ASTM F1673-10
(Specification)Standard Specification for Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) Corrosive Waste Drainage Systems
Standard Specification for Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) Corrosive Waste Drainage Systems
ABSTRACT
This specification covers requirements for polyvinylidene drainage systems for corrosive applications. Requirements for material, pipe and fittings are included. Polyvinylidene fluoride includes emulsion/suspension polymerization and copolymers of vinylidene fluoride/hexafluoropropylene produced by either method. These requirements apply to Schedule 40 and 80 IPS and SDR 21 pipe sizes. Pipe and fittings are to be joined by heat fusion or mechanical methods. The following tests shall be performed: chemical resistance; water absorption; joint tests— hydrostatic pressure tests; mechanical joint pullout test; threads; flattening; and impact resistance for PVDF pipe and fittings.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers requirements for polyvinylidene fluoride drainage systems for corrosive applications. Requirements for material, pipe and fittings are included. Polyvinylidene fluoride includes emulsion/suspension polymerization and copolymers of vinylidene fluoride/hexafluoropropylene produced by either method.
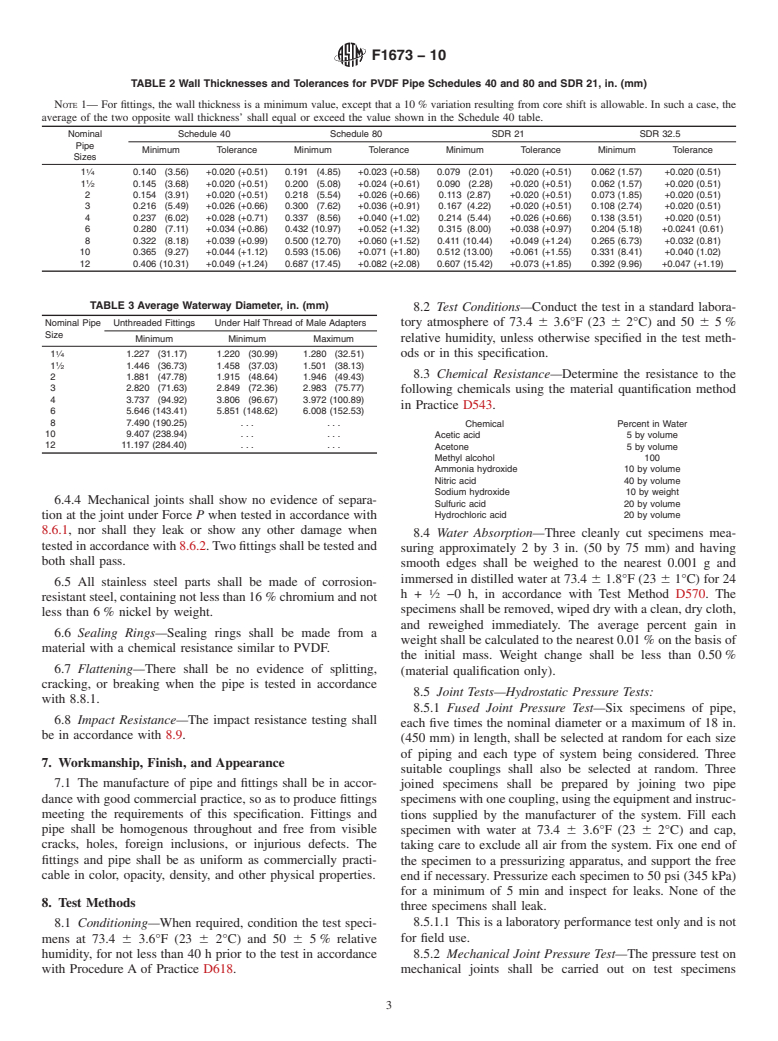
1.2 These requirements apply to Schedule 40 and 80 IPS, SDR 32.5, and SDR 21 pipe sizes. Pipe and fittings are to be joined by heat fusion or mechanical methods using the equipment supplied by the manufacturers.
1.3 This specification is not intended to provide for interchangeability between plastic pipe and fittings from different manufacturers, but it does allow for transition fittings for joining one manufacturer's product to another's product, provided the joining technique used is other than heat fusion.
1.4 This specification is not for polyvinylidene pressure systems.
1.5 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.6 Notes and appendixes are not a mandatory part of this specification.
1.7 The following safety hazard caveat pertains only to the test method portion, Section 8, of this specification: This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:F1673 −10
StandardSpecification for
Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) Corrosive Waste Drainage
1
Systems
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F1673; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* 2. Referenced Documents
2
1.1 This specification covers requirements for polyvi- 2.1 ASTM Standards:
nylidene fluoride drainage systems for corrosive applications. D543Practices for Evaluating the Resistance of Plastics to
Requirements for material, pipe and fittings are included. Chemical Reagents
Polyvinylidene fluoride includes emulsion/suspension polym- D570Test Method for Water Absorption of Plastics
erization and copolymers of vinylidene fluoride/ D618Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing
hexafluoropropylene produced by either method. D883Terminology Relating to Plastics
D1600TerminologyforAbbreviatedTermsRelatingtoPlas-
1.2 These requirements apply to Schedule 40 and 80 IPS,
tics
SDR 32.5, and SDR 21 pipe sizes. Pipe and fittings are to be
D2122Test Method for Determining Dimensions of Ther-
joined by heat fusion or mechanical methods using the equip-
moplastic Pipe and Fittings
ment supplied by the manufacturers.
D2321PracticeforUndergroundInstallationofThermoplas-
1.3 This specification is not intended to provide for inter-
tic Pipe for Sewers and Other Gravity-Flow Applications
changeability between plastic pipe and fittings from different
D2412Test Method for Determination of External Loading
manufacturers, but it does allow for transition fittings for
Characteristics of Plastic Pipe by Parallel-Plate Loading
joining one manufacturer’s product to another’s product, pro-
D2444Test Method for Determination of the Impact Resis-
vided the joining technique used is other than heat fusion.
tance of Thermoplastic Pipe and Fittings by Means of a
Tup (Falling Weight)
1.4 This specification is not for polyvinylidene pressure
systems. D3222Specification for Unmodified Poly(Vinylidene Fluo-
ride) (PVDF) Molding Extrusion and Coating Materials
1.5 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
D3311Specification for Drain, Waste, and Vent (DWV)
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
Plastic Fittings Patterns
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
D5575Classification System for Copolymers of Vinylidene
and are not considered standard.
Fluoride (VDF) with Other Fluorinated Monomers
1.6 Notes and appendixes are not a mandatory part of this
F412Terminology Relating to Plastic Piping Systems
specification.
F1498SpecificationforTaperPipeThreads60°forThermo-
1.7 The following safety hazard caveat pertains only to the plastic Pipe and Fittings
test method portion, Section 8, of this specification: This 2.2 Federal Standard:
3
standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns,
Fed. Std. No. 123Marking for Shipment
if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user
2.3 Military Standard:
3
of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health
MIL-STD129 Marking for Shipment and Storage
practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limita-
tions prior to use.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee F17 on Plastic Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Piping Systems and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F17.63 on DWV. the ASTM website.
3
Current edition approved Aug. 1, 2010. Published August 2010. Originally Available from Standardization Documents Order Desk, DODSSP, Bldg. 4,
approved in 1995. Last previous edition approved in 2009 as F1673-04(2009). Section D, 700 Robbins Ave., Philadelphia, PA 19111-5098, http://
DOI: 10.1520/F1673-10. www.dodssp.daps.mil.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
F1673−10
2.4 Other Standard: 6.1.1.2 Toe-In—The outside diameter, when measured in
4
Uniform Plumbing Code accordance with Method D2122, shall meet the requirements
of Table 1 and Table 2 at any point within 1.5 pipe diameters
3. Terminology
or 11.8 in. (300 mm), whichever is less, to the cut end of the
pipe length.
3.1 Definitions:
6.1.2 Fittings:
3.1.1 Definitionsusedinthisspecificationareinaccordance
withthedefinitionsgiveninTerminologiesD883andF412and 6.1.2.1 The minimum wall thick
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
An American National Standard
Designation:F1673–04 (Reapproved 2009) Designation: F1673 – 10
Standard Specification for
Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) Corrosive Waste Drainage
1
Systems
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F1673; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*
1.1 This specification covers requirements for polyvinylidene fluoride drainage systems for corrosive applications. Require-
ments for material, pipe and fittings are included. Polyvinylidene fluoride includes emulsion/suspension polymerization and
copolymers of vinylidene fluoride/hexafluoropropylene produced by either method.
1.2 These requirements apply to Schedule 40 and 80 IPS, SDR 32.5, and SDR 21 pipe sizes. Pipe and fittings are to be joined
by heat fusion or mechanical methods using the equipment supplied by the manufacturers.
1.3 This specification is not intended to provide for interchangeability between plastic pipe and fittings from different
manufacturers, but it does allow for transition fittings for joining one manufacturer’s product to another’s product, provided the
joining technique used is other than heat fusion.
1.4 This specification is not for polyvinylidene pressure systems.
1.5 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.6 Notes and appendixes are not a mandatory part of this specification.
1.7 The following safety hazard caveat pertains only to the test method portion, Section 8, of this specification: This standard
does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this
standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D543 Practices for Evaluating the Resistance of Plastics to Chemical Reagents
D570 Test Method for Water Absorption of Plastics
D618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing
D883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
D1599Test Method for Resistance to Short-Time Hydraulic Pressure of Plastic Pipe, Tubing, and Fittings
D1600 Terminology for Abbreviated Terms Relating to Plastics
D2122 Test Method for Determining Dimensions of Thermoplastic Pipe and Fittings
D2321 Practice for Underground Installation of Thermoplastic Pipe for Sewers and Other Gravity-Flow Applications
D2412 Test Method for Determination of External Loading Characteristics of Plastic Pipe by Parallel-Plate Loading
D2444 TestMethodforDeterminationoftheImpactResistanceofThermoplasticPipeandFittingsbyMeansofaTup(Falling
Weight)
D2657Practice for Heat Fusion Joining of Polyolefin Pipe and Fittings
D3222 Specification for Unmodified Poly(Vinylidene Fluoride) (PVDF) Molding Extrusion and Coating Materials
D3311 Specification for Drain, Waste, and Vent (DWV) Plastic Fittings Patterns
D5575 Classification System for Copolymers of Vinylidene Fluoride (VDF) with Other Fluorinated Monomers
F412 Terminology Relating to Plastic Piping Systems
F1290Practice for Electrofusion Joining Polyolefin Pipe and Fittings
F1498 Specification for Taper Pipe Threads 60 for Thermoplastic Pipe and Fittings
2.2 Federal Standard:
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F17 on Plastic Piping Systems and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F17.63 on DWV.
Current edition approved Aug. 1, 2009.2010. Published September 2009.August 2010. Originally approved in 1995. Last previous edition approved in 20042009 as
F1673-04(2009). DOI: 10.1520/F1673-04R09.10.1520/F1673-10.
2
ForreferencedASTMstandards,visittheASTMwebsite,www.astm.org,orcontactASTMCustomerServiceatservice@astm.org.For Annual Book ofASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
F1673 – 10
3
Fed. Std. No. 123 Marking for Shipment
2.3 Military Standard:
3
MIL-STD129 Marking for Shipment and Storage
3
Available from Standar
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.