ASTM D2050-87(1997)
(Terminology)Standard Terminology Relating to Zippers
Standard Terminology Relating to Zippers
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: D 2050 – 87 (Reapproved 1997)
Standard Terminology Relating to
Zippers
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 2050; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
INTRODUCTION
These definitions cover special terms or special meanings used in the zipper industry. When any of
the definitions in this standard are moved to another standard, limit the field of application of the
definition by inserting the delimiting phrase “in zippers,” after the dash at the beginning of the
definition.
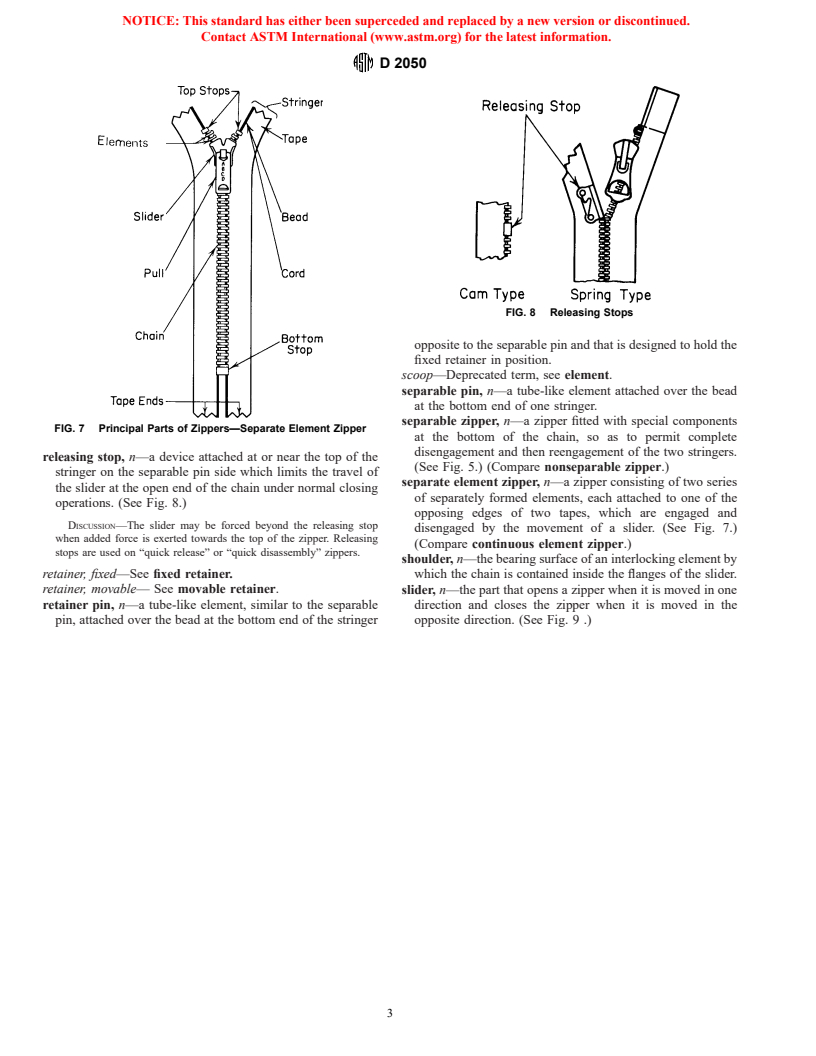
The principle parts of zippers are illustrated in Figs. 1-9. These illustrations are descriptive and are
not intended to be restrictive as to design.
automatic lock slider, n—a slider that provides involuntary,
positive locking action on the chain when the pull is
released.
bail, n—a portion or portions of the slider to which the pull or
pulls are attached. (Syn. lug.)
bead, n—in a separate element zipper, an enlarged section on
the inner edge of each tape to which interlockable elements
are affixed.
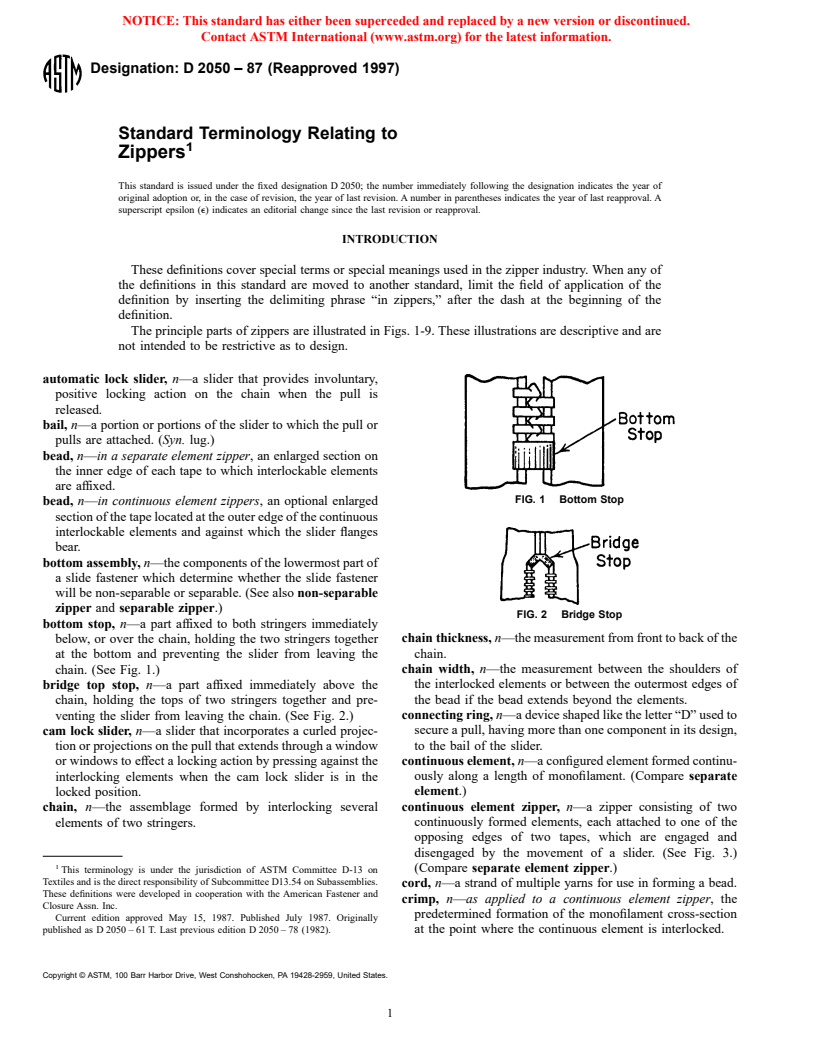
FIG. 1 Bottom Stop
bead, n—in continuous element zippers, an optional enlarged
section of the tape located at the outer edge of the continuous
interlockable elements and against which the slider flanges
bear.
bottom assembly, n—the components of the lowermost part of
a slide fastener which determine whether the slide fastener
will be non-separable or separable. (See also non-separable
zipper and separable zipper.)
FIG. 2 Bridge Stop
bottom stop, n—a part affixed to both stringers immediately
chain thickness, n—the measurement from front to back of the
below, or over the chain, holding the two stringers together
at the bottom and preventing the slider from leaving the chain.
chain width, n—the measurement between the shoulders of
chain. (See Fig. 1.)
bridge top stop, n—a part affixed immediately above the the interlocked elements or between the outermost edges of
the bead if the bead extends beyond the elements.
chain, holding the tops of two stringers together and pre-
venting the slider from leaving the chain. (See Fig. 2.) connecting ring, n—a device shaped like the letter “D” used to
secure a pull, having more than one component in its design,
cam lock slider, n—a slider that incorporates a curled projec-
tion or projections on the pull that extends through a window to the bail of the slider.
continuous element, n—a configured element formed continu-
or windows to effect a locking action by pressing against the
interlocking elements when the cam lock slider is in the ously along a length of monofilament. (Compare separate
element.)
locked position.
chain, n—the assemblage formed by interlocking several continuous element zipper, n—a zipper consisting of two
continuously formed elements, each attached to one of the
elements of two stringers.
opposing edges of two tapes, which are engaged and
disengaged by the movement of a slider. (See Fig. 3.)
(Compare separate element zipper.)
This terminology is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D-13 on
Textiles and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D13.54 on Subassemblies.
cord, n—a strand of multiple yarns for use in forming a bead.
These definitions were developed in cooperation with the American Fastener and
crimp, n—as applied to a continuous element zipper, the
Closure Assn. Inc.
predetermined formation of the monofilament cross-section
Current edition approved May 15, 1987. Published July 1987. Originally
published as D 2050 – 61 T. Last previous edition D 2050 – 78 (1982). at the point where the continuous element is interlocked.
Copyright © ASTM, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
D 2050
FIG. 5 Separating Parts
lug—See preferred term bail.
mouth, n—the opening in a slider that receives the chain.
mouth width, n—the measurement between the slider flanges
at the point where they bear against the shoulders of the
interlocked elements or at the outermost edges of the bead if
the bead extends beyond the elements.
FIG. 3 Principle Parts of Zippers—Continuous Element Zipper
movable retainer, n—a movable or sliding device performing
a similar function to that of the fixed retainer, the purpose
being to permit separation of the two stringers from the
cut-off, n—the measurement of a separate element from the
bottom, without the necessity of opening the zipper from the
head side to the pocket side of the legs.
top. (See Fig. 6.)
diamond, n—the wedge-shaped portion of a slider between the
throats.
DISCUSSION—This device is not removable from the bottom of the
element, n—a device designed for interlocking, capable of
zipper.
being affixed along the edge of a tape. (Compare continuous
element and separate element.) (See Fig. 4.)
FIG. 6 Movable Retainer
NOTE 1—Elements are of many designs but the nomenclature is
nonseparable zipper, n—a zipper having two stringers that are
generally the same for all types.
permanently attached to each other at one or both ends. (See
FIG. 4 Element
Fig. 7.) (Compare separable zipper.)
pin lock slider, n—a slider that incorporates a projection on
exposed tape width, n—the part of the tape extending beyond
the pull that fits between adjacent interlocking elements of a
the shoulders of the interlocking elements to the outer tape
zipper when a pin lock slider is in the locked position.
edge.
pin, retainer—See retainer pin.
fixed retainer, n—a device permanently attached to the re-
pin, separable— See separable pin.
tainer pin at the bottom of one stringer. (See Fig. 5.)
pocket, n—the cavity of an element designed to receive the
DISCUSSION—The fixed retainer has an opening
...






Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.