ASTM F2082-06
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determination of Transformation Temperature of Nickel-Titanium Shape Memory Alloys by Bend and Free Recovery (Withdrawn 2015)
Standard Test Method for Determination of Transformation Temperature of Nickel-Titanium Shape Memory Alloys by Bend and Free Recovery (Withdrawn 2015)
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
This test method provides a rapid, economical method for determination of transformation temperatures.
Measurement of the specimen motion closely parallels many shape memory applications and provides a result that is applicable to the function of the material.
This test method uses wire, tube, or strip samples; thus, it is able to provide an assessment of the product in its semifinished form.
This test method may be used on annealed samples to determine the transformation temperatures and assure the alloy formulation, since chemical analysis is not precise enough to determine adequately the nickel-to-titanium ratio of shape memory alloys.
Transformation temperatures derived from this test method may differ from those derived from other methods as a result of effects of strain and load on the transformation temperature.
The test method is applicable to shape memory alloys with Af temperatures in the range of approximately – 25 to +90°C.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method describes a procedure for determining the martensite-to-austenite transformation temperatures of either fully-annealed or heat-treated nickel titanium alloys by measuring the deformation recovered during the thermal transformation.
1.2 The values in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in inch-pound units are provided for information only.
This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
WITHDRAWN RATIONALE
This test method described a procedure for determining the martensite-to-austenite transformation temperatures of either fully-annealed or heat-treated nickel titanium alloys by measuring the deformation recovered during the thermal transformation.
Formerly under the jurisdiction of Committee F04 on Medical and Surgical Materials and Devices, this practice was withdrawn in January 2015 in accordance with section 10.6.3 of the Regulations Governing ASTM Technical Committees, which requires that standards shall be updated by the end of the eighth year since the last approval date.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: F2082 − 06
StandardTest Method for
Determination of Transformation Temperature of Nickel-
1
Titanium Shape Memory Alloys by Bend and Free Recovery
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F2082; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 3.3 Abbreviations:
3.3.1 LVDT—linear variable differential transducer.
1.1 This test method describes a procedure for determining
3.3.2 RVDT—rotary variable differential transducer.
the martensite-to-austenite transformation temperatures of ei-
ther fully-annealed or heat-treated nickel titanium alloys by
4. Summary of Test Method
measuring the deformation recovered during the thermal trans-
formation.
4.1 This test method involves cooling a test specimen to its
nominally fully martensitic phase, deforming the specimen,
1.2 The values in SI units are to be regarded as the standard.
and heating the specimen to its fully austenitic phase. During
The values given in inch-pound units are provided for infor-
heating, the motion of the specimen is measured and plotted
mation only.
versus the specimen temperature. For a two-stage
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
transformation, the R’ , R’, A , and A, as defined in Terminol-
s f s f
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
ogy F2005, are determined. For a single-stage transformation,
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
the A and A are determined.
s f
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
5. Significance and Use
2. Referenced Documents
5.1 This test method provides a rapid, economical method
2
for determination of transformation temperatures.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
E177 Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in
5.2 Measurement of the specimen motion closely parallels
ASTM Test Methods
many shape memory applications and provides a result that is
E220 Test Method for Calibration of Thermocouples By
applicable to the function of the material.
Comparison Techniques
5.3 This test method uses wire, tube, or strip samples; thus,
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
it is able to provide an assessment of the product in its
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
semifinished form.
F2005 Terminology for Nickel-Titanium Shape Memory
5.4 This test method may be used on annealed samples to
Alloys
determine the transformation temperatures and assure the alloy
3. Terminology
formulation, since chemical analysis is not precise enough to
determine adequately the nickel-to-titanium ratio of shape
3.1 Definitions—Specific technical terms used in this test
memory alloys.
method are found in Terminology F2005.
5.5 Transformation temperatures derived from this test
3.2 free recovery—unconstrained motion of a shape
method may differ from those derived from other methods as a
memory alloy upon heating and transformation to austenite
result of effects of strain and load on the transformation
after deformation in a lower temperature phase.
temperature.
5.6 The test method is applicable to shape memory alloys
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee F04 on Medical
and Surgical Materials and Devices and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee with A temperatures in the range of approximately – 25 to
f
F04.15 on Material Test Methods.
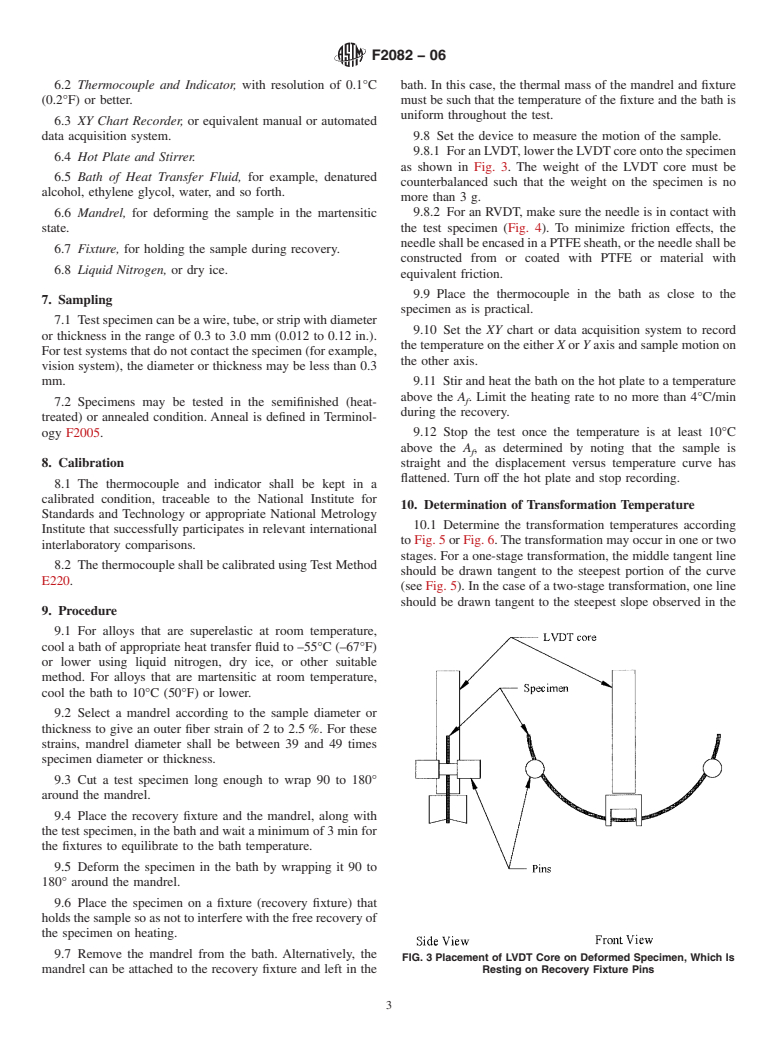
+90°C.
Current edition approved Aug. 15, 2006. Published August 2006. Originally
approved in 2001. Last previous edition approved in 2003 as F2082 – 03. DOI:
6. Apparatus
10.1520/F2082-06.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
6.1 LVDT, with range greater than half the mandrel diameter
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
(see 9.2), with power supply, mounted in an appropriate fixture
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. with counterbalanced probe (see Fig. 1); or RVDT with range
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
F2082 − 06
FIG. 1 Schematic Showing Side View of Test Apparatus Using a Vertically Mounted and Counterbalanced LVDT (LVDT Power Supply,
Thermocouple Indicator, and Data Acquisition System Are Not Shown)
greater than 45°, with power supply, mounted in an appropriate measuring sample displacement.
fixture (see Fig. 2); or vision system; or equivalent means of
FIG. 2 Schematic Showing Top View of Test Apparatus Using an
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.