ASTM C1202-97
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Electrical Indication of Concrete's Ability to Resist Chloride Ion Penetration
Standard Test Method for Electrical Indication of Concrete's Ability to Resist Chloride Ion Penetration
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the electrical conductance of concrete to provide a rapid indication of its resistance to the penetration of chloride ions. This test method is applicable to types of concrete where correlations have been established between this test procedure and long-term chloride ponding procedures such as those described in AASHTO T259. Examples of such correlations are discussed in Refs. (1-5).
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard, except where SI units are given first followed by inch-pound units in parentheses. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:C1202–97
Standard Test Method for
Electrical Indication of Concrete’s Ability to Resist Chloride
Ion Penetration
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C 1202; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope ride Ion Penetration
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the elec-
3. Summary of Test Method
trical conductance of concrete to provide a rapid indication of
3.1 This test method consists of monitoring the amount of
its resistance to the penetration of chloride ions. This test
electrical current passed through 2-in. (51-mm) thick slices of
method is applicable to types of concrete where correlations
4-in. (102-mm) nominal diameter cores or cylinders during a
have been established between this test procedure and long-
6-h period. A potential difference of 60 V dc is maintained
term chloride ponding procedures such as those described in
across the ends of the specimen, one of which is immersed in
AASHTO T 259. Examples of such correlations are discussed
2 a sodium chloride solution, the other in a sodium hydroxide
in Refs 1-5.
solution. The total charge passed, in coulombs, has been found
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
to be related to the resistance of the specimen to chloride ion
as the standard, except where SI units are given first followed
penetration.
by inch-pound units in parentheses. The values given in
parentheses are for information only.
4. Significance and Use
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
4.1 This test method covers the laboratory evaluation of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
electrical conductance of concrete samples to provide a rapid
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
indication of their resistance to chloride ion penetration. In
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
most cases the electrical conductance results have shown good
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
correlation with chloride ponding tests, such as AASHTO
T259, on companion slabs cast from the same concrete
2. Referenced Documents
mixtures (Refs 1-5).
2.1 ASTM Standards:
4.2 This test method is suitable for evaluation of materials
C 31 Practice for Making and Curing Concrete Test Speci-
3 and material proportions for design purposes and research and
mens in the Field
development.
C 42 Test Method for Obtaining and Testing Drilled Cores
3 4.3 The numerical results (total charge passed, in coulombs)
and Sawed Beams of Concrete
from this test method must be used with caution, especially in
C 192 Practice for Making and Curing Concrete Test Speci-
3 applicationssuchasqualitycontrolandacceptancetesting.The
mens in the Laboratory
qualitative terms in the right-hand column ofTable 1 should be
C 670 Practice for Preparing Precision and Bias Statements
3 used in most cases.
for Test Methods for Construction Purposes
4.4 Care should be taken in interpreting results of this test
2.2 AASHTO Standard:
when it is used on surface-treated concretes, for example,
T 259 Method of Test for Resistance of Concrete to Chlo-
concretes treated with penetrating sealers.The results from this
test on some such concretes indicate low resistance to chloride
ion penetration, while 90-day chloride ponding tests on com-
panion slabs show a higher resistance.
4.5 The details of the test method apply to 4-in. (102-mm)
ThistestmethodisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeC-9onConcrete
nominal diameter specimens. This includes specimens with
and ConcreteAggregatesand is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C09.66on
actual diameters ranging from 3.75 in. (95 mm) to 4.0 in. (102
Concrete’s Resistance to Fluid Penetration.
Current edition approved Jan. 10, 1997. Published March 1997. Originally
published as C 1202 – 91. Last previous edition C 1202 – 94.
2 4
The boldface numbers in parentheses refer to the list of references at the end of Methods of Sampling and Testing, 1986, American Association of State
this standard. Highway and Transportation Officials, 444 N. Capitol St., NW, Washington, DC
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 04.02. 20001.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
C1202–97
TABLE 1 Chloride Ion Penetrability Based on Charge Passed
5. Interferences
(1)1
5.1 This test method can produce misleading results when
Charge Passed (coulombs) Chloride Ion Penetrability
calcium nitrite has been admixed into a concrete. The results
>4,000 High
from this test on some such concretes indicate higher coulomb
2,000–4,000 Moderate
values, that is, lower resistance to chloride ion penetration,
1,000–2,000 Low
100–1,000 Very Low
than from tests on identical concrete mixtures (controls)
<100 Negligible
without calcium nitrite. However, long-term chloride ponding
tests indicate the concretes with calcium nitrite were at least as
resistant to chloride ion penetration as the control mixtures.
mm).Otherspecimendiametersmaybetestedwithappropriate
NOTE 1—Other admixtures might affect results of this test similarly.
changes in the applied voltage cell design (see 7.5 and Fig. 1).
Long term ponding tests are recommended if an admixture effect is
4.5.1 For specimen diameters other than 3.75 in. (95 mm),
suspected.
the test result value for total charge passed must be adjusted
5.2 Since the test results are a function of the electrical
following the procedure in 11.2. For specimens with diameters
resistance of the specimen, the presence of reinforcing steel or
less than 3.75 in. (95 mm), particular care must be taken in
other embedded electrically conductive materials may have a
coating and mounting the specimens to ensure that the con-
significant effect.The test is not valid for specimens containing
ductive solutions are able to contact the entire end areas during
reinforcing steel positioned longitudinally, that is, providing a
the test.
continuous electrical path between the two ends of the speci-
4.6 Sample age may have significant effects on the test
men.
results, depending on the type of concrete and the curing
6. Apparatus
procedure. Most concretes, if properly cured, become progres-
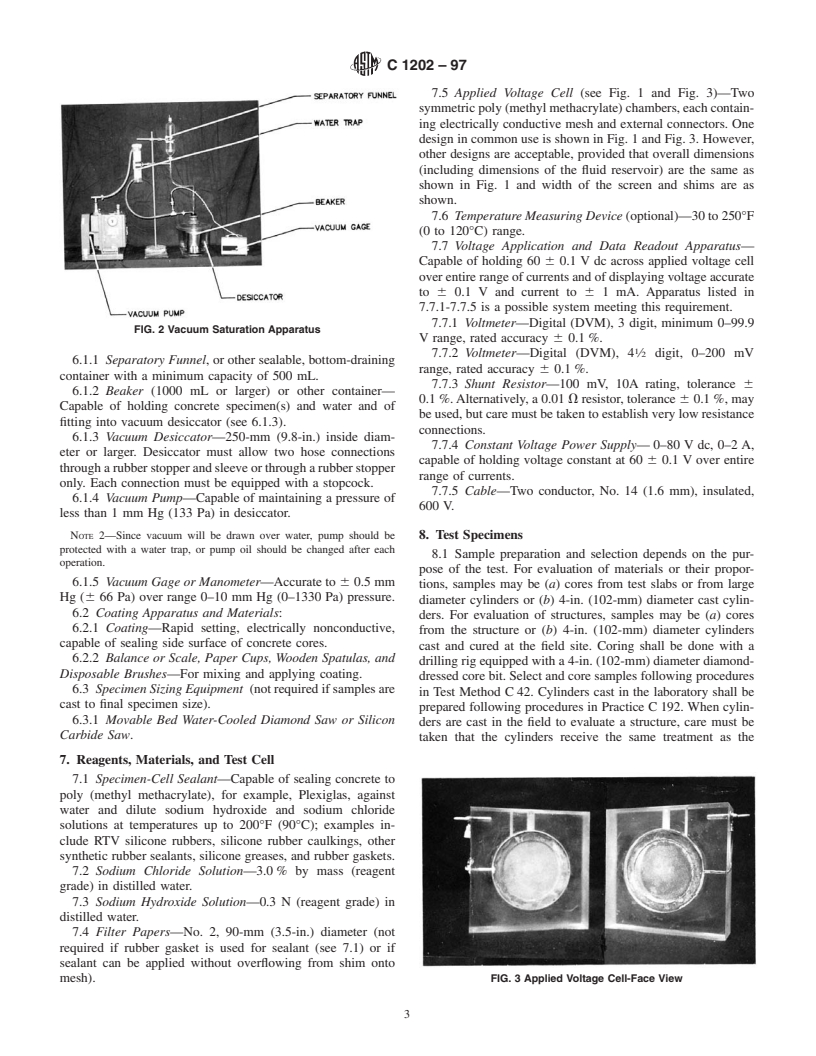
sively and significantly less permeable with time. 6.1 Vacuum SaturationApparatus (see Fig. 2 for example):
FIG. 1 Applied Voltage Cell (construction drawing)
C1202–97
7.5 Applied Voltage Cell (see Fig. 1 and Fig. 3)—Two
symmetricpoly(methylmethacrylate)chambers,eachcontain-
ing electrically conductive mesh and external connectors. One
design in common use is shown in Fig. 1 and Fig. 3. However,
other designs are acceptable, provided that overall dimensions
(including dimensions of the fluid reservoir) are the same as
shown in Fig. 1 and width of the screen and shims are as
shown.
7.6 TemperatureMeasuringDevice (optional)—30 to 250°F
(0 to 120°C) range.
7.7 Voltage Application and Data Readout Apparatus—
Capable of holding 60 6 0.1 V dc across applied voltage cell
over entire range of currents and of displaying voltage accurate
to 6 0.1 V and current to 6 1 mA. Apparatus listed in
7.7.1-7.7.5 is a possible system meeting this requirement.
7.7.1 Voltmeter—Digital (DVM), 3 digit, minimum 0–99.9
FIG. 2 Vacuum Saturation Apparatus
V range, rated accuracy 6 0.1 %.
7.7.2 Voltmeter—Digital (DVM), 4 ⁄2 digit, 0–200 mV
6.1.1 Separatory Funnel, or other sealable, bottom-draining
range, rated accuracy 6 0.1 %.
container with a minimum capacity of 500 mL.
7.7.3 Shunt Resistor—100 mV, 10A rating, tolerance 6
6.1.2 Beaker (1000 mL or larger) or other container—
0.1 %.Alternatively, a 0.01 V resistor, tolerance 6 0.1 %, may
Capable of holding concrete specimen(s) and water and of
be used, but care must be taken to establish very low resistance
fitting into vacuum desiccator (see 6.1.3).
connections.
6.1.3 Vacuum Desiccator—250-mm (9.8-in.) inside diam-
7.7.4 Constant Voltage Power Supply— 0–80 V dc, 0–2 A,
eter or larger. Desiccator must allow two hose connections
capable of holding voltage constant at 60 6 0.1 V over entire
througharubberstopperandsleeveorthrougharubberstopper
range of currents.
only. Each connection must be equipped with a stopcock.
7.7.5 Cable—Two conductor, No. 14 (1.6 mm), insulated,
6.1.4 Vacuum Pump—Capable of maintaining a pressure of
600 V.
less than 1 mm Hg (133 Pa) in desiccator.
8. Test Specimens
NOTE 2—Since vacuum will be drawn over water, pump should be
protected with a water trap, or pump oil should be changed after each
8.1 Sample preparation and selection depends on the pur-
operation.
pose of the test. For evaluation of materials or their propor-
6.1.5 Vacuum Gage or Manometer—Accurate to 6 0.5 mm
tions, samples may be (a) cores from test slabs or from large
Hg (6 66 Pa) over range 0–10 mm Hg (0–1330 Pa) pressure.
diameter cylinders or (b) 4-in. (102-mm) diameter cast cylin-
6.2 Coating Apparatus and Materials:
ders. For evaluation of structures, samples may be (a) cores
6.2.1 Coating—Rapid setting, electrically nonconductive,
from the structure or (b) 4-in. (102-mm) diameter cylinders
capable of sealing side surface of concrete cores.
cast and cured at the field site. Coring shall be done with a
6.2.2 Balance or Scale, Paper Cups, Wooden Spatulas, and
drilling rig equipped with a 4-in. (102-mm) diameter diamond-
Disposable Brushes—For mixing and applying coating.
dressed core bit. Select and core samples following procedures
6.3 SpecimenSizingEquipment (notrequiredifsamplesare
in Test Method C 42. Cylinders cast in the laboratory shall be
cast to final specimen size).
prepared following procedures in Practice C 192. When cylin-
6.3.1 Movable Bed Water-Cooled Diamond Saw or Silicon
ders are cast in the field to evaluate a structure, care must be
Carbide Saw.
taken that the cylinders receive the same treatment as the
7. Reagents, Materials, and Test Cell
7.1 Specimen-Cell Sealant—Capable of sealing concrete to
poly (methyl methacrylate), for example, Plexiglas, against
water and dilute sodium hydroxide and sodium chloride
solutions at temperatures up to 200°F (90°C); examples in-
clude RTV silicone rubbers, silicone rubber caulkings, other
synthetic rubber sealants, silicone greases, and rubber gaskets.
7.2 Sodium Chloride Solution—3.0 % by mass (reagent
grade) in distilled water.
7.3 Sodium Hydroxide Solution—0.3 N (reagent grade) in
distilled water.
7.4 Filter Papers—No. 2, 90-mm (3.5-in.) diameter (not
required if rubber gasket is used for sealant (see 7.1) or if
sealant can be applied without overflowing from shim onto
mesh). FIG. 3 Applied Voltage Cell-Face View
C1202–97
structure, for example, similar degree of consolidation, curing, 10.2 Specimen mounting (all sealants other than rubber
and temperature history during curing. gaskets; use 10.2.2 or 10.2.3, as appropriate):
10.2.1 If using two-part specimen-cell sealant, prepare ap-
NOTE 3—The maximum allowable aggregate size has not been estab-
proximately 0.7 to 1.4 oz (20 to 40 g).
lished for this test. Users have indicated that test repeatability is
10.2.2 Low Viscosity Specimen-Cell Sealant—If filter paper
satisfactory on specimens from the same concrete batch for aggregates up
to 25.0 mm (1 in.) nominal maximum size. is necessary, center filter paper over one screen of the applied
voltage cell. Trowel sealant over brass shims adjacent to
8.2 Transport the cores or field-cured cylinders to the
applied voltage cell body. Carefully remove filter paper. Press
laboratory in sealed (tied) plastic bags. If specimens must be
specimen onto screen; remove or smooth excess sealant which
shipped, they should be packed so as to be properly protected
has flowed out of specimen-cell boundary.
from freezing and from damage in transit or storage.
10.2.3 High Viscosity Specimen-Cell Sealant—Set speci-
8.3 Using the water-cooled diamond saw or silicon carbide
1 men onto screen. Apply sealant around specimen-cell bound-
saw,cuta2 6 ⁄8in.(51 63mm)slicefromthetopofthecore
ary.
or cylinder, with the cut parallel to the top of the core. This
10.2.4 Cover exposed face of specimen with an imperme-
slice will be the test specimen. Use a belt sander to remove any
able material such as rubber or plastic sheeting. Place rubber
burrs on the end of the specimen.
stopper in cell filling hole to restrict moisture movement.
8.4 Special processing is necessary for core samples where
Allow sealant to cure per manufacturer’s instructions.
the surface has been modified, for example, by texturing or by
10.2.5 Repeat steps 10.2.2 (or 10.2.3) and 10.2.4 on second
applying curing compounds, sealers, or other surface treat-
half of cell. (Specimen in applied voltage cell now appears as
ments, and where the intent of the test is not to include the
shown in Fig. 4.)
effect of the modifications. In those cases, the modified portion
1 10.3 Specimen mounting (rubber gasket alternative): Place
of the core shall be removed and the adjacent 2 6 ⁄8 in. (51 6
a 4-in. outside diameter by 3-in. inside diameter by ⁄4-in. (100
3 mm) slice shall be used for the test.
mm outside diameter by 75 mm inside diameter by 6 mm)
9. Conditioning
circular vulcanized rubber gasket in each half of the test cell.
Insert sample and clamp the two halves of the test cell together
9.1 Vigorously boil a litre or more of tapwater in a large
to seal.
sealable container. Remove container from heat, cap tightly,
and allow water to cool to ambient temperature. 10.4 Fill the side of the cell containing the top surface of the
specimen with 3.0 % NaCl solution. (That side of the cell will
9.2 Allow specimen prepared in Section 8 to surface dry in
air for at least 1 h. Prepare approximately ⁄2 oz (10 g) of rapid be connected to the negative terminal of the power supply in
10.5.) Fill the other side of the cell (which will be connected to
setting coating and brush onto the side surface of specimen.
Place the sample on a suitable support while coating to ensure the positive terminal of the power supply) with 0.3 N NaOH
solution.
complete coating of sides. Allow coating to cure according to
the manufacturer’s instructions. 10.5 Attach lead wires to cell banana posts. Make electrical
connections to voltage application and data readout apparatus
9.3 The coating should be allowed to cure until it is no
as appropriate; for example, for system listed in 7.7.1-7.7.5,
longerstickytothetouch.Fillanyapparentholesinthecoating
connect as shown in Fig. 5. Tur
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.