ASTM G138-12
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Calibration of a Spectroradiometer Using a Standard Source of Irradiance
Standard Test Method for Calibration of a Spectroradiometer Using a Standard Source of Irradiance
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 This method is intended for use by laboratories performing calibration of a spectroradiometer for spectral irradiance measurements using a spectral irradiance standard with known spectral irradiance values and associated uncertainties traceable to a national metrological laboratory that has participated in intercomparisons of standards of spectral irradiance, known uncertainties and known measurement geometry.
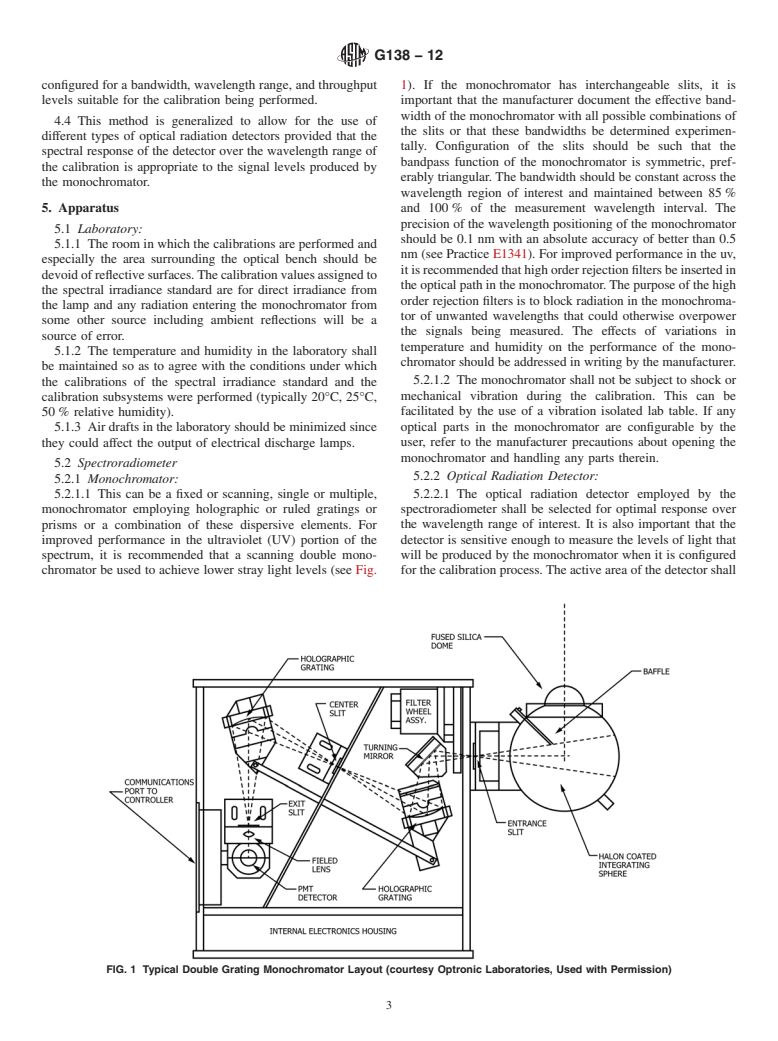
4.2 This method is generalized to allow for the use of different types of input optics provided that those input optics are suitable for the wavelength range and measurement geometry of the calibration.
4.3 This method is generalized to allow for the use of different types of monochromators provided that they can be configured for a bandwidth, wavelength range, and throughput levels suitable for the calibration being performed.
4.4 This method is generalized to allow for the use of different types of optical radiation detectors provided that the spectral response of the detector over the wavelength range of the calibration is appropriate to the signal levels produced by the monochromator.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the calibration of spectroradiometers for the measurement of spectral irradiance using a standard of spectral irradiance that is traceable to a national metrological laboratory that has participated in intercomparisons of standards of spectral irradiance.
1.2 This method is not limited by the input optics of the spectroradiometric system. However, choice of input optics affects the overall uncertainty of the calibration.
1.3 This method is not limited by the type of monochromator or optical detector used in the spectroradiometer system. Parts of the method may not apply to determine which parts apply to the specific spectroradiometer being used. It is important that the choice of monochromator and detector be appropriate for the wavelength range of interest for the calibration. Though the method generally applies to photodiode array detector based systems, the user should note that these types of spectroradiometers often suffer from stray light problems and have limited dynamic range. Diode array spectroradiometers are not recommended for use in the ultraviolet range unless these specific problems are addressed.
1.4 The calibration described in this method employs the use of a standard of spectral irradiance. The standard of spectral irradiance must have known spectral irradiance values at given wavelengths for a specific input current and clearly defined measurement geometry. Uncertainties must also be known for the spectral irradiance values. The values assigned to this standard must be traceable to a national metrological laboratory that has participated in intercomparisons of standards of spectral irradiance. These standards may be obtained from a number of national standards laboratories and commercial laboratories. The spectral irradiance standards consist mainly of tungsten halogen lamps with coiled filaments enclosed in a quartz envelope, though other types of lamps are used. Standards can be obtained with calibration values covering all or part of the wavelength range from 200 to 4500 nm.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.2
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: G138 − 12
Standard Test Method for
Calibration of a Spectroradiometer Using a Standard Source
1
of Irradiance
This standard is issued under the fixed designation G138; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
INTRODUCTION
Astandardized means of performing and reporting calibration of the spectroradiometer for spectral
irradiance measurements is desirable.
This test method presents specific technical requirements for a laboratory performing calibration of
a spectroradiometer for spectral irradiance measurements. A detailed procedure for performing the
calibration and reporting the results is outlined.
This test method for calibration is applicable to spectroradiometric systems consisting of at least a
monochromator, input optics, and an optical radiation detector, and applies to spectroradiometric
calibrations performed with a standard of spectral irradiance with known irradiance values traceable
to a national metrological laboratory that has participated in intercomparisons of standards of spectral
irradiance. The standard must also have known uncertainties and measurement geometry associated
with its irradiance values.
1. Scope calibration. Though the method generally applies to photo-
diode array detector based systems, the user should note that
1.1 This test method covers the calibration of spectroradi-
these types of spectroradiometers often suffer from stray light
ometers for the measurement of spectral irradiance using a
problems and have limited dynamic range. Diode array spec-
standard of spectral irradiance that is traceable to a national
troradiometers are not recommended for use in the ultraviolet
metrological laboratory that has participated in intercompari-
range unless these specific problems are addressed.
sons of standards of spectral irradiance.
1.2 This method is not limited by the input optics of the
1.4 The calibration described in this method employs the
spectroradiometric system. However, choice of input optics
use of a standard of spectral irradiance. The standard of
affects the overall uncertainty of the calibration.
spectral irradiance must have known spectral irradiance values
at given wavelengths for a specific input current and clearly
1.3 This method is not limited by the type of monochroma-
defined measurement geometry. Uncertainties must also be
tor or optical detector used in the spectroradiometer system.
known for the spectral irradiance values. The values assigned
Parts of the method may not apply to determine which parts
to this standard must be traceable to a national metrological
apply to the specific spectroradiometer being used. It is
important that the choice of monochromator and detector be laboratory that has participated in intercomparisons of stan-
appropriate for the wavelength range of interest for the
dards of spectral irradiance. These standards may be obtained
from a number of national standards laboratories and commer-
1 cial laboratories. The spectral irradiance standards consist
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee G03 on
Weathering and Durabilityand is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee G03.09
mainly of tungsten halogen lamps with coiled filaments en-
on Radiometry.
closed in a quartz envelope, though other types of lamps are
CurrenteditionapprovedJune1,2012.PublishedJuly2006.Originallyapproved
used. Standards can be obtained with calibration values cov-
in 1996. Last previous edition approved in 2003 as G138–03. DOI: 10.1520/
G0138-06. ering all or part of the wavelength range from 200 to 4500 nm.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
G138 − 12
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the 3.1.10 ultraviolet, adj—optical radiation at wavelengths be-
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the low 400 nanometres.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
3.2.1 calibration subsystems, n—the instruments used to
2
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
supply and monitor current to a standard lamp during
calibration, consisting of a DC power supply, a current shunt,
2. Referenced Documents
and a digital voltmeter.
3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
3.2.2 National Metrological Institution (NMI), n—A na-
E772Terminology of Solar Energy Conversion
tion‘s internationally recognized standardization laboratory.
E1341Practice
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: G138 − 06 G138 − 12
Standard Test Method for
Calibration of a Spectroradiometer Using a Standard Source
1
of Irradiance
This standard is issued under the fixed designation G138; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
INTRODUCTION
A standardized means of performing and reporting calibration of the spectroradiometer for spectral
irradiance measurements is desirable.
This test method presents specific technical requirements for a laboratory performing calibration of
a spectroradiometer for spectral irradiance measurements. A detailed procedure for performing the
calibration and reporting the results is outlined.
This test method for calibration is applicable to spectroradiometric systems consisting of at least a
monochromator, input optics, and an optical radiation detector, and applies to spectroradiometric
calibrations performed with a standard of spectral irradiance with known irradiance values traceable
to a national metrological laboratory that has participated in intercomparisons of standards of spectral
irradiance. The standard must also have known uncertainties and measurement geometry associated
with its irradiance values.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method covers the calibration of spectroradiometers for the measurement of spectral irradiance using a standard
of spectral irradiance that is traceable to a national metrological laboratory that has participated in intercomparisons of standards
of spectral irradiance.
1.2 This method is not limited by the input optics of the spectroradiometric system. However, choice of input optics affects the
overall uncertainty of the calibration.
1.3 This method is not limited by the type of monochromator or optical detector used in the spectroradiometer system. Parts
of the method may not apply to determine which parts apply to the specific spectroradiometer being used. It is important that the
choice of monochromator and detector be appropriate for the wavelength range of interest for the calibration. Though the method
generally applies to photodiode array detector based systems, the user should note that these types of spectroradiometers often
suffer from stray light problems and have limited dynamic range. Diode array spectroradiometers are not recommended for use
in the ultraviolet range unless these specific problems are addressed.
1.4 The calibration described in this method employs the use of a standard of spectral irradiance. The standard of spectral
irradiance must have known spectral irradiance values at given wavelengths for a specific input current and clearly defined
measurement geometry. Uncertainties must also be known for the spectral irradiance values. The values assigned to this standard
must be traceable to a national metrological laboratory that has participated in intercomparisons of standards of spectral irradiance.
These standards may be obtained from a number of national standards laboratories and commercial laboratories. The spectral
irradiance standards consist mainly of tungsten halogen lamps with coiled filaments enclosed in a quartz envelope, though other
types of lamps are used. Standards can be obtained with calibration values covering all or part of the wavelength range from 200
to 4500 nm.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee G03 on Weathering and Durabilityand is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee G03.09 on Radiometry.
Current edition approved June 1, 2006June 1, 2012. Published July 2006. Originally approved in 1996. Last previous edition approved in 2003 as G138 – 03. DOI:
10.1520/G0138-06.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
G138 − 12
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
2
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
E772 Terminology of Solar Energy Conversion
E1341 Practice for Obtaining Spectroradiometric Data from Radiant Sources for Colorimetry
2.2 Other Documents:
4
CIE Publication No. 63 The Spectrodiometric Measure
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.