ASTM D5006-96
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Measurement of Fuel System Icing Inhibitors (Ether Type) in Aviation Fuels
Standard Test Method for Measurement of Fuel System Icing Inhibitors (Ether Type) in Aviation Fuels
SCOPE
1.1 This test method describes a technique for measuring the concentration of Ethylene Glycol Monomethyl Ether (EGME) and Diethylene Glycol Monomethyl Ether (DiEGME) in aviation fuels. The HB and Brix scale refractometers are specified to determine the concentration of these fuel system icing inhibitors (FSII) by measuring the refractive index of a water extract. Precision estimates have been determined for the EGME and DiEGME additives using specific extraction ratios with a wide variety of fuel types. The extraction ratios are high enough that portable hand-held refractometers can be used, but not so high as to sacrifice accuracy or linearity, or both, in the 0.01 to 0.25 vol % range of interest.
1.2 This test method does not identify which FSII additive is present. The analyst must know which additive is to be measured prior to performing the test. Consult the appropriate fuel specification to determine which additive is to be measured.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific hazard statements, see 4.1, 8.2, 9.2.1.1, 9.3.1.1, 9.3.2, and 9.3.10
General Information
Relations
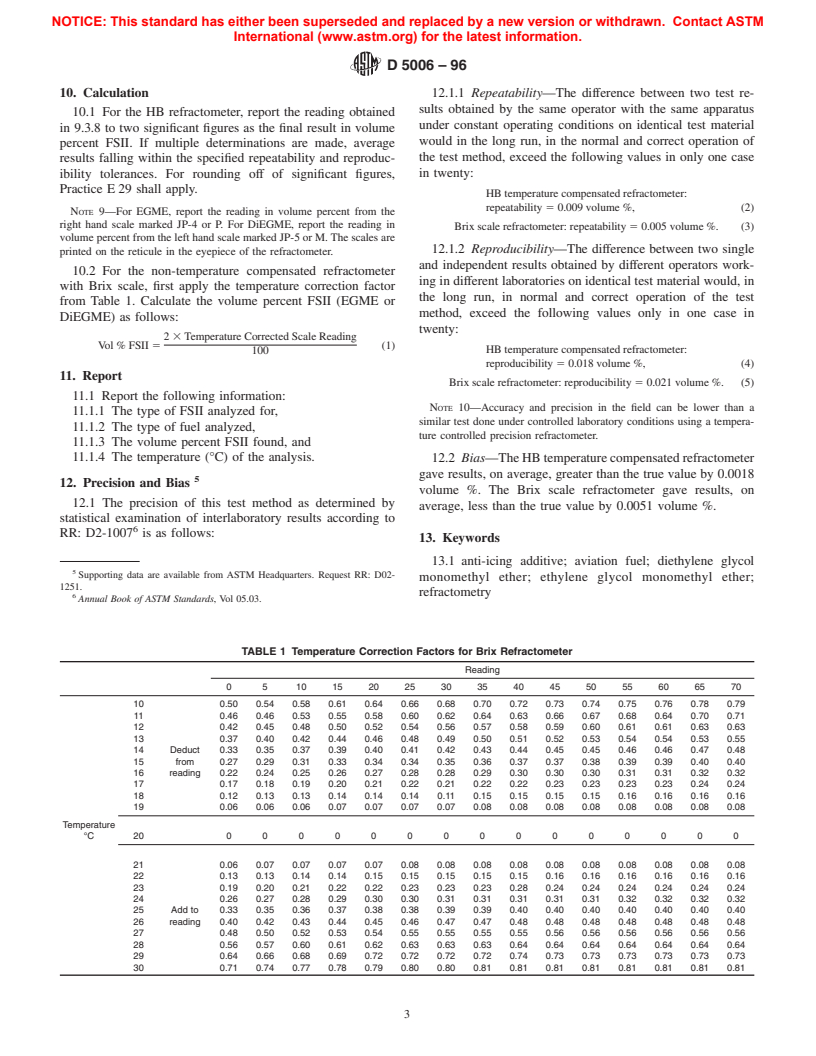
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn. Contact ASTM
International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
An American National Standard
Designation:D5006–96
Standard Test Method for
Measurement of Fuel System Icing Inhibitors (Ether Type) in
Aviation Fuels
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 5006; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope 3. Terminology
1.1 This test method describes a technique for measuring 3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
the concentration of Ethylene Glycol Monomethyl Ether 3.1.1 Brix scale—a refractometer with a refractive index
(EGME)andDiethyleneGlycolMonomethylEther(DiEGME) scale calibrated to weight percent cane sugar (sucrose).
in aviation fuels. The HB and Brix scale refractometers are 3.1.2 HB—a refractometer that can be used in a temperature
specified to determine the concentration of these fuel system range from 18 to 35°C without incorporating a temperature
icing inhibitors (FSII) by measuring the refractive index of a correction factor.
water extract. Precision estimates have been determined for the
4. Summary of Test Method
EGME and DiEGME additives using specific extraction ratios
with a wide variety of fuel types.The extraction ratios are high 4.1 In order to determine the concentration of fuel system
icing inhibitor in aviation fuel, a measured volume of fuel is
enough that portable hand-held refractometers can be used, but
not so high as to sacrifice accuracy or linearity, or both, in the extracted with a fixed ratio of water. The extraction procedure
includes sufficient agitation and contacting time to ensure that
0.01 to 0.25 vol % range of interest.
1.2 ThistestmethoddoesnotidentifywhichFSIIadditiveis equilibrium distributions are attained. With the HB refracto-
meter, several drops of the water extract are placed on the
present. The analyst must know which additive is to be
measured prior to performing the test. Consult the appropriate prism face and the volume percent FSII is read directly from a
custom graduated scale printed on the reticule. If the Brix
fuel specification to determine which additive is to be mea-
sured. refractometer is used, a temperature correction factor is first
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the applied to the reading, multiplied by 2 and divided by 100 to
calculate volume percent FSII.
standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
NOTE 1—Warning: Ethylene glycol monomethyl ether, (EGME).
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the 4
Combustible, toxic material.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
Precaution—In addition to other precautions, EGME has been shown
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica- to be a teratogen in animals.Avoid inhalation. Do not get in eyes, on skin,
or on clothing. Wash thoroughly after handling.
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific hazard
NOTE 2—Warning: Diethylene glycol monomethyl ether (Di-EGME),
statements, see Note 1, Note 2, Note 4, Note 5, Note 6, Note 7,
Slightly toxic material. This material caused slight embryo-fetal toxicity
and Note 8.
(delayed development) but no increase in birth defects in laboratory
animals. Consult the suppliers’ material safety data sheet.
2. Referenced Documents
NOTE 3—This test method is semi-quantitative if mixtures of the
2.1 ASTM Standards:
ether-type additives are used. Methanol is not detected because of the
E 1 Specification for ASTM Thermometers similarity of water/methanol refractive indices, and the presence of
methanol in fuel containing other additives results in lower than true
E 29 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to
measurements.
Determine Conformance with Specifications
5. Significance and Use
5.1 Fuel system icing inhibitors are miscible with water and
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D-2 on
can be readily extracted from the fuel by contact with water
Petroleum Products and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
D02.J0.09 on Additive-Related Properties.
Current edition approved Dec. 10, 1996. Published February 1997. Originally
published as D 5006 – 89. Last previous edition D 5006 – 90 (1995). For more detailed information on ethylene glycol monomethyl ether, refer to
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 14.03. the Federal Register, Vol 51, No. 97, dated Tuesday, May 20, 1986. Consult the
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 14.02. supplier’s material safety data sheet.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn. Contact ASTM
International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
D5006–96
during shipping and in storage. Methods are therefore needed 9.2.1.2 Fordiethyleneglycolmonomethylether(DiEGME),
to check the additive content in the fuel to ensure proper measure 80 mL of the fuel to be tested into the extraction
additive concentration in the aircraft. vessel.
5.2 This test method is applicable to analyses performed in 9.2.2 Measure 1.0 mL of water into the extraction vessel.
the field or in a laboratory. 9.3 Procedure for the Determination of Fuel System Icing
Inhibitor:
6. Apparatus 9.3.1 Shake the extraction vessel vigorously for a minimum
of 5 min for all fuels.
6.1 Refractometer—The HB temperature compensated, di-
9.3.1.1 Mechanical shakers may be used provided thorough
rect reading refractometer and the 0 to 30 or 0 to 16 Brix have
intermixing of the aqueous and fuel phases occurs, similar to
been found satisfactory for use.
that obtained by hand shaking.
6.2 Extraction Vessel—Any suitable vessel of at least 200
mL with provisions for isolating a small column of water
NOTE 6—Caution: Following the extraction procedures is most criti-
extract. Examples are separatory funnels, (glass or plastic), or
cal. Failure to extract for the specified time or failure to provide vigorous
plastic dropping bottles. agitation can result in false readings. If lower than expected readings are
obtained, a second test should be done with a longer extraction time.
6.3 Measuring Vessel—Any vessel capable of measuring up
to 160 mLof fuel to an accuracy of 62 mL, such as a 250-mL
9.3.2 Allow the extraction vessel to sit undisturbed at
graduated cylinder, or other calibrated container.
ambient temperature for a period of at least 2 min to allow the
6.4 Water Dispenser—2.0-mL pipettes are preferred, but
water to settle to the bottom.
syringes or burettes not exceeding 5.0-mL capacity that can
NOTE 7—Caution: Fuel entrained in the water causes an indistinct
dispense 2.0 6 0.2 mL may be used.
refractometer reading. In most cases fuel residue can be eliminated by
6.5 Thermometer—The thermometer must have suitable
SLOWLY lowering the refractometer cover. The surface tension of water
range to measure air and fuel temperature in the field.Accurate
will sweep fuel off the prism surface.
to 61°C and meeting Specification E 1.
9.3.3 Open the cover of the refractometer prism and wipe it
clean with a tissue. Place several drops of the water used for
7. Reagents and Materials.
the extraction on the prism face.
7.1 Water—Distilled or deionized water is preferred for the
9.3.4 Close the cover and view the scale through the
extraction procedure, but potable water may be used.
eyepiece. Adjust the focus if necessary to bring the numbered
scale into focus. Observe the position of the shadow line on the
8. Calibration
numbered scale.
8.1 Calibration of the HB or Brix scale refractometer 9.3.5 Rotate the zero adjustment knob or set screw so that
the shadow line intersects at 0.0 on the HB or Brix scale
consists of setting the reading obtained with water at ambient
temperature to 0.0 with the zero adjustment. refractometer.
9.3.6 Open the prism cover and wipe the surface clean with
8.2 Thecalibrationstepisincorporatedintotheprocedureto
minimizetheeffectoftemperaturechangesbetweenthetimeof a tissue.
9.3.7 Isolate several drops of the water extract from the
calibration and measurement.
extraction vessel and place
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.