ASTM D4711-89(1995)e1
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Sulfonic and Sulfuric Acids in Alkylbenzene Sulfonic Acids
Standard Test Method for Sulfonic and Sulfuric Acids in Alkylbenzene Sulfonic Acids
SCOPE
1.1 This test method is applicable to the determination of sulfonic and sulfuric acids in branched and linear alkylbenzene sulfonic acids used as intermediates in synthetic detergents.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Material Safety Data Sheets are available for reagents and materials. Review them for hazards prior to usage.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
e1
Designation: D 4711 – 89 (Reapproved 1995)
Standard Test Method for
Sulfonic and Sulfuric Acids in Alkylbenzene Sulfonic Acids
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 4711; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
e NOTE—Keywords were added editorially in February 1995.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method is applicable to the determination of
sulfonic and sulfuric acids in branched and linear alkylbenzene
sulfonic acids used as intermediates in synthetic detergents.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. Material Safety
Data Sheets are available for reagents and materials. Review
them for hazards prior to usage.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D 459 Terminology Relating to Soaps and Other Deter-
gents
E 180 Practice for Determining the Precision of ASTM
Methods for Analysis and Testing of Industrial Chemicals
3. Summary of Test Method
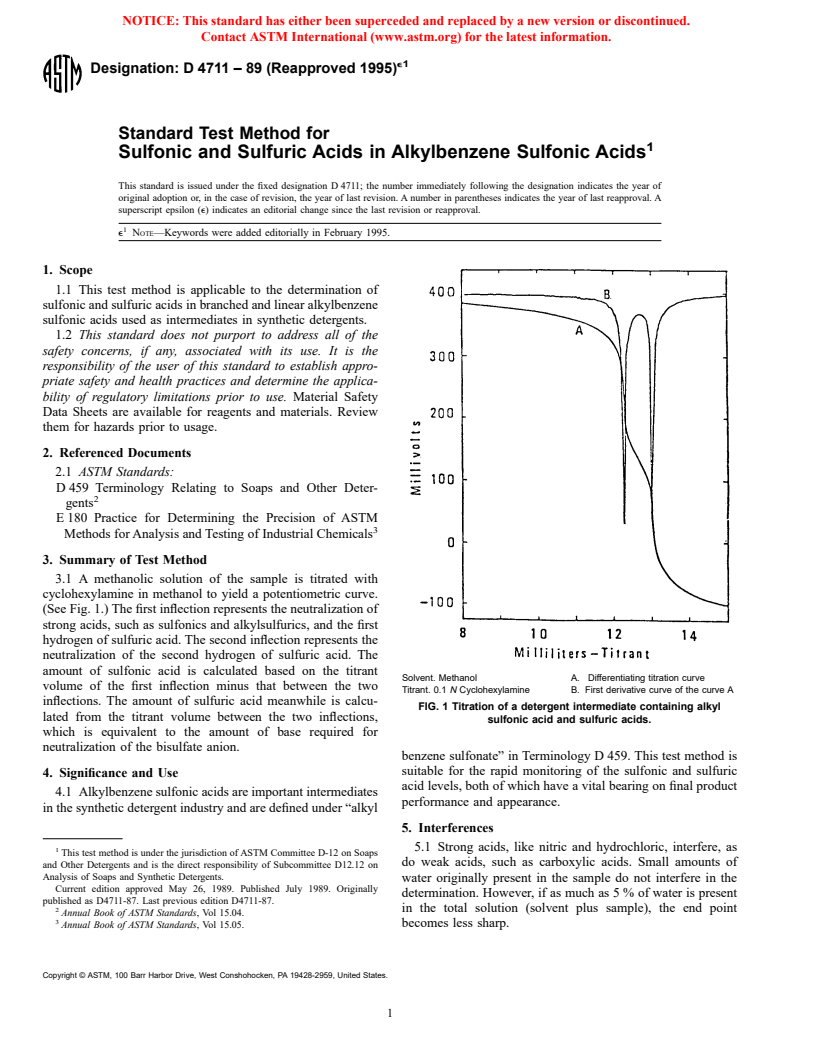
3.1 A methanolic solution of the sample is titrated with
cyclohexylamine in methanol to yield a potentiometric curve.
(See Fig. 1.) The first inflection represents the neutralization of
strong acids, such as sulfonics and alkylsulfurics, and the first
hydrogen of sulfuric acid. The second inflection represents the
neutralization of the second hydrogen of sulfuric acid. The
amount of sulfonic acid is calculated based on the titrant
Solvent. Methanol A. Differentiating titration curve
volume of the first inflection minus that between the two
Titrant. 0.1 N Cyclohexylamine B. First derivative curve of the curve A
inflections. The amount of sulfuric acid meanwhile is calcu-
FIG. 1 Titration of a detergent intermediate containing alkyl
lated from the titrant volume between the two inflections,
sulfonic acid and sulfuric acids.
which is equivalent to the amount of base required for
neutralization of the bisulfate anion.
benzene sulfonate” in Terminology D 459. This test method is
suitable for the rapid monitoring of the sulfonic and sulfuric
4. Significance and Use
acid levels, both of which have a vital bearing on final product
4.1 Alkylbenzene sulfonic acids are important intermediates
performance and appearance.
in the synthetic detergent industry and are defined under “alkyl
5. Interferences
1 5.1 Strong acids, like nitric and hydrochloric, interfere, as
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D-12 on Soaps
do weak acids, such as carboxylic acids. Small amounts of
and Other Detergents and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D12.12 on
Analysis of Soaps and Synthetic Detergents.
water originally present in the sample do not interfere in the
Current edition approved May 26, 1989. Published July 1989. Originally
determination. However, if as much as 5 % of water is present
published as D4711-87. Last previous edition D4711-87.
in the total solution (solvent plus sample), the end point
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 15.04.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 15.05. becomes less sharp.
Copyright © ASTM, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
D 4711
6. Apparatus 10. Calculation
6.1 Potentiometric Titrator, and combination calomel ref-
10.1 Calculate the weight percent sulfuric acid (H SO ) and
2 4
erence electrode.
weight percent sulfonic acid (RSO H) as follows:
6.2 Buret Assembly, having a 20 mL buret.
% H SO 5 ~V 2 V !~N!~98.08!~100!/~W!~1000! (3)
2 4 2 1
6.3 Beaker, 180 mL tall form.
%RSO H 5 ~2V 2 V !~N!~MW!~100!/~W!~1000! (4)
3 1 2
6.4 Volumetric Flask, Class A, 500 mL.
6.5 Magnetic Stirrer, and stirring bar.
where:
V , V 5 millilitres of titrant at the first and the second end
1 2
7. Reagents and Materials
points respectively.
7.1 Methanol, anhydrous,
N 5 normality of titrant,
7.2 Cyclohexylamine (0.10 N)—Dissolve 10 g of reagent W 5 sample weight, g, and
cyclohexylamine in 1000 mL of anhydrous methanol. Stan- MW 5 average equivalent weight of sulfonic acid.
dardize against sulfamic acid as described in Section 8.
,
6 7
7.3 Sulfamic Acid, acidimetric standard. 11. Precision and Bias
11.1 Repeatability (Single Analyst)—The standard deviation
8. Standardization of 0.10 N Cyclohexylamine
of results (each the average of duplicates) obtained by the same
8.1 All standardizations should be run in triplicate. This
analyst on different days, has been estimated to be 0.03 %
means separate weighings for solution preparations in 8.2.
absolute at 14 degrees of freedom. Two such averages should
8.2 Using an analytical balance, accurately weigh 0.10 to
be considered suspect (95 % confidence level) if they differ by
0.12 g of s
...






Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.