ASTM F1441-03(2009)
(Specification)Standard Specification for Soft-Tissue Expander Devices
Standard Specification for Soft-Tissue Expander Devices
ABSTRACT
This specification covers the requirements for single use saline inflatable, smooth and textured tissue expansion devices to be used intraoperatively or implanted for typically less than 6 months and then removed. This specification applies only to soft-tissue expander devices fabricated with elastomer shells. It does not necessarily cover any custom fabricated soft tissue expander device manufactured to any other specification. The device shall be classified as: Type I; Type II; and Type III. Biocompatibility, tensile set, breaking force, tubing shell junction, injection port competence, overexpansion, tubing length adapter strength, needle stop penetration, and fused or adhered joints tests shall be performed to conform with the specified requirements.
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
This specification contains requirements based on state-of-art science and technology as applicable to various considerations that have been identified as important to ensure reasonable safety and efficacy as it relates to the biocompatibility and the mechanical integrity of the device components in soft tissue expander devices.
This specification is not intended to limit the science and technology that may be considered and applied to ensure performance characteristics of subject device in intended applications. When new information becomes available or changes in state-of-art science and technology occur and relevance to subject devices has been established by valid science, it is intended that this specification will be revised in accordance with ASTM guidelines.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers the requirements for single use saline inflatable, smooth and textured tissue expansion devices to be used intraoperatively or implanted for typically less than 6 months and then removed.
1.2 Limitations:
1.2.1 This specification applies only to soft-tissue expander devices fabricated with elastomer shells. It does not necessarily cover any custom fabricated soft tissue expander device manufactured to any other specification.
1.2.2 This specification applies, in part, to combination “expander/mammary” devices as classified in Section 4.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard, values in parentheses are for information only.
1.4 The following statement pertains only to the test methods and requirements portion, Section 9, of this specification. This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:F1441 −03(Reapproved 2009)
Standard Specification for
Soft-Tissue Expander Devices
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F1441; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope F1251 Terminology Relating to Polymeric Biomaterials in
Medical and Surgical Devices (Withdrawn 2012)
1.1 This specification covers the requirements for single use
F2038 GuideforSiliconeElastomers,Gels,andFoamsUsed
saline inflatable, smooth and textured tissue expansion devices
in Medical Applications Part I—Formulations and Un-
to be used intraoperatively or implanted for typically less than
cured Materials
6 months and then removed.
F2042 GuideforSiliconeElastomers,Gels,andFoamsUsed
1.2 Limitations:
in Medical Applications Part II—Crosslinking and Fabri-
1.2.1 This specification applies only to soft-tissue expander
cation
devicesfabricatedwithelastomershells.Itdoesnotnecessarily
F2051 Specification for Implantable Saline Filled Breast
cover any custom fabricated soft tissue expander device
Prosthesis
manufactured to any other specification.
2.2 Other Documents:
1.2.2 This specification applies, in part, to combination
Federal Register, Title 21, Part 820
“expander/mammary” devices as classified in Section 4.
USP (United States Pharmacopoeia)
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
Association for the Advance of Medical Instrumentation:
standard, values in parentheses are for information only.
ANSI/AAMI/ISO 10993-1 Biological Testing of Medical
and Dental Materials and Devices—Part 1: Guidance on
1.4 The following statement pertains only to the test meth-
ods and requirements portion, Section 9, of this specification. Selection of Tests
ANSI/AAMI/ST50 Dry Heat (Heated Air) Sterilizers
This standard does not purport to address all of the safety
concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility ANSI/AAMI/ISO 11135 Medical Devices—Validation and
Routine Control of Ethylene Oxide Sterilization
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and
health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory ANSI/AAMI/ISO 11137 Sterilization of Health Care
Products—Requirements for Validation and Routine and
limitations prior to use.
Routine Control—Radiation Sterilization
2. Referenced Documents
ANSI/AAMI/ISO 11134 Sterilization of Health Care
Products—Requirements for Validation and Routine
2.1 ASTM Standards:
Control—Industrial Moist Heat Sterilization
D412 Test Methods forVulcanized Rubber andThermoplas-
Parenteral Drug Association 1981 Technical Report No. 3,
tic Elastomers—Tension
Validation of Dry Heat Processes Used for Sterilization
D624 Test Method for Tear Strength of Conventional Vul-
and Depyrogenation
canized Rubber and Thermoplastic Elastomers
D1349 Practice for Rubber—Standard Temperatures for
3. Terminology
Testing
F703 Specification for Implantable Breast Prostheses
3.1 Definitions:
F748 PracticeforSelectingGenericBiologicalTestMethods
for Materials and Devices
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
www.astm.org.
1 4
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F04 on AvailablefromU.S.GovernmentPrintingOfficeSuperintendentofDocuments,
Medical and Surgical Materials and Devices and is the direct responsibility of 732 N. Capitol St., NW, Mail Stop: SDE, Washington, DC 20401, http://
Subcommittee F04.32 on Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. www.access.gpo.gov.
Current edition approved April 1, 2009. Published April 2009. Originally United States Pharmacopeia, Vol XXI, Mack Publishing Company, Easton, PA
approved in 1992. Last previous edition approved in 2003 as F1441 – 03. DOI: 1989. Available from Pharmacopeia Convention, Inc., 12601 Twinbrook Parkway,
10.1520/F1441-03R09. Rockville, NC 00852.
2 6
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or Available fromAmerican National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St.,
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available from the Parenteral Drug Association, 3 Bethesda Medical Center,
the ASTM website. Suite 1500, Bethesda, MD 20814.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
F1441−03 (2009)
3.1.1 injection port—the port through which an injection to 4.3.1 Gel/Saline—Expansion indications for devices of this
inflate or deflate the variable volume device is made. type shall confirm to this specification in addition to Specifi-
cation F703, as applicable.
3.1.1.1 remote port—a port that is remote from the shell and
4.3.2 Saline Only—Expansionindicationsfordevicesofthis
attached to the shell by means of tubing.
type shall confirm to this specification in addition to Specifi-
3.1.1.2 self-contained (integrated) port—a port that is inte-
cation F2051, as applicable.
gral to the device shell.
5. Significance and Use
3.1.2 injection surface—the area of the injection port rec-
ommended by the manufacturer for needle insertion to inflate 5.1 This specification contains requirements based on state-
or deflate the device.
of-art science and technology as applicable to various consid-
erations that have been identified as important to ensure
3.1.3 needle stop—the injection port component used to
reasonable safety and efficacy as it relates to the biocompat-
limit hypodermic needle penetration through the port.
ibility and the mechanical integrity of the device components
3.1.4 silicone elastomer—an elastomer containing cross-
in soft tissue expander devices.
linked silicone polymer and fumed amorphous (non-
5.1.1 This specification is not intended to limit the science
crystalline) silica as a reinforcing filler.
and technology that may be considered and applied to ensure
3.1.5 reinforced silicone elastomer—a composite of silicone performance characteristics of subject device in intended
elastomer and an embedded textile made from polyethylene applications. When new information becomes available or
terephthalate (such as Dacron (trademark)) fibers. changes in state-of-art science and technology occur and
relevance to subject devices has been established by valid
3.1.6 shell—a silicone elastomer continuous layer or mem-
science, it is intended that this specification will be revised in
brane container (sac) which encloses a lumen of a soft tissue
accordance with ASTM guidelines.
expander.
6. Volume and Dimensions
3.1.7 patch or base—a piece of silicone elastomer or rein-
forced silicone elastomer, which covers and seals the hole
6.1 Volumes of Devices—The designed or minimum and
which results from the manufacturing process of shell fabrica-
maximum recommended volume of saline fill shall be listed in
tion.
instructions for use.
3.1.8 lumen—a cavity within a shell and patch or base,
6.2 Dimensions—Therangesofshapes,volumes,basesizes,
accessible by an injection port, to facilitate the addition of
and anterior projections are determined by the manufacturer.
saline to adjust the volume of the soft tissue expander.
Pertinent information shall be contained in the package insert.
3.1.9 tubing length adapter—the tissue expander compo-
7. Fixation Sites
nent used to connect more than one piece of remote port
tubing.
7.1 The presence of fixation sites on any type of soft tissue
expander device is optional. When used, the size and locations
3.1.10 tubing/shell junction—thejunctionoftheremoteport
of fixation sites shall be clearly stated in instructions for use.
tubing to the shell of the tissue expander.
3.1.11 fused or adhered joints (seams)—sites in the shell or
8. Orientation Means
other parts of the tissue expander device where materials have
8.1 Orientation means are optional features of subject de-
been joined (fused or bonded) together, with or without
vices. When orientation means are claimed, the location and
adhesive, as part of the manufacturing process.
recommended techniques for use shall be clearly described in
3.1.12 orientation means—any mark or palpable portion of
instructions for use.
a soft tissue expander to assist the surgeon in positioning.
9. Test Methods and Requirements
3.1.13 saline—only sodium chloride for injection (USP) is
9.1 Biocompatibility:
recommended for filling lumens of soft tissue expanders.
9.1.1 Practice F748—New or existing materials shall be in
3.2 For other terms used in this specification see Terminol-
compliance with Practice F748 or other accepted standards
ogy F1251.
such as ANSI/AAMI/ISO 10993-1. Assays recommended by
Practice F748 include Cell Culture CytotoxicityAssays, Short-
4. Classification
Term Intramuscular Implantation Assay, Short-Term Subcuta-
neous Assay, Carcinogenicity, Long-Term Implant Test, Sys-
4.1 Type I: Chronic Tissue Expansion Device—Asoft tissue
temic Injection (Acute Toxicity) Assay, Sensitization Assay,
expander device intended to be inflated postoperatively.
Mutagenicity, and Pyrogenicity.
4.2 Type II: Immediate Tissue Expansion Device—A soft
9.1.2 Soft Tissue Expander Devices—Test specimens for
tissue expander device only intended for intraoperative use.
chronic implantation assays (carcinogenicity and long term
4.3 Type III: Combination Expander/Mammary Device—A implanttests)shallbefabricatedfromthesamecombinationof
specific type of soft tissue expander device intended to be silicone elastomer and by the same or similar procedures and
implanted for postoperative expansion of the breast and further conditionsusedinfabricatingdevices.Thethicknessofshellin
indicated for long term implantation as a breast prosthesis. specimens shall be typical of thickness used in devices.
F1441−03 (2009)
9.1.3 Prior Biocompatibility Assays—When prior biocom- 9.2.3 Tubing Shell Junction—The tubing/shell junction of
patibility data are available for silicone elastomer in clinical Type I tissue expanders shall not fail when tested under the
use for tissue expansion, even if not done by the exact following conditions:
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:F1441–92 (Reapproved 1998) Designation: F 1441 – 03 (Reapproved 2009)
Standard Specification for
Soft-Tissue Expander Devices
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F 1441; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This specification covers the requirements for single use saline inflatable, smooth and textured tissue expansion devices to
be used intraoperatively or implanted for typically less than 6 months and then removed.
1.2 Limitations—This specification applies only to soft-tissue expander devices fabricated with elastomer shells. It does not
necessarily cover any custom fabricated soft tissue expander device manufactured to any other specification. :
1.2.1 This specification applies only to soft-tissue expander devices fabricated with elastomer shells. It does not necessarily
cover any custom fabricated soft tissue expander device manufactured to any other specification.
1.2.2 This specification applies, in part, to combination “expander/mammary” devices as classified in Section 4.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard, values in parentheses are for information only.
1.4 The following statement pertains only to the test methods and requirements portion, Section 79, of this specification. This
standard does not purport to address all of the safety problems,concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of
the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D 412 Test Methods for Rubber Properties in Tension
Test Methods for Vulcanized Rubber and Thermoplastic ElastomersTension
D 624 Test Method for Rubber Property—Tear Resistance
Test Method for Tear Strength of Conventional Vulcanized Rubber and Thermoplastic Elastomers
D 1349 Practice for Rubber—Standard Temperatures for Testing
F604Classification for Silicon Elastomers Used in Medical Applications
Practice for RubberStandard Temperatures for Testing
F 703 Specification for Implantable Breast Prostheses
F 748 Practice for Selecting Generic Biological Test Methods for Materials and Devices
F 1251 Terminology Relating to Polymeric Biomaterials in Medical and Surgical Devices
2.2 Federal Register:
Title 21,Part 820 Terminology Relating to Polymeric Biomaterials in Medical and Surgical Devices
F 2038 Guide for Silicone Elastomers, Gels, and Foams Used in Medical Applications Part IFormulations and Uncured
Materials
F 2042 Guide for Silicone Elastomers, Gels, and Foams Used in Medical Applications Part IICrosslinking and Fabrication
F 2051 Specification for Implantable Saline Filled Breast Prosthesis
2.2 Other Documents:
Federal Register, Title 21, Part 820
USP (United States Pharmacopoeia)
Association for the Advance of Medical Instrumentation:
This specification is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee F-4F04 on Medical and Surgical Materials and Devices and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
F04.06F04.32 on Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery.
Current edition approved Dec. 15, 1992. Published February 1993.
Current edition approved April 1, 2009. Published April 2009. Originally approved in 1992. Last previous edition approved in 2003 as F 1441 – 03.
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
, Vol 09.01.volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 13.01.
Available from U.S. Government Printing Office Superintendent of Documents, 732 N. Capitol St., NW, Mail Stop: SDE, Washington, DC 20401, http://
www.access.gpo.gov.
Available from U.S. Government Printing Office, Superintendent of Documents, Washington, DC 20402.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
F 1441 – 03 (2009)
ANSI/AAMI/ISO 10993-1 Biological Testing of Medical and Dental Materials and Devices—Part 1: Guidance on Selection of
Tests
ANSI/AAMI/ST50 Dry Heat (Heated Air) Sterilizers
ANSI/AAMI/ISO 11135 Medical Devices—Validation and Routine Control of Ethylene Oxide Sterilization
ANSI/AAMI/ISO 11137 Sterilization of Health Care Products—Requirements for Validation and Routine and Routine
Control—Radiation Sterilization
ANSI/AAMI/ISO 11134 Sterilization of Health Care Products—Requirements for Validation and Routine Control—Industrial
Moist Heat Sterilization
Parenteral Drug Association 1981 Technical Report No. 3, Validation of Dry Heat Processes Used for Sterilization and
Depyrogenation
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 injection port—the port through which an injection to inflate or deflate the variable volume device is made.
3.1.1.1 remote port—a port that is remote from the shell and attached to the shell by means of tubing.
3.1.1.2 self-contained (integrated) port—a port that is integral to the device shell.
3.1.2 injection surface—theareaoftheinjectionportrecommendedbythemanufacturerforneedleinsertiontoinflateordeflate
the device.
3.1.3 needle stop—the injection port component used to limit hypodermic needle penetration through the port.
3.1.4 reinforced silicone elastomer—a composite of silicone elastomer and an embedded textile made from polyethylene
terephthalate (Dacront) fibres. silicone elastomer—an elastomer containing cross-linked silicone polymer and fumed amorphous
(non-crystalline) silica as a reinforcing filler.
3.1.5 shell—an outer sac of the device which is comprised of silicone elastomer (or other appropriate material). reinforced
silicone elastomer—a composite of silicone elastomer and an embedded textile made from polyethylene terephthalate (such as
Dacron (trademark)) fibers.
3.1.6 shell—a silicone elastomer continuous layer or membrane container (sac) which encloses a lumen of a soft tissue
expander.
3.1.7 patch or base—a piece of silicone elastomer or reinforced silicone elastomer, which covers and seals the hole which
results from the manufacturing process of shell fabrication.
3.1.8 lumen—a cavity within a shell and patch or base, accessible by an injection port, to facilitate the addition of saline to
adjust the volume of the soft tissue expander.
3.1.9 tubing length adapter—the tissue expander component used to connect more than one piece of remote port tubing.
3.1.7
3.1.10 tubing/shell junction—the junction of the remote port tubing to the shell of the tissue expander.
3.2For other terms used in this specification see Terminology F1251
3.1.11 fused or adhered joints (seams)—sites in the shell or other parts of the tissue expander device where materials have been
joined (fused or bonded) together, with or without adhesive, as part of the manufacturing process.
3.1.12 orientation means—any mark or palpable portion of a soft tissue expander to assist the surgeon in positioning.
3.1.13 saline—only sodium chloride for injection (USP) is recommended for filling lumens of soft tissue expanders.
3.2 For other terms used in this specification see Terminology F 1251.
4. Classification
4.1 Type I: Chronic Tissue Expansion Device—A soft tissue expander device intended to be inflated postoperatively.
4.2 Type II: Immediate Tissue Expansion Device—A soft tissue expander device only intended for intraoperative use.
4.3 TypeIII:CombinationExpander/MammaryDevice—Aspecifictypeofsofttissueexpanderdeviceintendedtobeimplanted
for postoperative expansion of the breast and further indicated for long term implantation as a breast prosthesis.
4.3.1 Gel/Saline—Expansion indications for devices of this type shall confirm to this specification in addition to Specification
F 703, as applicable.
4.3.2 Saline Only—Expansion indications for devices of this type shall confirm to this specification in addition to Specification
F 2051, as applicable.
5. Significance and Use
5.1The devices described in this specification are intended for use in soft tissue expansion. This specification identifies those
United States Pharmacopeia, Vol XXI, Mack Publishing Company, Easton, PA 1989. Available from Pharmacopeia Convention, Inc., 12601 Twinbrook Parkway,
Rockville, NC 00852.
Available from U.S. Pharmacopeia, Vol XX, Mack Publishing Co., Easton, PA.
Available from American National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St., 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
The Precision Glide hypodermic needle, available from Becton Dickinson, One Becton Drive, Franklin Lakes, NJ 07417, or its equivalent, has been found satisfactory
for this purpose.
Available from the Parenteral Drug Association, 3 Bethesda Medical Center, Suite 1500, Bethesda, MD 20814.
F 1441 – 03 (2009)
factors felt to be important to ensure safety as it relates to the device biocompatibility and the mechanical integrity of the device
components.
5.1 Thisspecificationcontainsrequirementsbasedonstate-of-artscienceandtechnologyasapplicabletovariousconsiderations
that have been identified as important to ensure reasonable safety and efficacy as it relates to the biocompatibility and the
mechanical integrity of the device components in soft tissue expander devices.
5.1.1 This specification is not intended to limit the science and technology that may be considered and applied to ensure
performance characteristics of subject device in intended applications. When new information becomes available or changes in
state-of-art science and technology occur and relevance to subject devices has been established by valid science, it is intended that
this specification will be revised in accordance with ASTM guidelines.
6. Requirements Volume and Dimensions
6.1 Volumes of Devices—The designed or minimum and maximum recommended volume of saline fill shall be listed in
instructions for use.
6.2 Dimensions—The ranges of shapes, volumes, base sizes, and anterior projections are determined by the manufacturer.
Pertinent information shall be contained in the package insert.
7. Fixation Sites
7.1 The presence of fixation sites on any type of soft tissue expander device is optional. When used, the size and locations of
fixation sites shall be clearly stated in instructions for use.
8. Orientation Means
8.1 Orientation means are optional features of subject devices. When orientation means are claimed, the location and
recommended techniques for use shall be clearly described in instructions for use.
9. Test Methods and Requirements
9.1 Biocompatibility:
6.1.1Biological testing to ensure safety of soft tissue expander devices shall be selected and conducted in accordance with
Practice F748.
6.1.2In addition to biological testing as recommended by Practice F748, other biological testing may be appropriate.
6.2
9.1.1 Practice F 748—New or existing materials shall be in compliance with Practice F 748 or other accepted standards such
as ANSI/AAMI/ISO 10993-1. Assays recommended by Practice F 748 include Cell Culture Cytotoxicity Assays, Short-Term
Intramuscular ImplantationAssay, Short-Term SubcutaneousAssay, Carcinogenicity, Long-Term Implant Test, Systemic Injection
(Acute Toxicity) Assay, Sensitization Assay, Mutagenicity, and Pyrogenicity.
9.1.2 Soft Tissue Expander Devices—Test specimens for chronic implantation assays (carcinogenicity and long term implant
tests) shall be fabricated from the same combination of silicone elastomer and by the same or similar procedures and conditions
used in fabricating devices. The thickness of shell in specimens shall be typical of thickness used in devices.
9.1.3 Prior Biocompatibility Assays— When prior biocompatibility data are available for silicone elastomer in clinical use for
tissue expansion, even if not done by the exact protocols described in more standards, such data may satisfy all or part of the
specific biocompatibility requirements of Practice F 748 or equivalent methodology.
9.2 Physical Properties:
6.2.1Tensile Set—Maximum set shall be less than 10% when tested in accordance with 7.2.1
9.2.1 Tissue expander or component designs, or both, shall demonstrate an acceptable response to the following tests. Devices
for testing should be selected from standard production batches which have gone through all manufacturing processes, including
sterilization. Unless otherwise specified, the standard temperature for testing shall be 23 6 2°C (73.4 6 3.6°F). Condition the test
specimens for at least 3 h when the test temperature is not 23 6 2°C. If the material is affected by moisture, maintain the relative
humidity at 50 6 5 % and condition the specimen for at least 24 h prior to testing. When testing at any other temperature is
required, use one of the temperatures specified in Practice D 1349.
6.2.2Breaking Force—Ultimate breaking force in tension shall be no less than 11.12 N (2.5 lb) when tested in accordance with
7.2.3.
6.2.3Tear Resistance—Tear resistance shall be 3.5584 N (0.8 lb) minimum when tested in accordance with 7.2.3.
7.Test Methods
7.1Tissue expander or component designs, or both, shall demonstrate an acceptable response to the following tests. Unless
otherwisespecified,thestandardtemperaturefortestingshallbe23 62°C(73.4 63.6°F).Conditionthetestspecimensforatleast
3 h when the test temperature is 23 6 2°C. If the material is affected by moisture, maintain the relative humidity at 50 6 5% and
condition the specimen for at least 24 h prior to testing. When testing at any other temperature is required, use one of the
temperatures specified in Practice D1349.
7.2
F 1441 – 03 (2009)
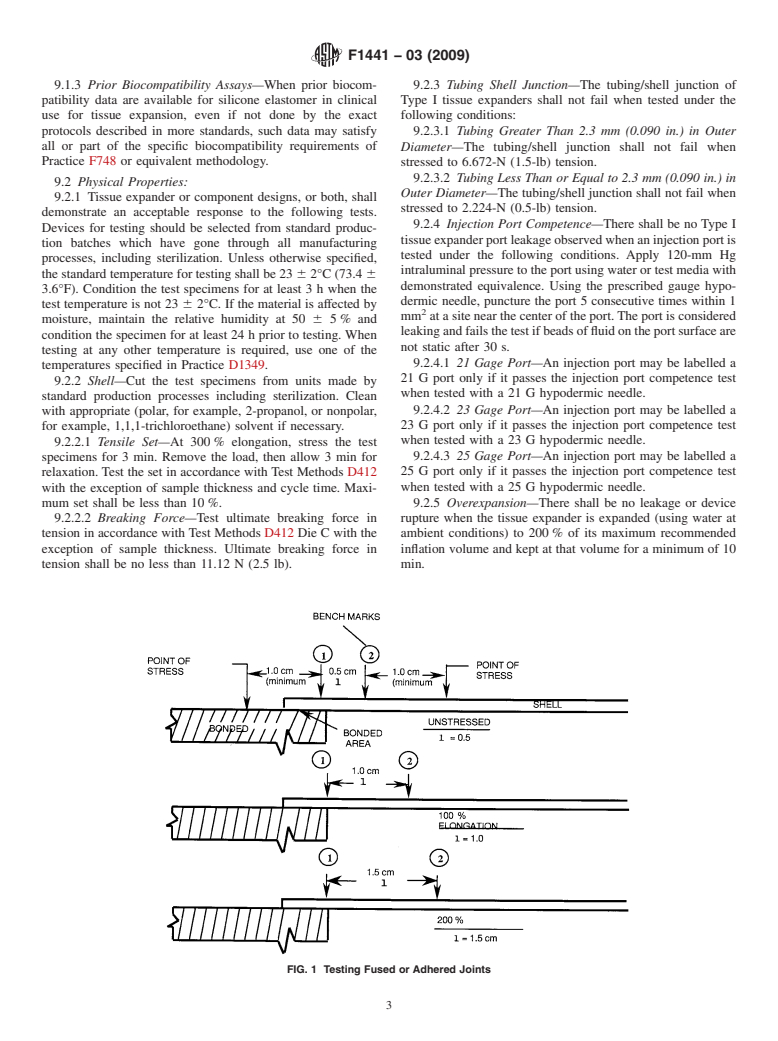
FIG. 1 Testing Fused or Adhered Joints
9.2.2 Shell—Cut the test specimens from units made by standard production processes including sterilization. Clean with
appropriate (polar, for example, 2-propanol, or nonpolar, for example, 1,1,1-trichloroethane) solvent if necessary.
7.2.1
9.2.2.1 Tensile Set—At300 %elongation,stressthetestspecimensfor3min.Removetheload,thenallow3minforrelaxation.
Test the set in accordance with Test Methods D 412 with the exception of sample thickness and cycle time.
7.2.2with the exception of sample thickness and cycle time. Maximum set shall be
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.