposure period due to deterioration.
the test begins. Use india ink or pencil unless this part of the
panel will be covered during exposure. Leave spaces to record
8. Procedure
the date when Reference 3 shows a color change, the date
8.1 Positionthebackingpanelcontainingthespecimensand
Reference 3 matches the color chips on the Mask II (Reference
Blue Wool Reference Card in a window. In the northern
6 shows a color change), and if desired, the date when
hemisphere, the window should face south or southwest if
reference 7 shows a color change. Beside each specimen
possible. This will shorten the time
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.