ASTM D2878-95(2009)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Estimating Apparent Vapor Pressures and Molecular Weights of Lubricating Oils
Standard Test Method for Estimating Apparent Vapor Pressures and Molecular Weights of Lubricating Oils
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
The vapor pressure of a substance as determined by measurement of evaporation reflects a property of the bulk sample. Little weight is given by the procedure to the presence of low concentrations of volatile impurities.
Vapor pressure, per se, is a thermodynamic property that is dependent only upon composition and temperature for stable systems. In the present method, composition changes occur during the course of the test so that the contribution of minor amounts of volatile impurities is minimized.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers a calculation procedure for converting data obtained by Test Method D972 to apparent vapor pressures and molecular weights. It has been demonstrated to be applicable to petroleum-based and synthetic ester lubricating oils, at temperatures of 395 to 535K (250 to 500°F). However, its applicability to lubricating greases has not been established.
Note 1—Most lubricants boil over a fairly wide temperature range, a fact recognized in discussion of their vapor pressures. For example, the apparent vapor pressure over the range 0 to 0.1 % evaporated may be as much as 100 times that over the range 4.9 to 5.0 % evaporated.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. In cases in which materials, products, or equipment are available in inch-pound units only, SI units are omitted.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability or regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific warning statements, see 6.2, 7.1, 8.2, and Annex A2.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D2878–95 (Reapproved 2009)
Standard Test Method for
Estimating Apparent Vapor Pressures and Molecular
1
Weights of Lubricating Oils
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D2878; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope D92 Test Method for Flash and Fire Points by Cleveland
Open Cup Tester
1.1 This test method covers a calculation procedure for
D972 Test Method for Evaporation Loss of Lubricating
converting data obtained by Test Method D972 to apparent
Greases and Oils
vapor pressures and molecular weights. It has been demon-
D2503 Test Method for Relative Molecular Mass (Molecu-
strated to be applicable to petroleum-based and synthetic ester
2 lar Weight) of Hydrocarbons by Thermoelectric Measure-
lubricating oils, at temperatures of 395 to 535K (250 to
ment of Vapor Pressure
500°F). However, its applicability to lubricating greases has
D2595 Test Method for Evaporation Loss of Lubricating
not been established.
Greases Over Wide-Temperature Range
NOTE 1—Most lubricants boil over a fairly wide temperature range, a
D2883 Test Method for ReactionThresholdTemperature of
fact recognized in discussion of their vapor pressures. For example, the
Liquid and Solid Materials
apparent vapor pressure over the range 0 to 0.1% evaporated may be as
E1 Specification for ASTM Liquid-in-Glass Thermometers
much as 100 times that over the range 4.9 to 5.0% evaporated.
E659 Test Method for Autoignition Temperature of Liquid
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
Chemicals
standard. In cases in which materials, products, or equipment
are available in inch-pound units only, SI units are omitted.
3. Terminology
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
3.1.1 apparent vapor pressure (p), n—the time-averaged
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
value of the vapor pressure from the start to the end of the
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
evaporation test.
bility or regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific
3.1.1.1 Discussion—Whilethismayincludesomeeffectsof
warning statements, see 6.2, 7.1, 8.2, and Annex A2.
differences in nonideality of the vapor, heat of vaporization,
surface tension, and viscosity between the m-terphenyl and the
2. Referenced Documents
lubricating oil, these factors have been demonstrated to be
3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
negligible.Unlessstated,thisaverageshallcovertherange0to
A240/A240M Specification for Chromium and Chromium-
5 61%.
Nickel Stainless Steel Plate, Sheet, and Strip for Pressure
3.1.2 cell constant (k), n—the ratio of the amount of
Vessels and for General Applications
m-terphenylorlubricatingoilcarriedoffperunitvolumeofgas
to that predicted by Dalton’s law.
k 522.41 PW/VpM (1)
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of Committee D02 on Petroleum
ProductsandLubricantsandisthedirectresponsibilityofSubcommitteeD02.11on
where:
Engineering Sciences of High Performance Fluids and Solids.
k = call constant
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2009. Published November 2009. Originally
approved in 1970. Last previous edition approved in 2005 as D2878–95(2005).
P = ambient atmospheric pressure, torr
DOI: 10.1520/D2878-95R09.
W = mass of lubricant evaporated, g
2
Coburn, J. F., “Lubricant Vapor Pressure Derived from Evaporation Loss,”
V = volume of gas passed through all litres at 273K and
Transactions, American Society of Lubricating Engineers, ASLTA, Vol 12, 1969,
101.3 kPa (760 torr)
pp. 129–134.
3
p = apparent vapor pressure, torr
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
M = mole average molecular weight of lubricant vapor,
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
g/mole
the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D2878–95 (2009)
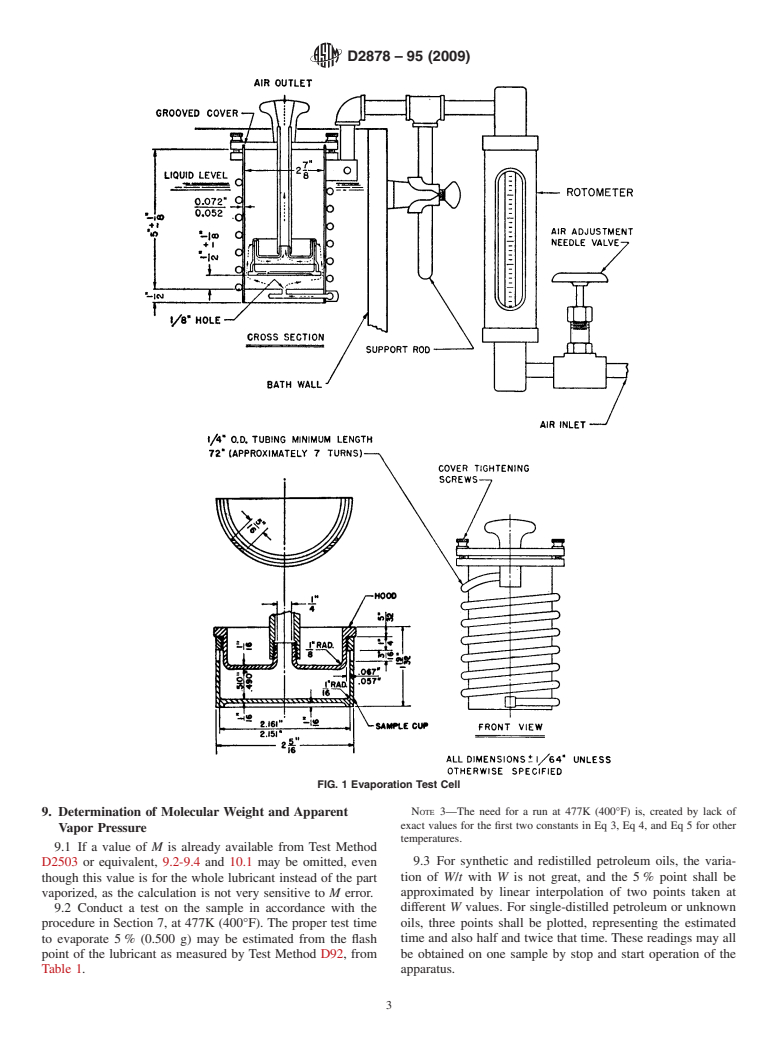
6.6 Oil Sample Cup, as described in Fig. 1 and A1.1.2.
T = test temperature, K
Ithasbeenempiricallydeterminedthatfor m-terphenylinair
7. Calibration of Equipment
k 50.1266 212.60/~ T 2273! (2)
7.1 ItisassumedthatequipmentconformingtoTestMethod
and that the cell constant is independent of the composition
D972 in design and installation needs no calibration. If
of the lubricant.
questions arise, carry out the procedure using m-terphenyl
3.1.3 Test
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.