ASTM D7899-13
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Measuring the Merit of Dispersancy of In-Service Engine Oils with Blotter Spot Method
Standard Test Method for Measuring the Merit of Dispersancy of In-Service Engine Oils with Blotter Spot Method
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 Dispersancy is the property that allows oil to suspend and carry away pollutants of diverse sources such as soot from combustion, metallic particles from wear, corrosion of mechanical parts, and insoluble products resulting from the aging of the oil.
5.2 When poured on a specific filter paper, oil that is properly dispersing soot and other insolubles produces an evenly graduated spot. The distribution of the different zones (Fig. 1) will reflect the status of oil dispersancy.
5.3 While the oil spreads out on the filter paper, the oil carries contaminants, and due to the lamination phenomenon of the oil film, the particles of same size deposit on the paper on the same concentric zones.
5.4 This test method provides a simple technique for condition monitoring of the dispersancy property of in-service lubricants.
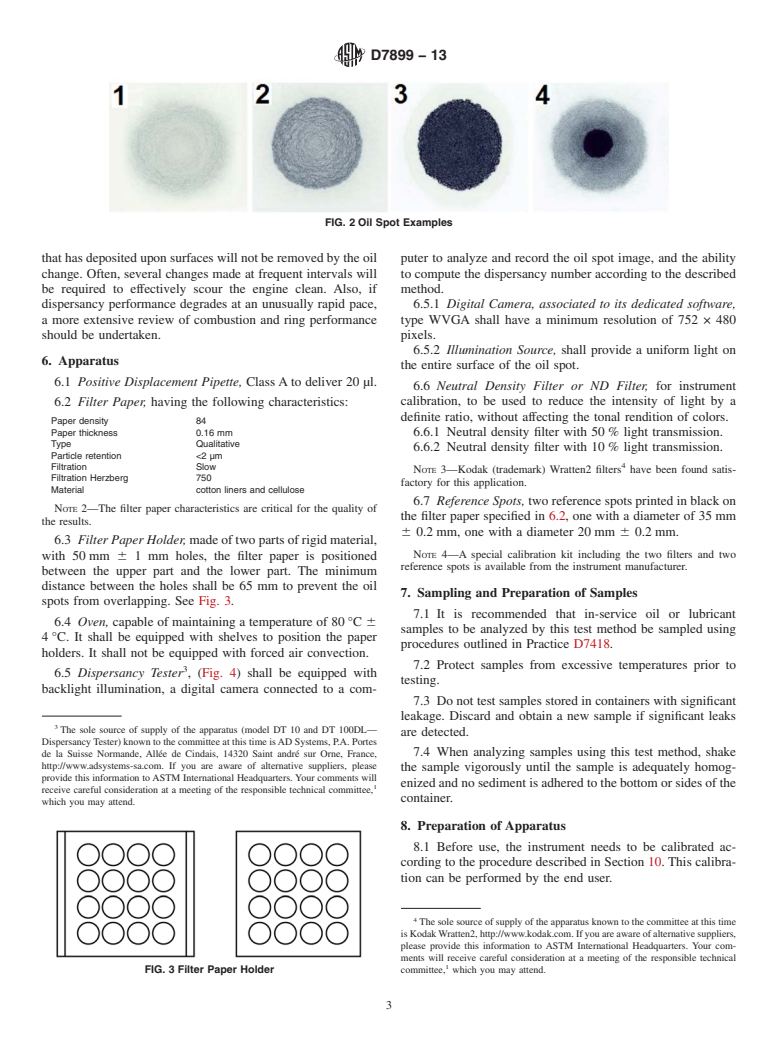
5.5 An oil that is properly dispersing soot and other insolubles produces an evenly graduated blotter (see Fig. 2—Spot 1). A ring of light debris on the outer circumference of the circular spot also indicates that the oil has retained its dispersancy properties.
5.6 A blotter indicating a high soot load, but even graduation, suggests the oil is still fit for service, but should be watched closely for degradation (see Fig. 2—Spot 2).
5.7 When dispersancy begins to fail, the insolubles begin to form a dense ring on the exterior of the absorbing oil drop as in Fig. 2—Spot 3. A brown or yellow stain on the blotter spot indicates oxidation.
5.8 Fig. 2—Spot 4 indicates the characteristic dense black dot and sharp periphery that indicates sludge and the loss of dispersancy as the particles have settled in the center and the oil has wicked outward.
5.9 From a maintenance perspective, when the ring begins to form around the exterior of the oil blotter, it is time to look at scheduling a drain. If the black dot is allowed to form, the situation is problematic because the undispersed portion of soot that has deposited upon surfaces will not be...
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers a procedure for determination of the merit of dispersancy of diesel crankcase engine oils as well as other types of engine oils where pollutants of diverse sources such as soot from combustion, metallic particles from wear, corrosion of mechanical parts, and insoluble products resulting from the oxidation of the oil may contaminate the lubricant.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.Note 1—It is not the intent of this test method to establish or recommend normal, cautionary, warning, or alert limits for any machinery. Such limits should be established in conjunction with advice and guidance from the machinery manufacturer and maintenance group.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D7899 − 13
Standard Test Method for
Measuring the Merit of Dispersancy of In-Service Engine
1
Oils with Blotter Spot Method
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7899; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope certain properties. Inhibition of engine rusting, deposit
formation, valve train wear, oil oxidation, and foaming are
1.1 This test method covers a procedure for determination
examples.
of the merit of dispersancy of diesel crankcase engine oils as
well as other types of engine oils where pollutants of diverse
3.1.2 diesel engine, n—a reciprocating or rotary engine in
sources such as soot from combustion, metallic particles from
whichignitionofthemainfuelcharge,asitisintroducedtothe
wear, corrosion of mechanical parts, and insoluble products
combustionchamber,shallbebytheheatofcompressionofthe
resulting from the oxidation of the oil may contaminate the
charge of combustion air, during regular operation of the
lubricant.
engine from idle speeds up to full speed, regardless of whether
miscellaneous methods to augment such heat of compression
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
are used to facilitate starting of the engine under normal
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
conditionsorunderlowambienttemperatureconditionsorlow
standard.
intake air temperature conditions.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
3.1.2.1 Discussion—Engines that are designed to operate
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
withacontinuouslyhotspotorbulborotherdevicetofacilitate
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
ignition or combustion, or both, of low cetane fuels, or any
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
fuels slow to ignite or to burn, or both, shall be considered to
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
be diesel engines for purposes of this test method.
NOTE 1—It is not the intent of this test method to establish or
recommendnormal,cautionary,warning,oralertlimitsforanymachinery. 3.1.3 engine oil, n—aliquidthatreducesfrictionorwear,or
Suchlimitsshouldbeestablishedinconjunctionwithadviceandguidance
both, between the moving parts within an engine; removes
from the machinery manufacturer and maintenance group.
heat, particularly from the underside of pistons; and serves as
a combustion gas sealant for piston rings.
2. Referenced Documents
3.1.3.1 Discussion—It may contain additives to enhance
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
certain properties. Inhibition of engine rusting, deposit
D7418Practice for Set-Up and Operation of Fourier Trans-
formation, valve train wear, oil oxidation, and foaming are
form Infrared (FT-IR) Spectrometers for In-Service Oil
examples.
Condition Monitoring
3.1.4 oxidation, n—ofengineoil,thereactionoftheoilwith
an electron acceptor, generally oxygen, which can produce
3. Terminology
deleterious acidic or resinous materials often manifested as
3.1 Definitions:
sludge formation, varnish formation, viscosity increase, or
3.1.1 diesel crankcase engine oils, n—an engine oil used in
corrosion, or a combination thereof.
the crankcase of the internal combustion diesel engine.
3.1.5 sludge, n—in internal combustion engines, a deposit,
3.1.1.1 Discussion—It may contain additives to enhance
principally composed of insoluble resins and oxidation prod-
uctsfromfuelcombustionandthelubricantthatdoesnotdrain
from engine parts but can be removed by wiping with a cloth.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on
Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
SubcommitteeD02.96.02onChemistryfortheEvaluationofIn-ServiceLubricants.
3.2.1 dispersancy—the property that allows oil to suspend
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2013. Published January 2014. DOI: 10.1520/
D7899-13.
and carry away pollutants of diverse sources such as soot from
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
combustion, metallic particles from wear, corrosion of me-
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
chanical parts, and insoluble products resulting from the aging
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. of the oil.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D7899 − 13
4. Summary of Test Method the oil fi
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.