ASTM D746-20
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Brittleness Temperature of Plastics and Elastomers by Impact
Standard Test Method for Brittleness Temperature of Plastics and Elastomers by Impact
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 This test method establishes the temperature at which 50 % of the specimens tested would probably fail when subjected to the conditions specified herein. The test provides for the evaluation of long-time effects such as crystallization, or those effects that are introduced by low-temperature incompatibility of plasticizers in the material under test. Plastics and elastomers are used in many applications requiring low-temperature flexing with or without impact. Use data obtained by this method to predict the behavior of plastic and elastomeric materials at low temperatures only in applications in which the conditions of deformation are similar to those specified in this test method. This test method has been found useful for specification purposes, but does not necessarily measure the lowest temperature at which the material is suitable for use.
FIG. 1 Dimensional Requirements Between Specimen Clamp and Striking Edge (Type A)
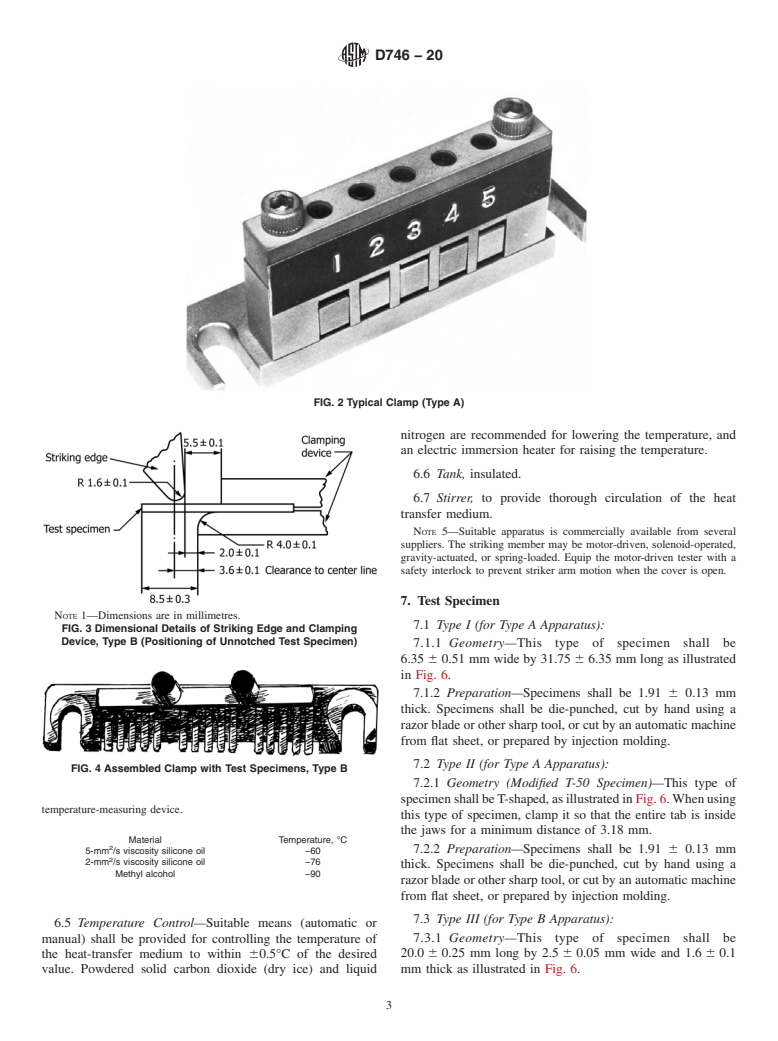
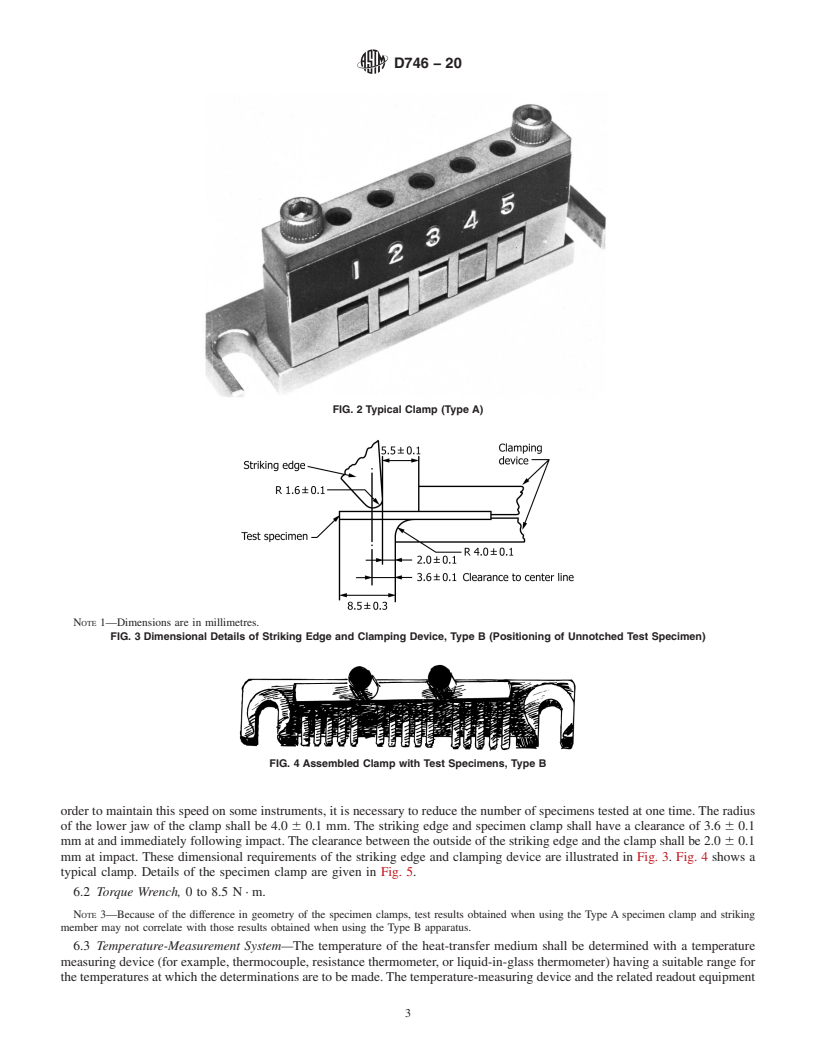
FIG. 2 Typical Clamp (Type A)
FIG. 3 Dimensional Details of Striking Edge and Clamping Device, Type B (Positioning of Unnotched Test Specimen)
Note 1: Dimensions are in millimetres.
FIG. 4 Assembled Clamp with Test Specimens, Type B
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the temperature at which plastics and elastomers (as defined by Terminology D883) exhibit brittle failure under specified impact conditions. Two routine inspection and acceptance procedures are also provided.
Note 1: When testing rubbers for impact brittleness use Test Method D2137. When testing plastic sheeting for impact brittleness, use Test Method D1790.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard.
1.3 Due to the potential safety and environmental hazards associated with mercury-filled thermometers, the use of alternative temperature measuring devices (such as thermocouples and RTDs) is encouraged.
Warning—Mercury has been designated by many regulatory agencies as a hazardous material that can cause serious medical issues. Mercury, or its vapor, has been demonstrated to be hazardous to health and corrosive to materials. Caution should be taken when handling mercury and mercury containing products. See the applicable product Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for additional information. Users should be aware that selling mercury and/or mercury containing products into your state or country may be prohibited by law.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
Note 2: This test method and ISO 974 address the same subject matter, but differ in technical content.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D746 − 20
Standard Test Method for
Brittleness Temperature of Plastics and Elastomers by
1
Impact
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D746; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope* ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the tem-
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
perature at which plastics and elastomers (as defined by
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Terminology D883) exhibit brittle failure under specified
impact conditions. Two routine inspection and acceptance
2. Referenced Documents
procedures are also provided.
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
NOTE 1—When testing rubbers for impact brittleness use Test Method
D618Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing
D2137. When testing plastic sheeting for impact brittleness, use Test
D832Practice for Rubber Conditioning For Low Tempera-
Method D1790.
ture Testing
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
D883Terminology Relating to Plastics
standard.
D1790Test Method for Brittleness Temperature of Plastic
1.3 Due to the potential safety and environmental hazards
Sheeting by Impact
associated with mercury-filled thermometers, the use of alter-
D2137TestMethodsforRubberProperty—BrittlenessPoint
native temperature measuring devices (such as thermocouples
of Flexible Polymers and Coated Fabrics
and RTDs) is encouraged.
E1Specification for ASTM Liquid-in-Glass Thermometers
Warning—Mercury has been designated by many regula-
E77Test Method for Inspection and Verification of Ther-
tory agencies as a hazardous material that can cause serious
mometers
medicalissues.Mercury,oritsvapor,hasbeendemonstratedto
E608/E608MSpecification for Mineral-Insulated, Metal-
be hazardous to health and corrosive to materials. Caution
Sheathed Base Metal Thermocouples
should be taken when handling mercury and mercury contain-
E1137/E1137MSpecification for Industrial Platinum Resis-
ing products. See the applicable product Safety Data Sheet
tance Thermometers
(SDS) for additional information. Users should be aware that
2.2 ISO Standard:
selling mercury and/or mercury containing products into your
ISO974Plastics—Determination of the Brittleness Tem-
state or country may be prohibited by law. 3
perature by Impact
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the 3. Terminology
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
3.1 General—The definitions of plastics used in this test
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
method are in accordance with Test Method D883 unless
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
otherwise specified.
NOTE 2—This test method and ISO974 address the same subject
3.2 brittleness temperature—that temperature, estimated
matter, but differ in technical content.
statistically, at which 50% of the specimens would probably
1.5 This international standard was developed in accor-
fail.
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
1
ThistestmethodisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeD20onPlastics contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.30 on Thermal Proper- Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
ties.30.07). the ASTM website.
3
Current edition approved June 1, 2020. Published June 2020. Originally ISO Standards Handbook 21,Vol1.ISOStandardsareavailablefromAmerican
approved in 1943. Last previous edition approved in 2014 as D746–14. DOI: National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St., 4th Floor, New York, NY
10.1520/D0746-20. 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D746 − 20
3.3 failed specimen—the division of a specimen into two or 6.35 60.25 mm at and immediately following impact. These
more completely separated pieces or as any crack in the dimensionalrequi
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D746 − 14 D746 − 20
Standard Test Method for
Brittleness Temperature of Plastics and Elastomers by
1
Impact
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D746; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope*
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the temperature at which plastics and elastomers (as defined by Terminology
D883) exhibit brittle failure under specified impact conditions. Two routine inspection and acceptance procedures are also
provided.
NOTE 1—When testing rubbers for impact brittleness use Test Method D2137. When testing plastic sheeting for impact brittleness, use Test Method
D1790.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard.
1.3 Due to the potential safety and environmental hazards associated with mercury-filled thermometers, the use of alternative
temperature measuring devices (such as thermocouples and RTDs) is encouraged.
Warning—Mercury has been designated by many regulatory agencies as a hazardous material that can cause serious medical
issues. Mercury, or its vapor, has been demonstrated to be hazardous to health and corrosive to materials. Caution should be taken
when handling mercury and mercury containing products. See the applicable product Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for additional
information. Users should be aware that selling mercury and/or mercury containing products into your state or country may be
prohibited by law.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety safety, health, and healthenvironmental practices and determine the
applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
NOTE 2—This test method and ISO 974 address the same subject matter, but differ in technical content.
NOTE 2—This test method and ISO 974 address the same subject matter, but differ in technical content.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing
D832 Practice for Rubber Conditioning For Low Temperature Testing
D883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
D1790 Test Method for Brittleness Temperature of Plastic Sheeting by Impact
D2137 Test Methods for Rubber Property—Brittleness Point of Flexible Polymers and Coated Fabrics
E1 Specification for ASTM Liquid-in-Glass Thermometers
E77 Test Method for Inspection and Verification of Thermometers
E608/E608M Specification for Mineral-Insulated, Metal-Sheathed Base Metal Thermocouples
E1137/E1137M Specification for Industrial Platinum Resistance Thermometers
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D20 on Plastics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.30 on Thermal Properties.30.07).
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2014June 1, 2020. Published December 2014June 2020. Originally approved in 1943. Last previous edition approved in 20132014 as
D746 – 13.D746 – 14. DOI: 10.1520/D0746-14.10.1520/D0746-20.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D746 − 20
2.2 ISO Standard:
3
ISO 974 Plastics—Determination of the Brittleness Temperature by Impact
2.3 ASTM Adjuncts:
4
Detailed Drawing of a Typical Clamp
3. Terminology
3.1 General—The definitions of plastics used in this test method are in accordance with Test Method D883 unless otherwise
specified.
3.2 brittleness temperature—that temperature, estimated statistically, at which 50 % of the specimens would pro
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.