ASTM D351-14
(Classification)Standard Classification for Natural Muscovite Block Mica and Thins Based on Visual Quality
Standard Classification for Natural Muscovite Block Mica and Thins Based on Visual Quality
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 The properties included in this standard are those required to control the visual quality, usable area, thickness, hardness, and stiffness.
SCOPE
1.1 This classification covers the determination of commercially available natural muscovite block mica and is intended to be independent of the basic color of the mica or its source.
1.2 Muscovite mica is characterized by having an optical axial angle between 50 and 75° (see Appendix X1); and has a weight loss when heated for 5 min at 600°C not exceeding 0.2 % (based on the weight after drying at 120°C).
1.3 The visual system of classifying the quality of natural muscovite mica covered by this specification is based upon relative amounts of visible foreign inclusions such as air bubbles, stains, and spots in combination with relative amounts and types of waviness, as well as other physical properties. In this system, a perfectly clear, transparent, flat specimen of mica is the visual standard of perfection. Increasing amounts of visual defects lower the visual quality, and a total of 13 levels of visual quality are covered by this standard. This method of classification, generally known as the Bengal India System, is purely qualitative and is entirely dependent on personal opinion and judgment.
1.4 The standards for visual quality classification that are covered in this classification are the best commercially available concept of the various qualities and their relative positions. Variations in the methods of using and applying these standards from those herein defined may be specified by the purchaser, or defined by agreement between the supplier and the purchaser.
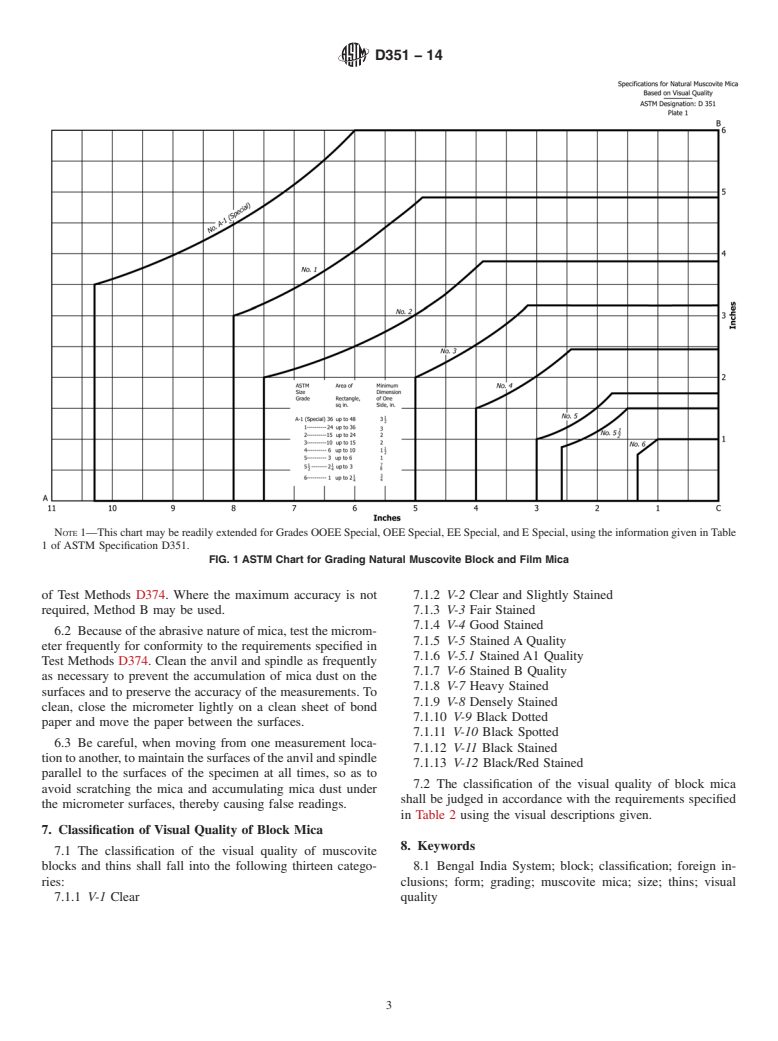
1.5 Standard size classifications are defined, based upon available usable rectangular areas and the minimum dimensions of the rectangles that the pieces will yield. Precautions to be taken in making thickness measurements are also described.
1.6 This standard covers the following two definite forms of commercial preparation:
1.6.1 Form 1—Full-trimmed natural block mica, 0.007 in. (0.178 mm) minimum thickness.
1.6.2 Form 2—Partially-trimmed natural block mica, 0.007 in. minimum thickness.
1.7 The basic color of mica, such as white, ruby, light green, dark green, brownish green, and rum, as well as other colors, and the method of controlling the color and other problems associated with the basic color, are not a part of this classification.
1.8 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.9 Section 5 is technically identical to procedures specified in ISO 67-1981.
1.10 Section 6 differs somewhat in procedure from ISO 5972-1978, but data obtained by either should be identical.
1.11 Section 7 is technically identical to procedures specified in ISO 2185-1972.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D351 −14
Standard Classification for
Natural Muscovite Block Mica and Thins Based on Visual
1
Quality
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D351; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope 1.6.1 Form 1—Full-trimmed natural block mica, 0.007 in.
(0.178 mm) minimum thickness.
1.1 This classification covers the determination of commer-
1.6.2 Form 2—Partially-trimmed natural block mica, 0.007
ciallyavailablenaturalmuscoviteblockmicaandisintendedto
in. minimum thickness.
be independent of the basic color of the mica or its source.
1.7 Thebasiccolorofmica,suchaswhite,ruby,lightgreen,
1.2 Muscovite mica is characterized by having an optical
dark green, brownish green, and rum, as well as other colors,
axial angle between 50 and 75° (see Appendix X1); and has a
and the method of controlling the color and other problems
weight loss when heated for 5 min at 600°C not exceeding
associated with the basic color, are not a part of this classifi-
0.2 % (based on the weight after drying at 120°C).
cation.
1.3 The visual system of classifying the quality of natural
1.8 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
muscovite mica covered by this specification is based upon
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
relative amounts of visible foreign inclusions such as air
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
bubbles,stains,andspotsincombinationwithrelativeamounts
and are not considered standard.
and types of waviness, as well as other physical properties. In
thissystem,aperfectlyclear,transparent,flatspecimenofmica 1.9 Section 5 is technically identical to procedures specified
is the visual standard of perfection. Increasing amounts of in ISO 67-1981.
visual defects lower the visual quality, and a total of 13 levels
1.10 Section 6 differs somewhat in procedure from ISO
of visual quality are covered by this standard. This method of
5972-1978, but data obtained by either should be identical.
classification, generally known as the Bengal India System, is
1.11 Section 7 is technically identical to procedures speci-
purely qualitative and is entirely dependent on personal opin-
fied in ISO 2185-1972.
ion and judgment.
1.4 The standards for visual quality classification that are
2. Referenced Documents
covered in this classification are the best commercially avail-
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
able concept of the various qualities and their relative posi-
D374 Test Methods for Thickness of Solid Electrical Insu-
tions. Variations in the methods of using and applying these
lation (Metric) D0374_D0374M
standards from those herein defined may be specified by the
D1711 Terminology Relating to Electrical Insulation
purchaser, or defined by agreement between the supplier and
the purchaser. 2.2 ISO Publications:
ISO 67-1981 Muscovite Mica Blocks, Thins, and Films—
1.5 Standard size classifications are defined, based upon
3
Grading by Size
available usable rectangular areas and the minimum dimen-
ISO 2185-1972 Muscovite Mica Blocks,Thins, and Films—
sions of the rectangles that the pieces will yield. Precautions to
3
Visual Classification
be taken in making thickness measurements are also described.
ISO 5972-1978 Mica Blocks, Thins, Films, and Splittings—
3
1.6 This standard covers the following two definite forms of
Measurement of Thickness
commercial preparation:
1 2
This classification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D09 on For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Electrical and Electronic Insulating Materials and is the direct responsibility of contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Subcommittee D09.01 on Electrical Insulating Products. Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Current edition approved Jan. 15, 2014. Published March 2014. Originally the ASTM website.
ε1 3
approved in 1932. Last previous edition approved in 2008 as D351 – 97 (2008) . Available from American National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St.,
DOI: 10.1520/D0351-14. 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D351−14
3. Terminology rectangles. This would constitute a minimum yield of 65 %.
For Grades 5 and smaller, the average area of the pieces shall
3.1 For definitions of terms relating to mic
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
´1
Designation: D351 − 97 (Reapproved 2008) D351 − 14 An American National Standard
Standard Classification for
Natural Muscovite Block Mica and Thins Based on Visual
1
Quality
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D351; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1
ε NOTE—The units statement in subsection 1.8 was corrected editorially in July 2008.
1. Scope
1.1 This classification covers the determination of commercially available natural muscovite block mica and is intended to be
independent of the basic color of the mica or its source.
1.2 Muscovite mica is characterized by having an optical axial angle between 50 and 75° (see Appendix X1); and has a weight
loss when heated for 5 min at 600°C not exceeding 0.2 % (based on the weight after drying at 120°C).
1.3 The visual system of classifying the quality of natural muscovite mica covered by this specification is based upon relative
amounts of visible foreign inclusions such as air bubbles, stains, and spots in combination with relative amounts and types of
waviness, as well as other physical properties. In this system, a perfectly clear, transparent, flat specimen of mica is the visual
standard of perfection. Increasing amounts of visual defects lower the visual quality, and a total of 13 levels of visual quality are
covered by this standard. This method of classification, generally known as the Bengal India System, is purely qualitative and is
entirely dependent on personal opinion and judgment.
1.4 The standards for visual quality classification that are covered in this classification are the best commercially available
concept of the various qualities and their relative positions. Variations in the methods of using and applying these standards from
those herein defined may be specified by the purchaser, or defined by agreement between the supplier and the purchaser.
1.5 Standard size classifications are defined, based upon available usable rectangular areas and the minimum dimensions of the
rectangles that the pieces will yield. Precautions to be taken in making thickness measurements are also described.
1.6 This standard covers the following two definite forms of commercial preparation:
1.6.1 Form 1—Full-trimmed natural block mica, 0.007 in. (0.178 mm) minimum thickness.
1.6.2 Form 2—Partially-trimmed natural block mica, 0.007 in. minimum thickness.
1.7 The basic color of mica, such as white, ruby, light green, dark green, brownish green, and rum, as well as other colors, and
the method of controlling the color and other problems associated with the basic color, are not a part of this classification.
1.8 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.9 Section 5 is technically identical to procedures specified in ISO 67-1981.
1.10 Section 6 differs somewhat in procedure from ISO 5972-1978, but data obtained by either should be identical.
1.11 Section 7 is technically identical to procedures specified in ISO 2185-1972.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
3
D374 Test Methods for Thickness of Solid Electrical Insulation (Withdrawn 2013)
1
This classification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D09 on Electrical and Electronic Insulating Materials and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
D09.19 on Dielectric Sheet and Roll Products.
Current edition approved May 1, 2008Jan. 15, 2014. Published July 2008March 2014. Originally approved in 1932. Last previous edition approved in 20032008 as
ε1
D351 – 97(2003)(2008) . DOI: 10.1520/D0351-97R08E01.10.1520/D0351-14.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on www.astm.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D351 − 14
D1711 Terminology Relating
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.