ASTM D5292-99(2004)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Aromatic Carbon Contents of Hydrocarbon Oils by High Resolution Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
Standard Test Method for Aromatic Carbon Contents of Hydrocarbon Oils by High Resolution Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the aromatic hydrogen content (Procedures A and B) and aromatic carbon content (Procedure C) of hydrocarbon oils using high-resolution nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectrometers. Applicable samples include kerosenes, gas oils, mineral oils, lubricating oils, coal liquids, and other distillates that are completely soluble in chloroform at ambient temperature. For pulse Fourier transform (FT) spectrometers, the detection limit is typically 0.1 mol % aromatic hydrogen atoms and 0.5 mol % aromatic carbon atoms. For continuous wave (CW) spectrometers, which are suitable for measuring aromatic hydrogen contents only, the detection limit is considerably higher and typically 0.5 mol % aromatic hydrogen atoms.
1.2 The reported units are mole percent aromatic hydrogen atoms and mole percent aromatic carbon atoms.
1.3 This test method is not applicable to samples containing more than 1 mass % olefinic or phenolic compounds.
1.4 This test method does not cover the determination of the percentage mass of aromatic compounds in oils since NMR signals from both saturated hydrocarbons and aliphatic substituents on aromatic ring compounds appear in the same chemical shift region. For the determination of mass or volume percent aromatics in hydrocarbon oils, chromatographic, or mass spectrometry methods can be used.
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard.
This standard does not purport to address all of the safety problems, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific precautionary statements are given in 7.2 and 7.4.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
An American National Standard
Designation:D5292–99 (Reapproved 2004)
Standard Test Method for
Aromatic Carbon Contents of Hydrocarbon Oils by High
Resolution Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D5292; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 2. Referenced Documents
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the aro- 2.1 ASTM Standards:
matic hydrogen content (Procedures A and B) and aromatic D3238 Test Method for Calculation of Carbon Distribution
carbon content (Procedure C) of hydrocarbon oils using and Structural Group Analysis of Petroleum Oils by the
high-resolution nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectrom- n-d-M Method
eters. Applicable samples include kerosenes, gas oils, mineral D3701 Test Method for Hydrogen Content of Aviation
oils, lubricating oils, coal liquids, and other distillates that are TurbineFuelsbyLowResolutionNuclearMagneticReso-
completely soluble in chloroform at ambient temperature. For nance Spectrometry
pulse Fourier transform (FT) spectrometers, the detection limit D4057 Practice for Manual Sampling of Petroleum and
istypically0.1mol%aromatichydrogenatomsand0.5mol% Petroleum Products
aromatic carbon atoms. For continuous wave (CW) spectrom- E386 Practice for Data Presentation Relating to High-
eters, which are suitable for measuring aromatic hydrogen ResolutionNuclearMagneticResonance(NMR)Spectros-
contents only, the detection limit is considerably higher and copy
typically 0.5 mol % aromatic hydrogen atoms. 2.2 Energy Institute Methods:
1.2 The reported units are mole percent aromatic hydrogen IP Proposed Method BD Aromatic Hydrogen and Aromatic
atoms and mole percent aromatic carbon atoms. CarbonContentsofHydrocarbonOilsbyHighResolution
1.3 Thistestmethodisnotapplicabletosamplescontaining Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
more than 1 mass % olefinic or phenolic compounds.
3. Terminology
1.4 Thistestmethoddoesnotcoverthedeterminationofthe
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
percentage mass of aromatic compounds in oils since NMR
signals from both saturated hydrocarbons and aliphatic sub- 3.1.1 aromatic carbon content—mole percent aromatic car-
bon atoms or the percentage of aromatic carbon of the total
stituents on aromatic ring compounds appear in the same
chemicalshiftregion.Forthedeterminationofmassorvolume carbon:
percent aromatics in hydrocarbon oils, chromatographic, or
aromatic carbon content 5100
mass spectrometry methods can be used.
3 ~aromatic carbon atoms!/~total carbon atoms! (1)
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
3.1.1.1 Discussion—For example, the aromatic carbon con-
standard.
tent of toluene is 100 3(6/7) or 85.7 mol % aromatic carbon
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the
atoms.
safety problems, if any, associated with its use. It is the
3.1.2 aromatic hydrogen content—mole percent aromatic
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
hydrogen atoms or the percentage of aromatic hydrogen of the
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
total hydrogen:
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific precau-
aromatic hydrogen content 5100
tionary statements are given in 7.2 and 7.4.
3 ~aromatic hydrogen atoms!/~total hydrogen atoms! (2)
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
PetroleumProductsandLubricantsandisthedirectresponsibilityofSubcommittee Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
D02.04 on Absorption Spectroscopic Methods. the ASTM website.
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2004. Published November 2004. Originally Available from Energy Institute, 61 New Cavendish St., London, WIG 7AR,
approved in 1992. Last previous edition approved in 1999 as D5292–99. U.K.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
D5292–99 (2004)
3.1.2.1 Discussion—For example, the aromatic hydrogen contentsandareapplicabletoawiderangeofhydrocarbonoils
content of toluene is 100 3(5/8) or 62.5 mol % aromatic that are completely soluble in chloroform at ambient tempera-
hydrogen atoms. ture.
3.2 Definitions of chemical shift (reported in parts per 5.3 The aromatic hydrogen and aromatic carbon contents
million (ppm)), internal reference, spectral width, and other determinedbythistestmethodcanbeusedtoevaluatechanges
NMR terminology used in this test method can be found in in aromatic contents of hydrocarbon oils due to changes in
Practice E386. processing conditions and to develop processing models in
3.3 Chloroform-d refers to chloroform solvent in which which the aromatic content of the hydrocarbon oil is a key
hydrogen is replaced by deuterium, the heavier isotope of processing indicator.
hydrogen. Chloroform-d is available from a variety of chemi-
cal and isotope suppliers.
TABLE 1 Sample and Instrument Conditions for Continuous
Wave (CW) Measurements of H NMR Spectra
4. Summary of Test Method
Solvent Chloroform-d
Sample concentration Up to 50 % v/v for distillable oils
4.1 Hydrogen ( H) nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR)
Sample temperature Instrument ambient
spectra are obtained on solutions of the sample in
Internal lock None
chloroform-d, using a CW or pulse FT high-resolution NMR
Sample spinning rate As recommended by manufacturer, typically 20 Hz
r-f Power level As recommended by instrument manufacturer
spectrometer. Carbon ( C) NMR spectra are obtained on
Signal to noise level A minimum of 5:1 for the maximum height of the
solutions of the sample in chloroform-d using a pulse FT
smaller integrated absorption band
high-resolution NMR spectrometer. Tetramethylsilane is pre-
Chemical shift reference Preferably tetramethylsilane (0.0 ppm) at no
greater than 1 vol % concentration
ferred as an internal reference in these solvents for assigning
Integration Integrate over the range − 0.5 to 5.0 ppm for the
the 0.0 parts per million (ppm) chemical shift position in
aliphatic band and 5.0 to 10.0 ppm for the aromatic
1 13
both H and C NMR spectra.
band
4.2 The aromatic hydrogen content of the sample is mea-
sured by comparing the integral for the aromatic hydrogen
bandinthe HNMRspectrum(5.0to10.0ppmchemicalshift
6. Apparatus
region) with the sum of the integrals for both the aliphatic
6.1 High-Resolution Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
hydrogen band (−0.5 to 5.0 ppm region) and the aromatic
Spectrometer—A high-resolution continuous wave (CW) or
hydrogen band (5.0 to 10.0 ppm region).
pulse Fourier transform (FT) NMR spectrometer capable of
4.3 The aromatic carbon content of the sample is measured
beingoperatedaccordingtotheconditionsinTable1andTable
by comparing the integral for the aromatic carbon band in
2andofproducingpeakshavingwidthslessthanthefrequency
the C spectrum (100 to 170 ppm chemical shift region) with
ranges of the majority of chemical shifts and coupling con-
thesumoftheintegralsforboththealiphaticcarbonband(−10
stants for the measured nucleus.
to 70 ppm region) and the aromatic carbon band (100 to 170
6.1.1 H NMR spectra can be obtained using either CW or
ppm region).
pulse FT techniques but C measurements require signal
4.4 The integral of the aromatic hydrogen band must be
averaging and, therefore, currently require the pulse FT tech-
corrected for the NMR absorption line due to residual chloro-
nique. Low resolution NMR spectrometers and procedures are
form (7.25 ppm chemical shift) in the predominantly
not discussed in this test method (see Test Method D3701 for
chloroform-d solvent.
an example of the use of low resolution NMR).
4.5 The integrals of the aliphatic hydrogen band and of the
6.2 Tube Tubes—Usuallya5or10mm outside diameter
aliphatic carbon band must be corrected for the NMR absorp-
tube compatible with the configuration of the CW or pulse FT
tion line due to the internal chemical shift reference tetrameth-
spectrometer.
1 13
ylsilane (0.0 ppm chemical shift in both H and C spectra).
7. Reagents and Materials
5. Significance and Use
7.1 Purity of Reagents—Reagent grade chemicals shall be
5.1 Aromatic content is a key characteristic of hydrocarbon
used in all tests. Unless otherwise indicated, it is intended that
oilsandcanaffectavarietyofpropertiesoftheoilincludingits
all reagents shall conform to the specifications of the Commit-
boiling range, viscosity, stability, and compatibility of the oil
tee onAnalytical Reagents of theAmerican Chemical Society,
with polymers.
where such specifications are available. Other grades may be
5.2 Existing methods for estimating aromatic contents use
used, provided it is first ascertained that the reagent is of
physical measurements, such as refractive index, density, and
sufficiently high purity to permit its use.
numberaveragemolecularweight(seeTestMethodD3238)or
7.2 Chloroform-d—For H NMR, chloroform-d must con-
infrared absorbance and often depend on the availability of
tain less than 0.2 vol % residual chloroform. Care must be
suitable standards. These NMR procedures do not require
taken not to contaminate the solvent with water and other
standards of known aromatic hydrogen or aromatic carbon
“Reagent Chemicals, American Chemical Society Specification.” American
Brandes, G., “The Structural Groups of Petroleum Fractions. I. Structural Chemical Society, Washington, D.C. For suggestions on the testing of reagents not
GroupAnalysisWiththeHelpofInfraredSpectroscopy,” Brennstoff-ChemieVol37, listed by the American Chemical Society, see “Analar Standards for Laboratory
1956, p. 263. U.K. Chemicals,” BDH Ltd., Poole, Dorset, and the “United States Pharmacopeia.”
D5292–99 (2004)
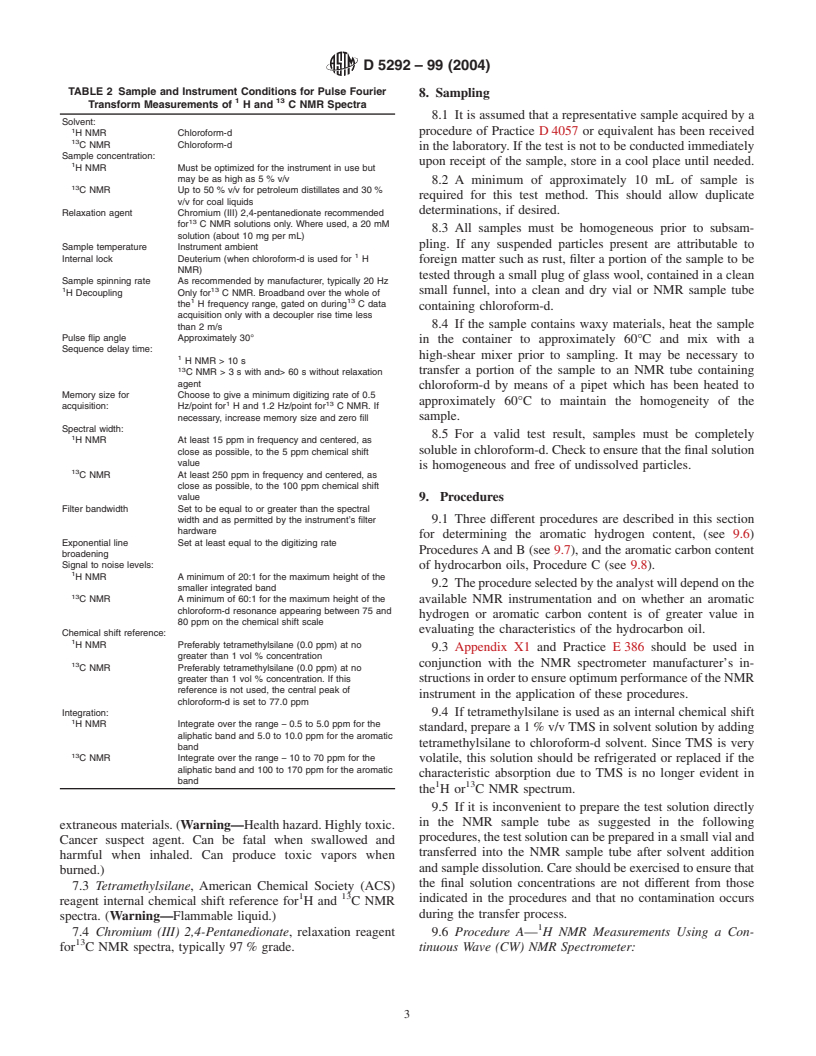
TABLE 2 Sample and Instrument Conditions for Pulse Fourier
8. Sampling
1 13
Transform Measurements of H and C NMR Spectra
8.1 It is assumed that a representative sample acquired by a
Solvent:
procedure of Practice D4057 or equivalent has been received
H NMR Chloroform-d
C NMR Chloroform-d
inthelaboratory.Ifthetestisnottobeconductedimmediately
Sample concentration:
upon receipt of the sample, store in a cool place until needed.
H NMR Must be optimized for the instrument in use but
may be as high as 5 % v/v
8.2 A minimum of approximately 10 mL of sample is
C NMR Up to 50 % v/v for petroleum distillates and 30 %
required for this test method. This should allow duplicate
v/v for coal liquids
determinations, if desired.
Relaxation agent Chromium (III) 2,4-pentanedionate recommended
for C NMR solutions only. Where used, a 20 mM
8.3 All samples must be homogeneous prior to subsam-
solution (about 10 mg per mL)
pling. If any suspended particles present are attributable to
Sample temperature Instrument ambient
Internal lock Deuterium (when chloroform-d is used for H
foreign matter such as rust, filter a portion of the sample to be
NMR)
tested through a small plug of glass wool, contained in a clean
Sample spinning rate As recommended by manufacturer, typically 20 Hz
1 13
small funnel, into a clean and dry vial or NMR sample tube
H Decoupling Only for C NMR. Broadband over the whole of
1 13
the H frequency range, gated on during C data
containing chloroform-d.
acquisition only with a decoupler rise time less
8.4 If the sample contains waxy materials, heat the sample
than2m/s
Pulse flip angle Approximately 30°
in the container to approximately 60°C and mix with a
Sequence delay time:
high-shear mixer prior to sampling. It may be necessary to
HNMR>10s
transfer a portion of the sample to an NMR tube containing
CNMR>3swith and> 60 s without relaxation
agent
chloroform-d by means of a pipet which has been heated to
Memory size for Choose to give a minimum digitizing rate of 0.5
approximately 60°C to maintain the homogeneity of the
1 13
acquisition: Hz/point for H and 1.2 Hz/point for C NMR. If
necessary, increase memory size and zero fill sample.
Spectral width:
8.5 For a valid test result, samples must be completely
H NMR At least 15 ppm in frequency and centered, as
solubleinchloroform-d.Checktoensurethatthefinalsolution
close as possible, to the 5 ppm chemical shift
value
is homogeneous and free of undissolved particles.
C NMR At least 250 ppm in frequency and centered, as
close as possible, to the 100 ppm chemical shift
value 9. Procedures
Filter bandwidth Set to be equal to or greater than the spectral
width and as permitted by the instrument’s filter 9.1 Three different procedures are described in this section
hardware
for determining the aromatic hydrogen content, (see 9.6)
Exponential line Set at least equal to the digitizing rate
ProceduresAand B (see 9.7), and the aromatic carbon content
broadening
Signal to noise levels: of hydrocarbon oils, Procedure C (see 9.8).
H NMR A minimum of 20:1 for the maximum height of the
9.2 Theprocedureselectedbytheanalystwilldependonthe
smaller integrated band
C NMR A minimum of 60:1 for the maximum height of the available NMR instrumentation and on whether an aromatic
chloroform-d resonance appearing between 75 and
hydrogen or aromatic carbon content is of greater value in
80 ppm on the chemical shift scale
evaluating the characteristics of the hydrocarbon oil.
Chemical shift reference:
H NMR Preferably tetramethylsilane (0.0 ppm) at no
9.3 Appendix X1 and Practice E386 should be used in
greater than 1 vol % concentration
13 conjunction with the NMR spectrometer manufacturer’s in-
C NMR Preferably tetramethylsilane (0.0 ppm) at no
greater than 1 vol % concentration. If this structionsinordertoensureoptimumperformanceoftheNMR
reference is not used, the central peak of
instrument in the application of these procedures.
chloroform-d is set to 77.0 ppm
Integration: 9.4 If tetramethylsilane is used as an internal chemical shift
H NMR Integrate over the range − 0.5 to 5.0 ppm for the
standard,preparea1%v/vTMSinsolventsolutionbyadding
aliphatic band and 5.0 to 10.0 ppm for the aromatic
tetramethylsilane to chloroform-d solvent. Since TMS is very
band
C NMR Integrate over the range − 10 to 70 ppm for the volatile, this solution should be refrigerated or replaced if the
aliphatic band and 100 to 170 ppm for the aromatic
characteristic absorption due to TMS is no longer evident in
band
1 13
theHor C NMR spectrum.
9.5 If it is inconvenient to prepare the test solution directly
in the NMR sampl
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.