ASTM D7318-19
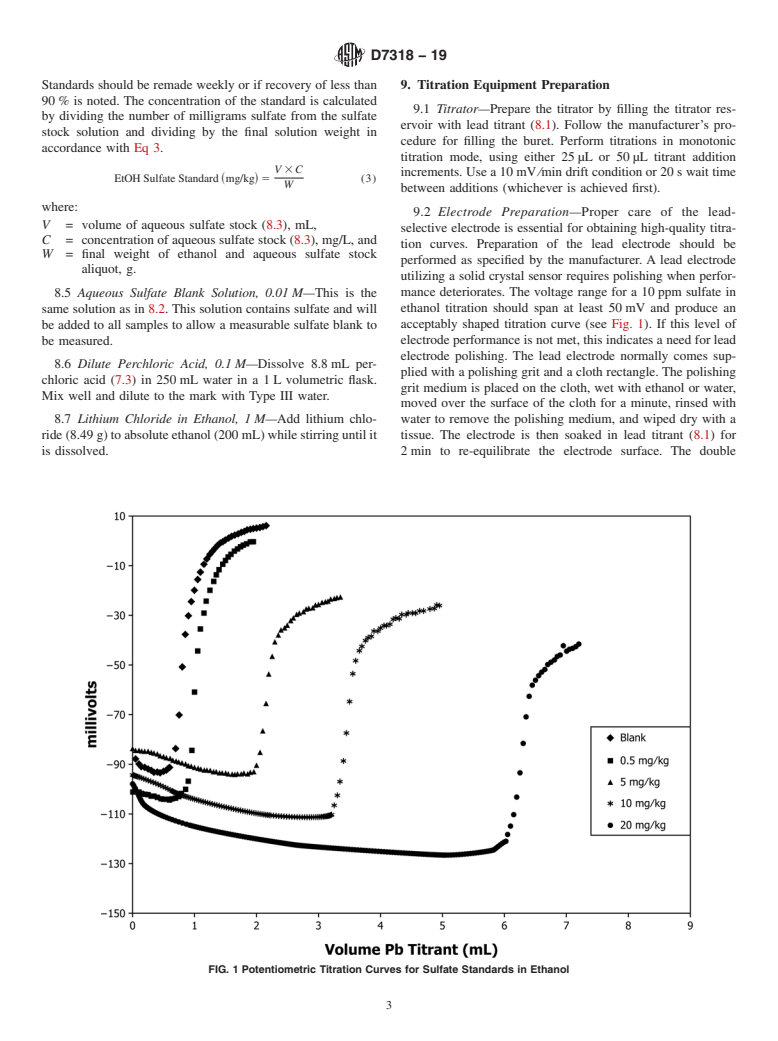
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Existent Inorganic Sulfate in Ethanol by Potentiometric Titration
Standard Test Method for Existent Inorganic Sulfate in Ethanol by Potentiometric Titration
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 Ethanol is used as a blending agent added to gasoline. Sulfates are indicated in filter plugging deposits and fuel injector deposits. When fuel ethanol is burned, sulfates may contribute to sulfuric acid emissions. Ethanol acceptability for use depends on the sulfate content. Sulfate content, as measured by this test method, can be used as one measure of determination of the acceptability of ethanol for automotive spark-ignition engine fuel use.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers a potentiometric titration procedure for determining the existent inorganic sulfate content of hydrous, anhydrous ethanol, and anhydrous denatured ethanol, which is added as a blending agent with spark ignition fuels. It is intended for the analysis of denatured ethanol samples containing between 1.0 mg/kg to 20 mg/kg existent inorganic sulfate.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Material Safety Data Sheets are available for reagents and materials. Review them for hazards prior to usage.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D7318 − 19
Standard Test Method for
Existent Inorganic Sulfate in Ethanol by Potentiometric
1
Titration
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7318; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
NOTE—Subsection 11.2.1 was corrected and the yeardate changed on February 14, 2019.
1. Scope* D4057 Practice for Manual Sampling of Petroleum and
Petroleum Products
1.1 This test method covers a potentiometric titration pro-
D4177 Practice for Automatic Sampling of Petroleum and
cedure for determining the existent inorganic sulfate content of
Petroleum Products
hydrous, anhydrous ethanol, and anhydrous denatured ethanol,
D6299 Practice for Applying Statistical Quality Assurance
which is added as a blending agent with spark ignition fuels. It
and Control Charting Techniques to Evaluate Analytical
is intended for the analysis of denatured ethanol samples
Measurement System Performance
containing between 1.0 mg⁄kg to 20 mg⁄kg existent inorganic
sulfate.
3. Terminology
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
3.1 Definitions:
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
3.1.1 existent inorganic sulfate, n—inorganic sulfate species
standard.
actually present in the sample at the time of analysis with no
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
oxidation treatment.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
3.1.1.1 Discussion—Specifically in this test method, inor-
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
ganic sulfate is present as sulfate in ethanol.
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
–2
3.1.2 inorganic sulfate, n—sulfate (SO ) species present
4
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
as sulfuric acid, ionic salts of this acid, or mixtures of these.
Material Safety Data Sheets are available for reagents and
materials. Review them for hazards prior to usage.
4. Summary of Test Method
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
4.1 An ethanol sample containing inorganic sulfate is
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
titrated in ethanolic medium with a standard lead nitrate
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
solution. Lead sulfate precipitate is formed during the titration.
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
Perchloric acid is added to remove possible interference from
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
carbonate. The endpoint is signaled by an increase in lead ion
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
activity, as measured by a lead-selective electrode.
2. Referenced Documents
5. Significance and Use
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
5.1 Ethanol is used as a blending agent added to gasoline.
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
Sulfates are indicated in filter plugging deposits and fuel
D4052 Test Method for Density, Relative Density, and API
injector deposits. When fuel ethanol is burned, sulfates may
Gravity of Liquids by Digital Density Meter
contribute to sulfuric acid emissions. Ethanol acceptability for
use depends on the sulfate content. Sulfate content, as mea-
1 sured by this test method, can be used as one measure of
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on
Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of
determination of the acceptability of ethanol for automotive
Subcommittee D02.03 on Elemental Analysis.
spark-ignition engine fuel use.
Current edition approved Feb. 14, 2019. Published February 2019. Originally
approved in 2007. Last previous edition approved in 2018 as D7318 – 18. DOI:
6. Apparatus
10.1520/D7318-19.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
6.1 Potentiometric Titration Assembly—A titration assem-
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
bly consisting of an automatic titrator fitted with a lead
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. ion-selective electrode, a double-junction reference electrode,
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D7318 − 19
buret, and stirring is used. Stirring may be accomplished by 7.7 Water—Type III reagent water conforming to Specifica-
means of magnetic or propeller type stirrer mechanisms. The tion D1193.
buret size should id
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D7318 − 18 D7318 − 19
Standard Test Method for
Existent Inorganic Sulfate in Ethanol by Potentiometric
1
Titration
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7318; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
NOTE—Subsection 11.2.1 was corrected and the yeardate changed on February 14, 2019.
1. Scope*
1.1 This test method covers a potentiometric titration procedure for determining the existent inorganic sulfate content of
hydrous, anhydrous ethanol, and anhydrous denatured ethanol, which is added as a blending agent with spark ignition fuels. It is
intended for the analysis of denatured ethanol samples containing between 1.0 mg ⁄kg to 20 mg ⁄kg existent inorganic sulfate.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of
regulatory limitations prior to use. Material Safety Data Sheets are available for reagents and materials. Review them for hazards
prior to usage.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
D4052 Test Method for Density, Relative Density, and API Gravity of Liquids by Digital Density Meter
D4057 Practice for Manual Sampling of Petroleum and Petroleum Products
D4177 Practice for Automatic Sampling of Petroleum and Petroleum Products
D6299 Practice for Applying Statistical Quality Assurance and Control Charting Techniques to Evaluate Analytical Measure-
ment System Performance
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 existent inorganic sulfate, n—inorganic sulfate species actually present in the sample at the time of analysis with no
oxidation treatment.
3.1.1.1 Discussion—
Specifically in this test method, inorganic sulfate is present as sulfate in ethanol.
–2
3.1.2 inorganic sulfate, n—sulfate (SO ) species present as sulfuric acid, ionic salts of this acid, or mixtures of these.
4
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
D02.03 on Elemental Analysis.
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2018Feb. 14, 2019. Published October 2018February 2019. Originally approved in 2007. Last previous edition approved in 20132018
as D7318 – 13.D7318 – 18. DOI: 10.1520/D7318-18.10.1520/D7318-19.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D7318 − 19
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 An ethanol sample containing inorganic sulfate is titrated in ethanolic medium with a standard lead nitrate solution. Lead
sulfate precipitate is formed during the titration. Perchloric acid is added to remove possible interference from carbonate. The
endpoint is signaled by an increase in lead ion activity, as measured by a lead-selective electrode.
5. Significance and Use
5.1 Ethanol is used as a blending agent added to gasoline. Sulfates are indicated in filter plugging deposits and fuel injector
deposits. When fuel ethanol is burned, sulfates may contribute to sulfuric acid emissions. Ethanol acceptability for use depends
on the sulfate content. Sulfate content, as measured by this test method, can be used as one measure of determination of the
acceptability of ethanol for automotive spark-ignition engine fuel use.
6. Apparatus
6.1 Potentiometric Titration Assembly—A titration asse
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.