ASTM C119-19
(Terminology)Standard Terminology Relating to Dimension Stone
Standard Terminology Relating to Dimension Stone
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: C119 − 19
Standard Terminology Relating to
1
Dimension Stone
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C119; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
INTRODUCTION
Dimension stone,asusedhere,isnaturalstonethathasbeenselectedandfabricatedtospecificsizes
or shapes, with or without one or more mechanically dressed or finished surfaces, for use as building
facing, curbing, paving stone, monuments and memorials, and various industrial products. The term
dimension stone is in contradistinction to crushed and broken stone, such as is used for aggregate,
roadstone, fill, or chemical raw materials. Because all stone is a natural material, the definition
excludes all manmade materials that simulate stone. In common practice, some dimension stones are
reinforced, filled, or surface treated.
Terms used in definitions and nomenclature shall be interpreted in accordance with commonly
accepted scientific and technical terms of the geological sciences except as otherwise specifically
noted.
Examples of such exceptions are the broader commercial definitions of granite and marble, which
have become well established in the dimension stone industry and trade. Definitions and terms
includedinthesedefinitionshavebeenformulatedinaccordancewithcommonindustrialusage where
this is not in conflict with current scientific usage.
GENERAL TERMS building stone—natural rock of adequate quality to be quar-
riedandcutasdimensionstoneasitexistsinnature,asused
anchor—in general, a metal shape inserted into a slot or hole
in the construction industry.
in the stone that provides for the transfer of loads from the
stone to the building structure, either directly or through an
chip—an irregularly shaped fragment dislodged from a stone
intermediate structure.
surface.
anchorage—the system consisting of stone, anchor and pri-
cladding—nonload-bearing stone used as the facing material
mary structure, secondary structure or back-up preventing
in wall construction that contains other materials.
lateral movement of the stone.
coping—dimension stone used as the top course of a masonry
arris—thejunctionoftwoplanesofthesamestoneformingan
wall, often sloped to shed water.
external edge.
ashlar—(1) a squared block of building stone; (2) a masonry crack—a partial break in the stone (see fracture, microcrack,
of such stones; (3) a thin-dressed rectangle of stone for seam).
facing of walls (often called ashlar veneer).
cubic stock—in general, a thick dimension stone unit which is
bearing check—a slot, generally not continuous, cut into the
not precisely defined in terms of thickness for every kind of
back or bed of dimension stone to accommodate a support-
stone, particularly for limestone and sandstone. For marble
ing angle or clip (see Fig. 1.)
or granite, cubic stock is a unit that is greater than 50 mm in
thickness. For limestone, cubic stock is a unit that is greater
1
This terminology is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C18 on
than 75 mm to 100 mm in thickness, and for sandstone, a
Dimension Stone and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C18.91 on
unit that is greater than 150 mm to 200 mm in thickness. (In
Nomenclature and Definitions.
contrast, see thin stone.)
Current edition approved May 1, 2019. Published June 2019. Originally
approved in 1926. Last previous edition approved in 2016 as C119–16. DOI:
10.1520/C0119-19. cut stone—stone fabricated to specific dimensions.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C119 − 19
fracture—a complete break in the stone (see crack,
microcrack, seam).
freestone—a stone having little or no preferential direction of
splitting which may be cut freely in any direction without
fracture or splitting.
grain—(1) a distinguishable rock constituent which itself has
a distinct identity, for example, a mineral crystal, an oolith,
a rock fragment (in sedimentary rocks), or clast.
(2)adirectioninarockbodyalongwhichitismoreeasily
broken, split, or cut. See rift.
granular—composed of particles visible to the unaided eye.
For sedimentary stone, the predominant particle distribution
is less than 4 mm in size.
hysteresis—the residual strain in stone after the stress causing
FIG. 1 Bearing Check
such strain is changed.
installation—theprocessofassemblingdimensionstoneintoa
structure.
dimension stone—natural stone that has been selected and
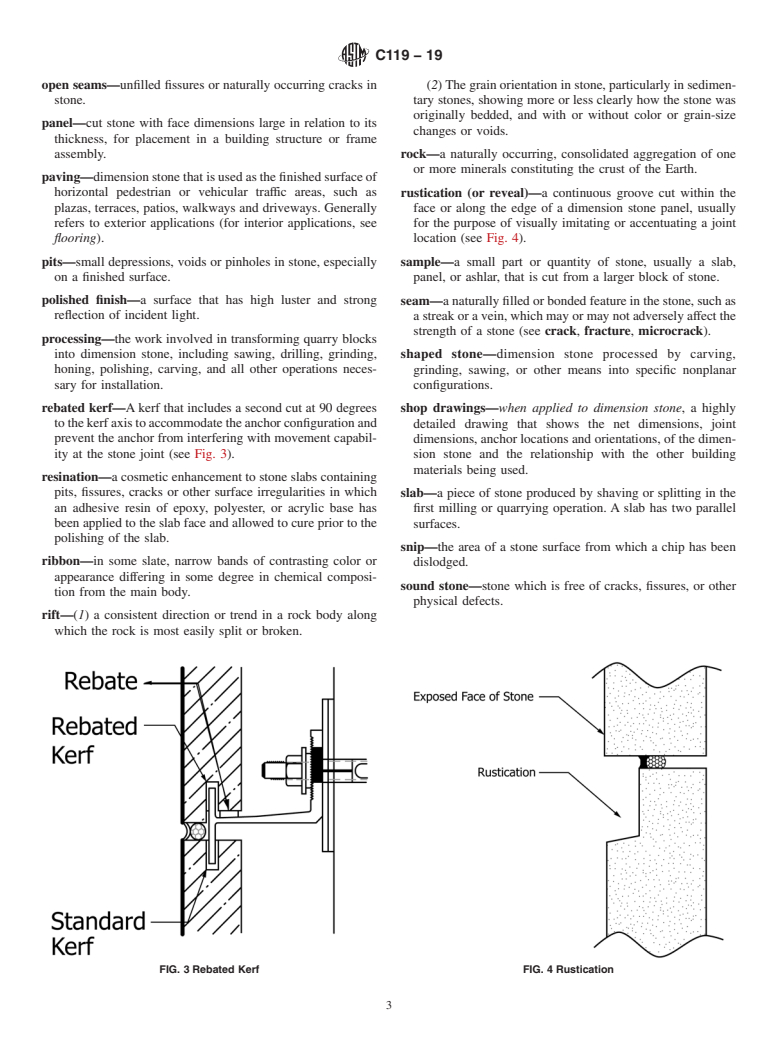
kerf—(1)aslot,eitherlocalorcontinuous,cutin
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: C119 − 16 C119 − 19
Standard Terminology Relating to
1
Dimension Stone
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C119; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
INTRODUCTION
Dimension stone, as used here, is natural stone that has been selected and fabricated to specific sizes
or shapes, with or without one or more mechanically dressed or finished surfaces, for use as building
facing, curbing, paving stone, monuments and memorials, and various industrial products. The term
dimension stone is in contradistinction to crushed and broken stone, such as is used for aggregate,
roadstone, fill, or chemical raw materials. Because all stone is a natural material, the definition
excludes all manmade materials that simulate stone. In common practice, some dimension stones are
reinforced, filled, or surface treated.
Terms used in definitions and nomenclature shall be interpreted in accordance with commonly
accepted scientific and technical terms of the geological sciences except as otherwise specifically
noted.
Examples of such exceptions are the broader commercial definitions of granite and marble, which
have become well established in the dimension stone industry and trade. Definitions and terms
included in these definitions have been formulated in accordance with common industrial usage where
this is not in conflict with current scientific usage.
GENERAL TERMS
anchor—in general, a metal shape inserted into a slot or hole in the stone that provides for the transfer of loads from the stone
to the building structure, either directly or through an intermediate structure.
anchorage—the system consisting of stone, anchor and primary structure, secondary structure or back-up preventing lateral
movement of the stone.
arris—the junction of two planes of the same stone forming an external edge.
ashlar—(1) a squared block of building stone; (2) a masonry of such stones; (3) a thin-dressed rectangle of stone for facing of
walls (often called ashlar veneer).
bearing check—a slot, generally not continuous, cut into the back or bed of dimension stone to accommodate a supporting angle
or clip (see Fig. 1.)
building stone—natural rock of adequate quality to be quarried and cut as dimension stone as it exists in nature, as used in the
construction industry.
chip—an irregularly shaped fragment dislodged from a stone surface.
cladding—nonload-bearing stone used as the facing material in wall construction that contains other materials.
coping—dimension stone used as the top course of a masonry wall, often sloped to shed water.
crack—a partial break in the stone (see fracture, microcrack, seam).
1
This terminology is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C18 on Dimension Stone and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C18.91 on Nomenclature and
Definitions.
Current edition approved May 1, 2016May 1, 2019. Published May 2016June 2019. Originally approved in 1926. Last previous edition approved in 20142016 as
ɛ1
C119 – 14C119 – 16. . DOI: 10.1520/C0119-16.10.1520/C0119-19.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C119 − 19
FIG. 1 Bearing Check
cubic stock—in general, a thick dimension stone unit which is not precisely defined in terms of thickness for every kind of stone,
particularly for limestone and sandstone. For marble or granite, cubic stock is a unit that is greater than 50 mm in thickness. For
limestone, cubic stock is a unit that is greater than 75 mm to 100 mm in thickness, and for sandstone, a unit that is greater than
150 mm to 200 mm in thickness. (In contrast, see thin stone.)
cut stone—stone fabricated to specific dimensions.
2
---------------------- Page: 2 ----------------------
C119 − 19
dimension stone—natural stone that has been selected and fabricated to specific sizes or shapes.
DISCUSSION—
The term dimension stone is in contradistinction to crushed and broken stone, such as is used for aggregate, roadstone, fill, or chemical raw materials.
In common practice, some dimension stones are reinforced, filled, or surface treated.
dressed stone—See cut stone, finished stone.
durability—the measure of
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.