ASTM D660-93(2011)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Evaluating Degree of Checking of Exterior Paints
Standard Test Method for Evaluating Degree of Checking of Exterior Paints
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
Since checking is not easily recognizable, this test method is intended to provide, through definition and illustrations, a means of evaluating the degree of this film failure.
SCOPE
1.1 The illustrated reference standards included in this test method are representative of degrees and types of checking of exterior paint films. These standards are primarily intended for comparative evaluation.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D660 − 93 (Reapproved 2011)
Standard Test Method for
Evaluating Degree of Checking of Exterior Paints
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D660; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope the breaks running from a center and forming an angle of about
120° between the prongs.
1.1 The illustrated reference standards included in this test
4.1.5 Mosaic Type—Checking in which the breaks in the
method are representative of degrees and types of checking of
surface of the film form straight sided, geometric patterns
exterior paint films. These standards are primarily intended for
which join on all sides.
comparative evaluation.
4.1.6 Shrinkage Type—Checking in which the breaks in the
surface of the film usually form individual short breaks with
2. Terminology
shorter irregular breaks progressing at right angles.
2.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
4.1.7 Short, Random Type—Checking in which breaks in the
2.1.1 checking, n—that phenomenon manifested in paint
surface of the film form short, irregular patterns. These breaks
films by slight breaks in the film that do not penetrate through
are usually individual and do not join.
the last applied coating.
4.1.8 Sigmoid Type—Checking in which the breaks in the
2.1.1.1 Discussion—Where precision is necessary in evalu-
surface of the film form oval patterns. These oval shapes rarely
ating a paint film, checking may be described as visible (as
complete their circle.
seen with the naked eye) or as microscopic (as observed under
a magnification up to ten diameters).
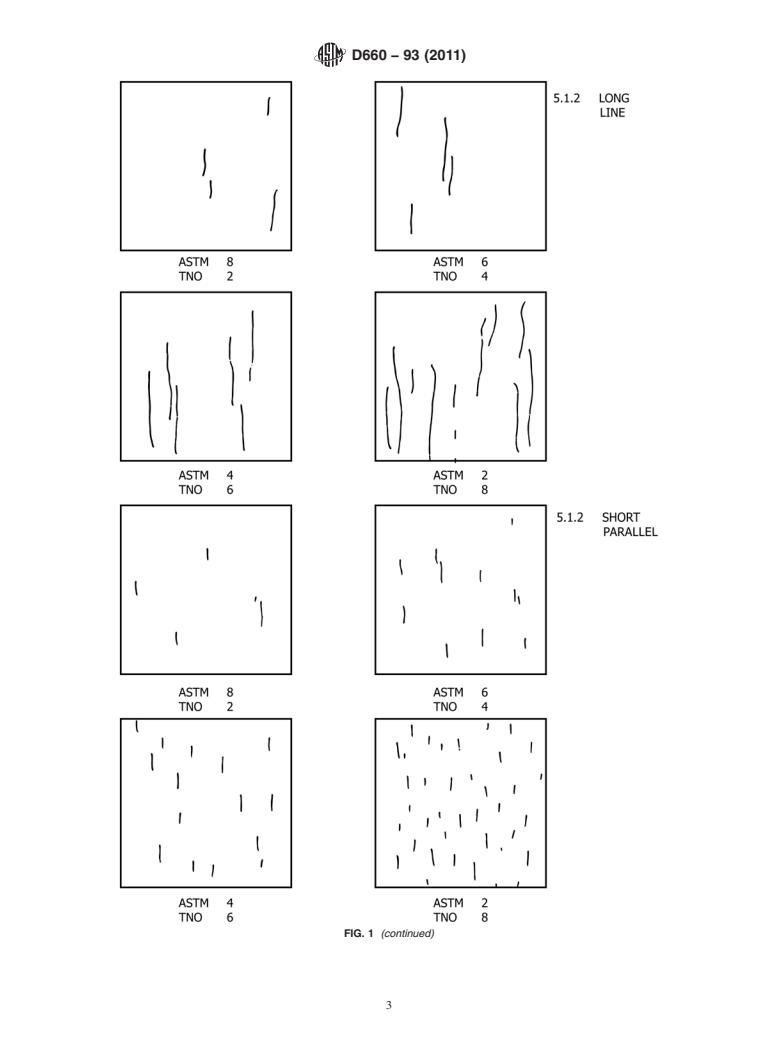
5. Use of Illustrated Reference Standards
5.1 The use of the reference standards shown in Fig. 1
3. Significance and Use
requires the following precautions:
3.1 Since checking is not easily recognizable, this test
5.1.1 Since the type and degree of failure may vary over any
method is intended to provide, through definition and
given area, a representative portion should be rated. It is
illustrations, a means of evaluating the degree of this film
recommended that ratings be made at several locations, noting
failure.
types and degree of failure.
5.1.2 Care must be taken to recognize that several types of
4. Types of Checking
checking may be present on the same surface.
4.1 Many types of checking are recognized, of which some
5.1.3 Paint films may collect excessive quantities of dirt,
are:
which may mask the type and degree of failure. If necessary,
4.1.1 Irregular Pattern Type—Checking in which the breaks
dirt should be removed by careful and gentle brushing with a
develop in the surface of the film in no definite pattern.
moderately soft brush. Care must be taken not to damage the
4.1.2 Line and Short Parallel Type—Checking in which the
finish.
breaks in the surface of the film are generally arranged in
5.1.4 Fig. 2 illustrates microscopic checking under 10-
parallel lines.
diameter magnification.
4.1.3 Switch Type—Checking in which the breaks in the
5.1.5 For convenience in recording the data obtained, the
surface of th
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.