ASTM E1797-03
(Specification)Standard Specification for Reinforced Liquid Coating Encapsulation Products for Leaded Paint in Buildings
Standard Specification for Reinforced Liquid Coating Encapsulation Products for Leaded Paint in Buildings
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers minimum material performance requirements and laboratory test procedures for reinforced liquid coating encapsulation products (single- or multiple-coat systems) for leaded paint in buildings. Performance properties addressed in this specification are:
1.1.1 Impact Resistance,
1.1.2 Adhesion,
1.1.3 Dry Abrasion Resistance,
1.1.4 Water Vapor Transmission,
1.1.5 Water and Chemical Resistance,
1.1.6 Surface Burning Characteristics,
1.1.7 Volatile Organic Compound (VOC) Content,
1.1.8 Weathering,
1.1.9 Aging,
1.1.10 Scrub Resistance,
1.1.11 Mildew Resistance,
1.1.12 Paintability/Repairability,
1.2 This specification does not address the selection of an encapsulation product for specific use conditions. Specific use conditions may require performance values other than those stated in this specification. See Guide E 1796 for guidance.
1.3 This specification complements Specification E 1795 for non-reinforced liquid coating encapsulation products.
1.4 This specification does not cover the use of encapsulation products on industrial steel structures nor residential exterior coated metal surfaces because no corrosion control requirements are included.
1.5 This specification applies to any liquid-applied product incorporating reinforcement materials as part of the system. Reinforcement materials are continuous fabric or mesh and are applied in the field. These materials are typically applied between a base and top coat. These products are used to encapsulate a leaded paint surface with the intent of reducing human exposure to lead in paint.
1.6 The results of the test methods included in this specification will not necessarily predict field performance.
1.7 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.8 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: E 1797 – 03
Standard Specification for
Reinforced Liquid Coating Encapsulation Products for
1
Leaded Paint in Buildings
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E 1797; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 1.7 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
1.1 This specification covers minimum material perfor-
only.
mance requirements and laboratory test procedures for rein-
1.8 This standard does not purport to address all of the
forced liquid coating encapsulation products (single- or
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
multiple-coat systems) for leaded paint in buildings. Perfor-
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
mance properties addressed in this specification are:
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
1.1.1 Impact Resistance,
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.1.2 Adhesion,
1.1.3 Dry Abrasion Resistance,
2. Referenced Documents
1.1.4 Water Vapor Transmission,
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
1.1.5 Water and Chemical Resistance,
D 16 Terminology for Paint, Related Coatings, Materials,
1.1.6 Surface Burning Characteristics,
and Applications
1.1.7 Volatile Organic Compound (VOC) Content,
D 823 Practices for Producing Films of Uniform Thickness
1.1.8 Weathering,
of Paint, Varnish, and Related Products on Test Panels
1.1.9 Aging,
D 1005 Test Methods for Measurement of Dry-Film Thick-
1.1.10 Scrub Resistance,
ness of Organic Coatings Using Micrometers
1.1.11 Mildew Resistance,
D 1186 Test Methods for Nondestructive Measurement of
1.1.12 Paintability/Repairability,
Dry Film Thickness of Nonmagnetic Coatings Applied to
1.2 This specification does not address the selection of an
a Ferrous Base
encapsulation product for specific use conditions. Specific use
D 1212 Test Methods for Measurement of Wet Film Thick-
conditions may require performance values other than those
ness of Organic Coatings
stated in this specification. See Guide E 1796 for guidance.
D 1308 Test Method for Effect of Household Chemicals on
1.3 This specification complements Specification E 1795
Clear and Pigmented Organic Finishes
for non-reinforced liquid coating encapsulation products.
D 1475 Test Method for Density of Liquid Coatings, Inks,
1.4 This specification does not cover the use of encapsula-
and Related Products
tion products on industrial steel structures nor residential
D 1653 Test Methods for Water Vapor Transmission of
exterior coated metal surfaces because no corrosion control
Organic Coating Films
requirements are included.
D 2486 Test Method for Scrub Resistance of Wall Paints
1.5 This specification applies to any liquid-applied product
D 2794 Test Method for Resistance of Organic Coatings to
incorporating reinforcement materials as part of the system.
the Effects of Rapid Deformation (Impact)
Reinforcement materials are continuous fabric or mesh and are
D 3273 Test Method for Resistance to Growth of Mold on
applied in the field. These materials are typically applied
the Surface of Interior Coatings in an Environmental
between a base and top coat. These products are used to
Chamber
encapsulate a leaded paint surface with the intent of reducing
D 3274 Test Method for Evaluating Degree of Surface
human exposure to lead in paint.
Disfigurement of Paint Films by Microbial (Fungal or
1.6 The results of the test methods included in this specifi-
Algal) Growth or Soil and Dirt Accumulation
cation will not necessarily predict field performance.
D 3359 Test Methods for Measuring Adhesion by Tape Test
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E06 on
2
Performance of Buildings and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E06.23 For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
on Lead Hazards Associated With Buildings. contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2003. Published October 2003. Originally Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
approved in 1995. Last previous edition approved in 2000 as E 1797 – 00. the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E1797–03
D 3924 Specification for Standard Environment for Condi- 5. Performance Requirements
tioning and Testing Paint, Varnish, Lacquers, and Related
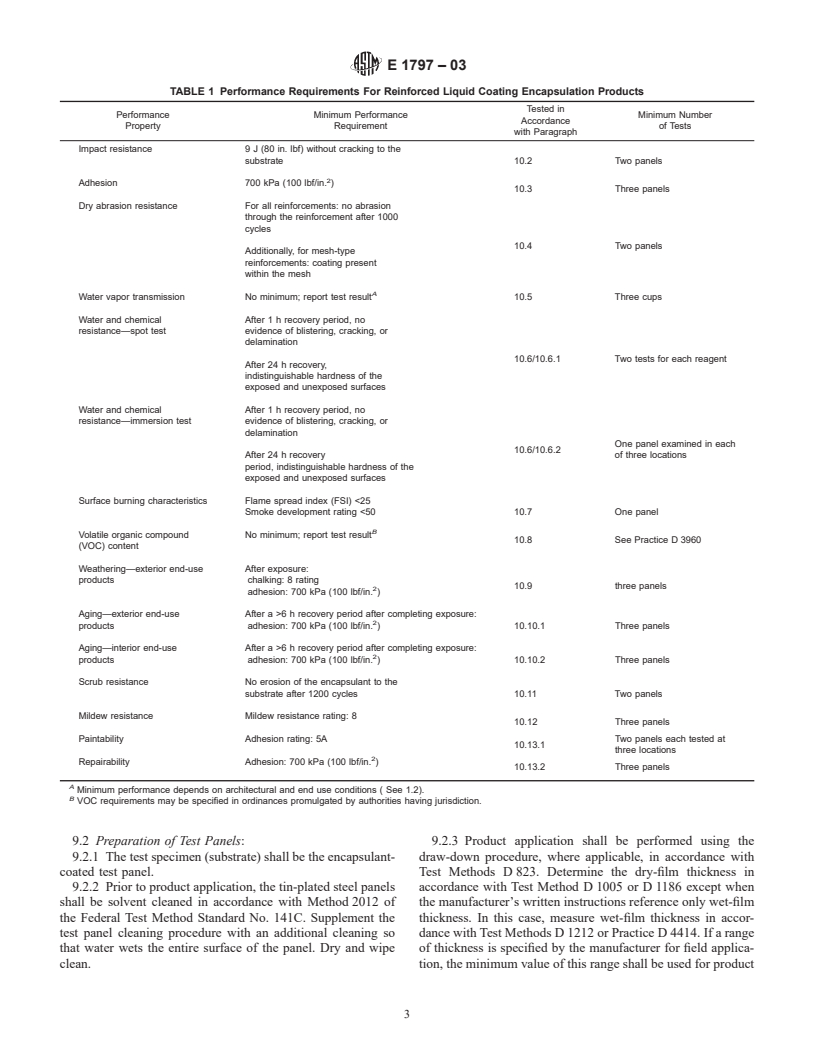
5.1 Performance requirements that shall be met for
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.