ASTM D746-98e1
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Brittleness Temperature of Plastics and Elastomers by Impact
Standard Test Method for Brittleness Temperature of Plastics and Elastomers by Impact
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the temperature at which plastics and elastomers exhibit brittle failure under specified impact conditions. Two routine inspection and acceptance procedures are also provided.
Note 1—When testing rubbers for impact brittleness use Test Methods D2137.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
Note 2—This test method and ISO 974-1980 (E) are technically equivalent when using the Type B fixture and the Type III specimen, however, the minimum number of specimens that are required to be tested may be significantly different when using this test method. The ISO method requires that a minimum of 100 specimens be tested.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
e1
Designation: D 746 – 98
Standard Test Method for
Brittleness Temperature of Plastics and Elastomers by
Impact
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 746; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
e NOTE—Editorially corrected 8.1.2 and 8.2.2 in April 2002.
1. Scope* E 220 Test Method for Calibration of Thermocouples by
Comparison Techniques
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the tem-
E 644 Test Methods for Testing Industrial Resistance Ther-
perature at which plastics and elastomers exhibit brittle failure
mometers
under specified impact conditions. Two routine inspection and
E 1137 Specification for Industrial Platinum Resistance
acceptance procedures are also provided.
Thermometers
NOTE 1—When testing rubbers for impact brittleness use Test Methods
2.2 ISO Standard:
D 2137.
ISO 974-1980 (E) Plastics—Determination of the Brittle-
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
ness Temperature by Impact
standard.
3. Terminology
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
3.1 General—The definitions of plastics used in this test
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
method are in accordance with Test Method D 883 unless
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
otherwise specified.
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
3.2 brittleness temperature—that temperature, estimated
statistically, at which 50 % of the specimens would probably
NOTE 2—This test method and ISO 974-1980 (E) are technically
fail.
equivalent when using the Type B fixture and the Type III specimen,
however, the minimum number of specimens that are required to be tested
4. Summary of Test Method
may be significantly different when using this test method. The ISO
method requires that a minimum of 100 specimens be tested.
4.1 To determine the brittleness temperature, specimens are
secured to a specimen holder with a torque wrench. The
2. Referenced Documents
specimen holder is immersed in a bath containing a heat-
2.1 ASTM Standards:
transfer medium that is cooled. The specimens are struck at a
D 618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics and Electrical
specified linear speed and then examined. The brittleness
Insulating Materials for Testing
temperature is defined as the temperature at which 50 % of the
D 832 Practice for Rubber Conditioning for Low-
specimens fail.
Temperature Testing
5. Significance and Use
D 883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
D 1898 Practice for Sampling of Plastics
5.1 This test method establishes the temperature at which
D 2137 Test Methods for Rubber Property—Brittleness
50 % of the specimens tested fail when subjected to the
Point of Flexible Polymers and Coated Fabrics
conditions specified herein. The test provides for the evaluation
E 77 Test Method for the Inspection and Verification of
of long-time effects such as crystallization, or those that may
Thermometers
be introduced by low-temperature incompatibility of plasticiz-
ers in the material under test. Plastics and elastomers are used
in many applications requiring low-temperature flexing with or
without impact. Data obtained by this test method may be used
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D-20 on Plastics
to predict the behavior of plastic and elastomeric materials at
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.30 on Thermal Properties
(Section D20.30.07).
Current edition approved July 10, 1998. Published January 1999. Originally
published as D 746 – 43 T. Last previous edition D 746 – 95.
2 5
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 08.01. ISO Standards Handbook 21, Vol 1. ISO Standards are available through
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 09.01. American National Standards Institute, 11 W. 42nd St., 13th Floor, New York, NY
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 14.03. 10036.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
e1
D 746–98
low temperatures only in applications in which the conditions and specimen clamp shall have a clearance of 3.6 6 0.1 mm at
of deformation are similar to those specified in this test and immediately following impact. The clearance between the
method. This test method has been found useful for specifica- outside of the striking edge and the clamp shall be 2.0 6 0.1
tion purposes, but does not necessarily measure the lowest mm at impact. These dimensional requirements of the striking
temperature at which the material may be used. edge and clamping device are illustrated in Fig. 3. Fig. 4 shows
a typical clamp. Details of the specimen clamp are given in Fig.
NOTE 3—Suitable apparatus is commercially available from several
5.
suppliers. The striking member may be motor-driven, solenoid-operated,
6.3 Torque Wrench, 0 to 8.5 N · m.
gravity-actuated, or spring-loaded. The motor-driven tester should be
equipped with a safety interlock to prevent striker arm motion when the
NOTE 4—Because of the difference in geometry of the specimen
cover is open.
clamps, test results obtained when using the Type A specimen clamp and
striking member may not correlate with those results obtained when using
6. Apparatus
the Type B apparatus.
6.1 Type A:
6.4 Temperature-Measurement System—The temperature of
6.1.1 Specimen Clamp and Striking Member—Design the
the heat-transfer medium shall be determined with a thermo-
specimen clamp to hold the specimen or specimens as a
couple or resistance thermometer having a suitable range for
cantilever beam. Each individual specimen shall be firmly and
the temperatures at which the determinations are to be made.
securely held in a separate clamp. The striking edge shall move
The temperature-measuring device and the related readout
relative to the specimens at a linear speed of 2000 6 200 mm/s
equipment shall be accurate to at least 60.5°C. The
at impact and during at least the following 6.4 mm of travel. In
temperature-measuring device shall be located as close to the
order to maintain this speed, it may be necessary to reduce the
specimens as possible. Thermocouples shall be calibrated in
number of specimens tested at one time. The distance between
accordance with Test Method E 220. Resistance temperature
the center line of the striking edge and the clamp shall be
devices shall comply with the requirements of Test Methods
7.87 6 0.25 mm at impact. The striking edge shall have a
E 644 and Specification E 1137.
radius of 1.6 6 0.1 mm. The striking arm and specimen clamp
shall have a clearance of 6.35 6 0.25 mm at and immediately
NOTE 5—A thermometer may be used if it can be shown to agree with
following impact. These dimensional requirements are illus-
the specified temperature measuring system. Mercury-in-glass thermom-
eters shall be calibrated for the depth of immersion in accordance with
trated in Fig. 1. Fig. 2 shows a typical clamp. Use free-fitting
Test Method E 77.
clamping screws, 10-32 National Fine Thread.
6.2 Type B:
6.5 Heat-Transfer Medium—Any liquid heat transfer me-
6.2.1 Specimen Clamp and Striking Member—Design the
dium that remains fluid at the test temperature and will not
specimen clamp to hold the specimen or specimens as a
appreciably affect the material tested may be used. Measure-
cantilever beam. Each individual specimen shall be firmly and
ment of selected physical properties prior to and after 15-min
securely held in a separate clamp. The striking edge shall move
exposure at the highest temperature used will provide an
relative to the specimens at a linear speed of 2000 6 200 mm/s
indication of the inertness of a plastic to the heat transfer
at impact and during at least the following 5.0 mm of travel. In
medium. There should be no significant difference between the
order to maintain this speed, it may be necessary to reduce the
results.
number of specimens tested at one time. The radius of the
6.5.1 Where a flammable or toxic solvent is used as the
lower jaw of the clamp shall be 4.0 6 0.1 mm. The striking
cooling medium, the customary precautions in handling such a
edge shall have a radius of 1.6 6 0.1 mm. The striking edge
material should be exercised. Methanol is the recommended
heat transfer medium for rubber.
NOTE 6—The following materials have been found suitable for use at
A detailed drawing of a typical clamp may be obtained from ASTM Headquar-
the indicated temperatures. When silicone oil is used, moisture from the
ters. Order Adjunct : ADJD0746.
air will condense on the surface of the oil, causing slush to form. This
slush may collect on the temperature-measuring device as ice and affect
temperature measurement. If this should occur, remove the ice from the
temperature-measuring device.
Material Temperature, °C
5-mm /s viscosity silicone oil −60
2-mm /s viscosity silicone oil −76
Methyl alcohol −90
6.6 Temperature Control—Suitable means (automatic or
manual) shall be provided for controlling the temperature of
the heat-transfer medium to within 60.5°C of the desired
value. Powdered solid carbon dioxide (dry ice) and liquid
nitrogen are recommended for lowering the temperature, and
an electric immersion heater for raising the temperature.
FIG. 1 Dimensional Requirements Between Specimen Clamp and
Striking Edge (Type A) 6.7 Tank, insulated.
e1
D 746–98
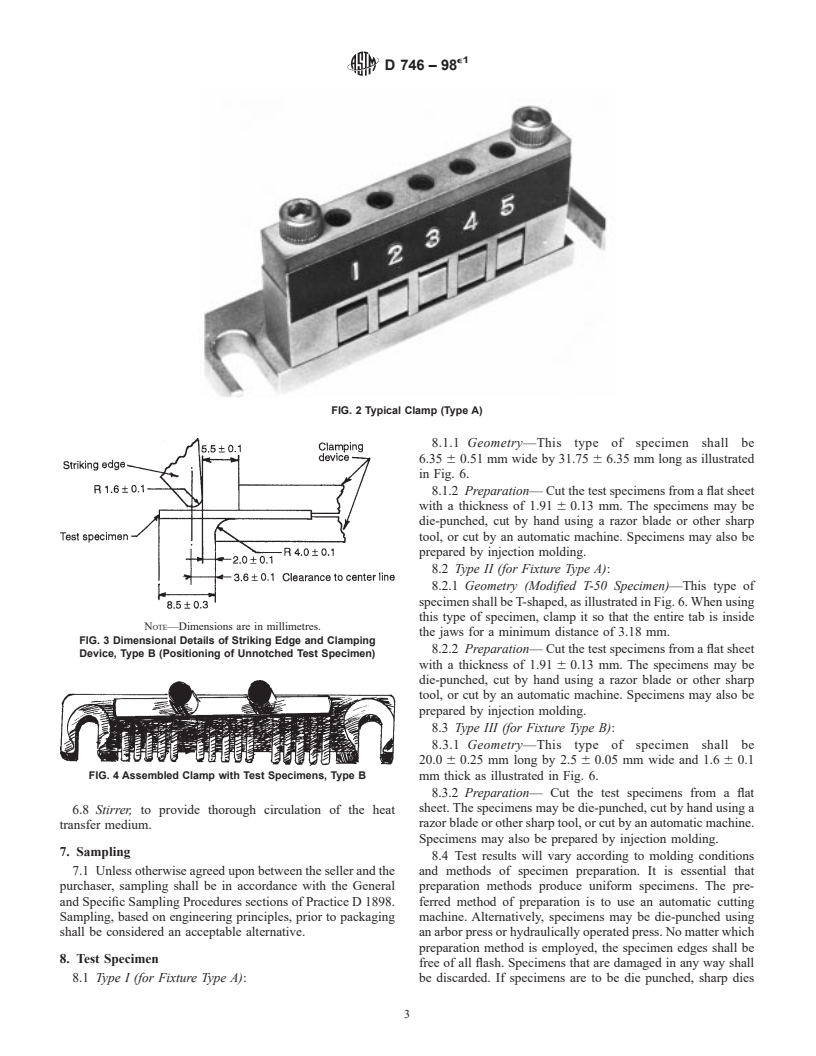
FIG. 2 Typical Clamp (Type A)
8.1.1 Geometry—This type of specimen shall be
6.35 6 0.51 mm wide by 31.75 6 6.35 mm long as illustrated
in Fig. 6.
8.1.2 Preparation— Cut the test specimens from a flat sheet
with a thickness of 1.91 6 0.13 mm. The specimens may be
die-punched, cut by hand using a razor blade or other sharp
tool, or cut by an automatic machine. Specimens may also be
prepared by injection molding.
8.2 Type II (for Fixture Type A):
8.2.1 Geometry (Modified T-50 Specimen)—This type of
specimen shall be T-shaped, as illustrated in Fig. 6. When using
this type of specimen, clamp it so that the entire tab is inside
NOTE—Dimensions are in millimetres.
the jaws for a minimum distance of 3.18 mm.
FIG. 3 Dimensional Details of Striking Edge and Clamping
8.2.2 Preparation— Cut the test specimens from a flat sheet
Device, Type B (Positioning of Unnotched Test Specimen)
with a thickness of 1.91 6 0.13 mm. The specimens may be
die-punched, cut by hand using a razor blade or other sharp
tool, or cut by an automatic machine. Specimens may also be
prepared by injection molding.
8.3 Type III (for Fixture Type B):
8.3.1 Geometry—This type of specimen shall be
20.0 6 0.25 mm long by 2.5 6 0.05 mm wide and 1.6 6 0.1
FIG. 4 Assembled Clamp with Test Specimens, Type B mm thick as illustrated in Fig. 6.
8.3.2 Preparation— Cut the test specimens from a flat
sheet. The specimens may be die-punched, cut by hand using a
6.8 Stirrer, to provide thorough circulation of the heat
razor blade or other sharp tool, or cut by an automatic machine.
transfer medium.
Specimens may also be prepared by injection molding.
7. Sampling
8.4 Test results will vary according to molding conditions
7.1 Unless otherwise agreed upon between the seller and the and methods of specimen preparation. It is essential that
purchaser, sampling shall be in accordance with the General preparation methods produce uniform specimens. The pre-
and Specific Sampling Procedures sections of Practice D 1898. ferred method of preparation is to use an automatic cutting
Sampling, based on engineering principles, prior to packaging machine. Alternatively, specimens may be die-punched using
shall be considered an acceptable alternative. an arbor press or hydraulically operated press. No matter which
preparation method is employed, the specimen edges shall be
8. Test Specimen
free of all flash. Specimens that are damaged in any way shall
8.1 Type I (for Fixture Type A): be discarded. If specimens are to be die punched, sharp dies
e1
D 746–98
NOTE—Dimensions are in millimetres.
FIG. 5 Details of One Form of Clamp Meeting the Requirements of 6.2
FIG. 6 Specimen Geometry
must be used in the preparation of specimens for this test if die may be judged by investigating the rupture point on any
reliable results are to be achieved. Careful maintenance of die series of broken specimens. When broken specimens are
cutting edges is of extreme importance and can be obtained by removed from the clamps of the testing machine it is advan-
daily lightly honing and touching up the cutting edges with tageous to pile these specimens and note if there is any
jewelers’ hard Arkansas honing stones. The condition of the tendency to break at or near the same portion of each specimen.
e1
D 746–98
Rupture points consistently at the same place may be the division of a specimen into two or more completely separated
indication that the die is dull, nicked, or bent at that particular pieces or as any crack in the specimen which is visible to the
position. unaided eye. Where a specimen has not completely separated,
it shall be bent to an angle of 90° in the same direction as the
bend caused by the impact. It should then be examined for
9. Conditioning
cracks at the bend. Record the number of failures and the
9.1 Conditioning— Condition the test specimens at
temperature at which they were tested.
23 6 2°C and 50 6 5 % relative humidity for not less than 40
10.7 Increase or decrease the temperature of the bath in
h prior to the test in accordance with Procedure A of Practice
uniform increments of 2 or 5°C and repeat the procedure until
D 618 for those tests where conditioning is required. In cases
the lowest temperature at which none of the specimens fail and
of disagreement, the tolerances shall be 61°C and 62%
the highest temperature at which all of the specimens fail is
relative humidity.
determined. A minimum of four tests shall be conducted in that
NOTE 7—Where long-time effects such as crystallization, incompatibil-
temperature range. Ten new specimens should be used for each
ity, etc., of materials are to be studied, the test specimens may be
test.
conditioned in accordance with Practice D 832.
11. Routine Inspection and Acceptance
10. Procedure
11.1 Procedure A— For routine inspection of materials
10.1 In establishing the brittleness temperature of a mate-
received from an approved supplier, it shall be satisfactory to
rial, it is recom
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.