ASTM D1056-14
(Specification)Standard Specification for Flexible Cellular Materials—Sponge or Expanded Rubber
Standard Specification for Flexible Cellular Materials—Sponge or Expanded Rubber
ABSTRACT
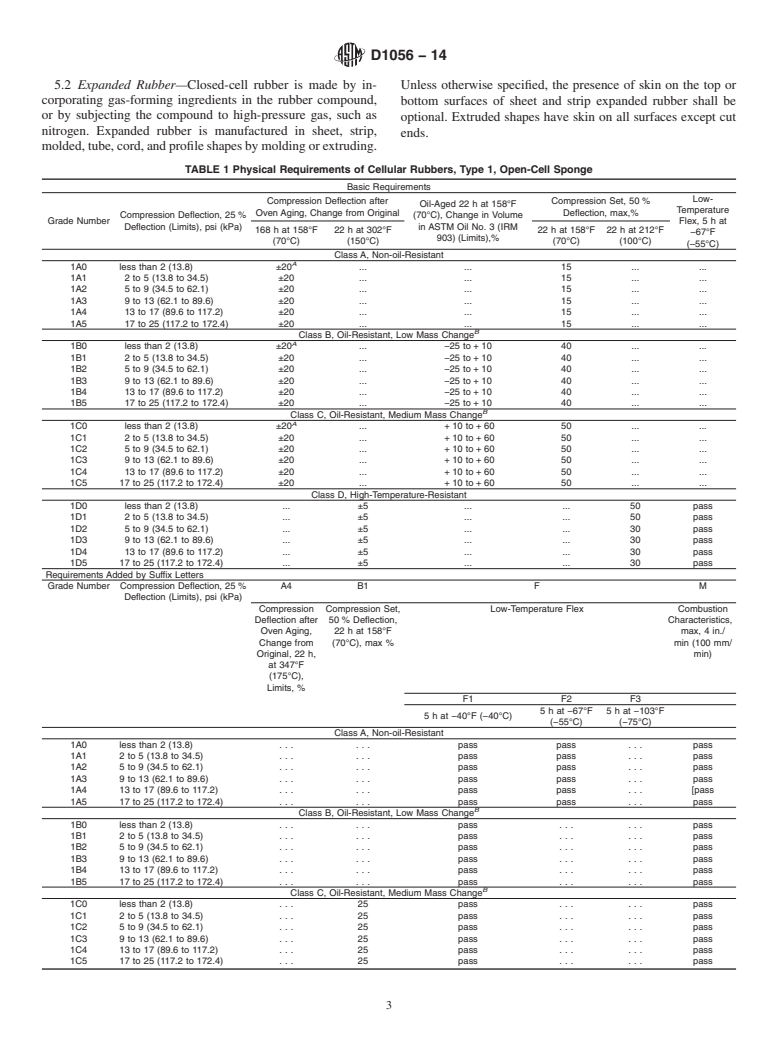
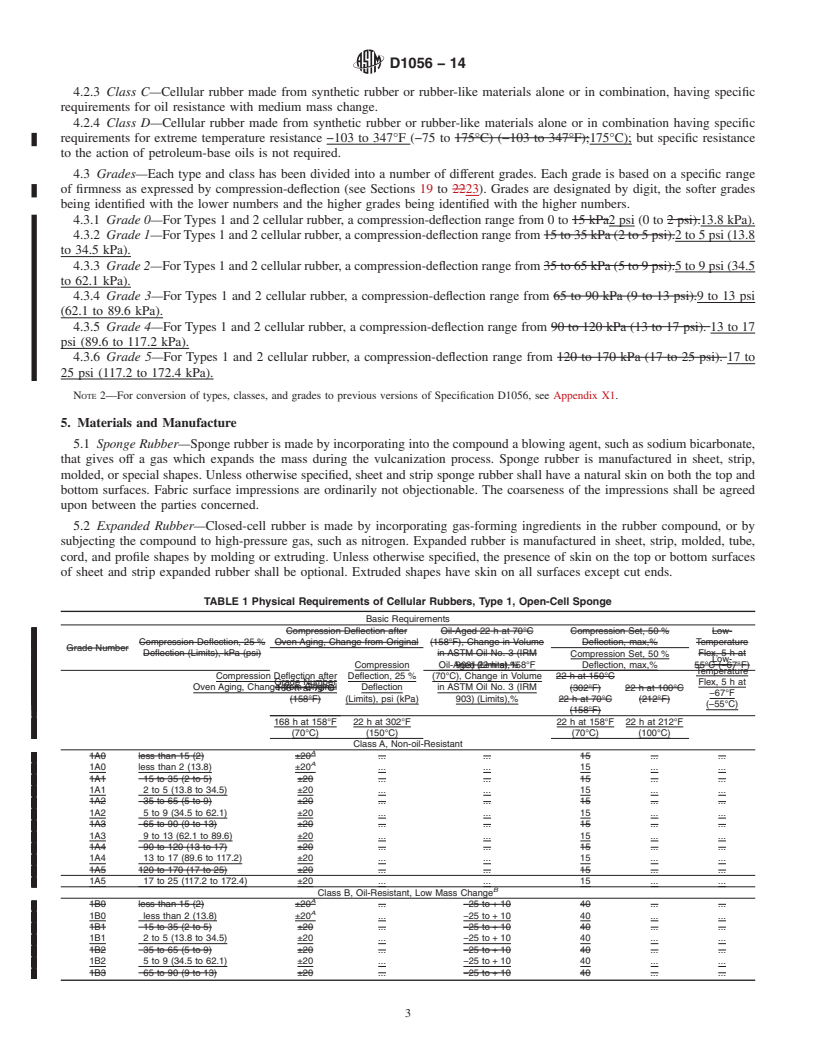
This specification covers flexible cellular rubber products known as sponge rubber and expanded rubber, but does not apply to latex foam rubber or ebonite cellular rubber. The base material for an open/closed cellular product may be made of synthetic, natural, or reclaimed rubber, or a mixture, and may contain other polymers or chemicals, or both, which may be modified by organic or inorganic additives. The cellular rubber shall be categorized by types, classes, suffixes, and grades: Types 1 and 2; Classes A, B, C, and D; Grades 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5. The various grades of cellular rubber shall conform to the requirements as to physical properties specified. The following test methods shall be performed: accelerated aging tests; compression-deflection tests; oil-immersion test (open-cell sponge); fluid immersion tests (closed cell); water absorption test; density tests; and low-temperature flex test.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers flexible cellular rubber products known as sponge rubber and expanded rubber, but does not apply to latex foam rubber or ebonite cellular rubber. The base material for an open/closed cellular product may be made of synthetic, natural, or reclaimed rubber, or a mixture, and may contain other polymers or chemicals, or both, which may be modified by organic or inorganic additives. These elastomeric materials have properties similar to those of vulcanized rubber, namely (1) the ability to be converted from a thermoplastic to a thermosetting state by crosslinking (vulcanization) or (2) the substantial recovery of their original shapes when strained or elongated, or both.
1.2 Extruded or molded shapes of sizes too small for cutting standard test specimens are difficult to classify or test by these methods and will usually require special testing procedures.
1.3 In case of conflict between the provisions of this general specification and those of detailed specifications or test methods for a particular product, the latter shall take precedence. Reference to the test methods in this specification should specifically state the particular test or tests desired.
1.4 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.5 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the test methods portions of this specification: This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Note 1—ISO 6916-1 is similar to this specification.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D1056 −14
Standard Specification for
1,2
Flexible Cellular Materials—Sponge or Expanded Rubber
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D1056; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope* standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices
and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior
1.1 This specification covers flexible cellular rubber prod-
to use.
ucts known as sponge rubber and expanded rubber, but does
not apply to latex foam rubber or ebonite cellular rubber. The
NOTE 1—ISO 6916-1 is similar to this specification.
base material for an open/closed cellular product may be made
2. Referenced Documents
of synthetic, natural, or reclaimed rubber, or a mixture, and
3
may contain other polymers or chemicals, or both, which may
2.1 ASTM Standards:
be modified by organic or inorganic additives. These elasto-
D395Test Methods for Rubber Property—Compression Set
meric materials have properties similar to those of vulcanized
D412TestMethodsforVulcanizedRubberandThermoplas-
rubber, namely (1) the ability to be converted from a thermo-
tic Elastomers—Tension
plastic to a thermosetting state by crosslinking (vulcanization)
D471Test Method for Rubber Property—Effect of Liquids
or (2) the substantial recovery of their original shapes when
D573Test Method for Rubber—Deterioration in an Air
strained or elongated, or both.
Oven
D575Test Methods for Rubber Properties in Compression
1.2 Extrudedormoldedshapesofsizestoosmallforcutting
D624Test Method for Tear Strength of Conventional Vul-
standard test specimens are difficult to classify or test by these
canized Rubber and Thermoplastic Elastomers
methods and will usually require special testing procedures.
D832Practice for Rubber Conditioning For Low Tempera-
1.3 Incaseofconflictbetweentheprovisionsofthisgeneral
ture Testing
specification and those of detailed specifications or test meth-
D883Terminology Relating to Plastics
ods for a particular product, the latter shall take precedence.
D1171Test Method for Rubber Deterioration—Surface
Reference to the test methods in this specification should
Ozone Cracking Outdoors or Chamber (Triangular Speci-
specifically state the particular test or tests desired.
mens)
1.4 Thevaluesstatedininch-poundunitsaretoberegarded
D2632Test Method for Rubber Property—Resilience by
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
Vertical Rebound
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
D3182PracticeforRubber—Materials,Equipment,andPro-
and are not considered standard.
cedures for Mixing Standard Compounds and Preparing
Standard Vulcanized Sheets
1.5 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the
D3183Practice for Rubber—Preparation of Pieces for Test
test methods portions of this specification:This standard does
Purposes from Products
not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any,
D5132Test Method for Horizontal Burning Rate of Poly-
associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this
meric Materials Used in Occupant Compartments of
Motor Vehicles
4
1
2.2 ISO Standard:
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D20 on
Plastics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.22 on Cellular
ISO 6916-1Flexible Cellular Polymeric Materials: Sponge
Materials - Plastics and Elastomers.
and Expanded Cellular Rubber Products—Specification
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of
Part 1 Sheet
Defense to replace Methods12001, 12005, 12011, 12021, 12031, 12041, 12151,
and12411 of Federal Test Method Standard No. 601.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of
3
Defense to replace MIL-STD-670 and MIL-STD-C 3133, which were discontinued For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
in 1986. contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Current edition approved March 1, 2014. Published April 2014. Originally Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
approved in 1949. Last previous edition approved in 2007 as D1056-07. DOI: the ASTM website.
4
10.1520/D1056-14. Available fromAmerican National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St.,
2
This version supersedes all prior versions of this specification. 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor D
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D1056 − 07 D1056 − 14
Standard Specification for
1,2
Flexible Cellular Materials—Sponge or Expanded Rubber
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D1056; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope*
1.1 This specification covers flexible cellular rubber products known as sponge rubber and expanded rubber, but does not apply
to latex foam rubber or ebonite cellular rubber. The base material for an open/closed cellular product may be made of synthetic,
natural, or reclaimed rubber, or a mixture, and may contain other polymers or chemicals, or both, which may be modified by
organic or inorganic additives. These elastomeric materials have properties similar to those of vulcanized rubber, namely (1) the
ability to be converted from a thermoplastic to a thermosetting state by crosslinking (vulcanization) or (2) the substantial recovery
of their original shapes when strained or elongated, or both.
1.2 Extruded or molded shapes of sizes too small for cutting standard test specimens are difficult to classify or test by these
methods and will usually require special testing procedures.
1.3 In case of conflict between the provisions of this general specification and those of detailed specifications or test methods
for a particular product, the latter shall take precedence. Reference to the test methods in this specification should specifically state
the particular test or tests desired.
1.4 The values stated in SIinch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.5 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the test methods portions of this specification:This standard does not
purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to
establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
NOTE 1—ISO 6916-1 is similar to this specification.
2. Referenced Documents
3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D395 Test Methods for Rubber Property—Compression Set
D412 Test Methods for Vulcanized Rubber and Thermoplastic Elastomers—Tension
D471 Test Method for Rubber Property—Effect of Liquids
D573 Test Method for Rubber—Deterioration in an Air Oven
D575 Test Methods for Rubber Properties in Compression
D624 Test Method for Tear Strength of Conventional Vulcanized Rubber and Thermoplastic Elastomers
D832 Practice for Rubber Conditioning For Low Temperature Testing
D883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
D1171 Test Method for Rubber Deterioration—Surface Ozone Cracking Outdoors or Chamber (Triangular Specimens)
D2632 Test Method for Rubber Property—Resilience by Vertical Rebound
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D20 on Plastics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.22 on Cellular Materials - Plastics
and Elastomers.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense to replace Methods 12001, 12005, 12011, 12021, 12031, 12041, 12151, and 12411
of Federal Test Method Standard No. 601.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense to replace MIL-STD-670 and MIL-STD-C 3133, which were discontinued in 1986.
Current edition approved March 1, 2007March 1, 2014. Published March 2007April 2014. Originally approved in 1949. Last previous edition approved in 20002007 as
D1056 - 00.D1056 - 07. DOI: 10.1520/D1056-07.10.1520/D1056-14.
2
This version supersedes all prior versions of this specification.
3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D1056 − 14
D3182 Practice for Rubber—Materials, Equipment, and Procedures for Mixin
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.