ASTM D6523-22
(Guide)Standard Guide for Evaluation and Selection of Alternative Daily Covers (ADCs) for Sanitary Landfills
Standard Guide for Evaluation and Selection of Alternative Daily Covers (ADCs) for Sanitary Landfills
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 This guide provides information which the regulator/permit officials, engineers, waste disposal operators, and others will find helpful to (1) understand and distinguish between the many choices available, (2) understand the performance feature considerations for living up to EPA regulations for landfill daily covers, and (3) understand the various requirements and differences for putting these covers into practice at landfills.
SCOPE
1.1 This guide is intended to assist specifiers and end users in assessing the different options available for sanitary landfill daily cover materials described as alternative (non-soil) daily covers (ADCs). Traditional daily cover consists of at least 6 in. (15 cm) of soil spread over the working faces of sanitary landfills. Alternative systems are attractive to landfill operations in order to conserve landfill disposal space, among other reasons.
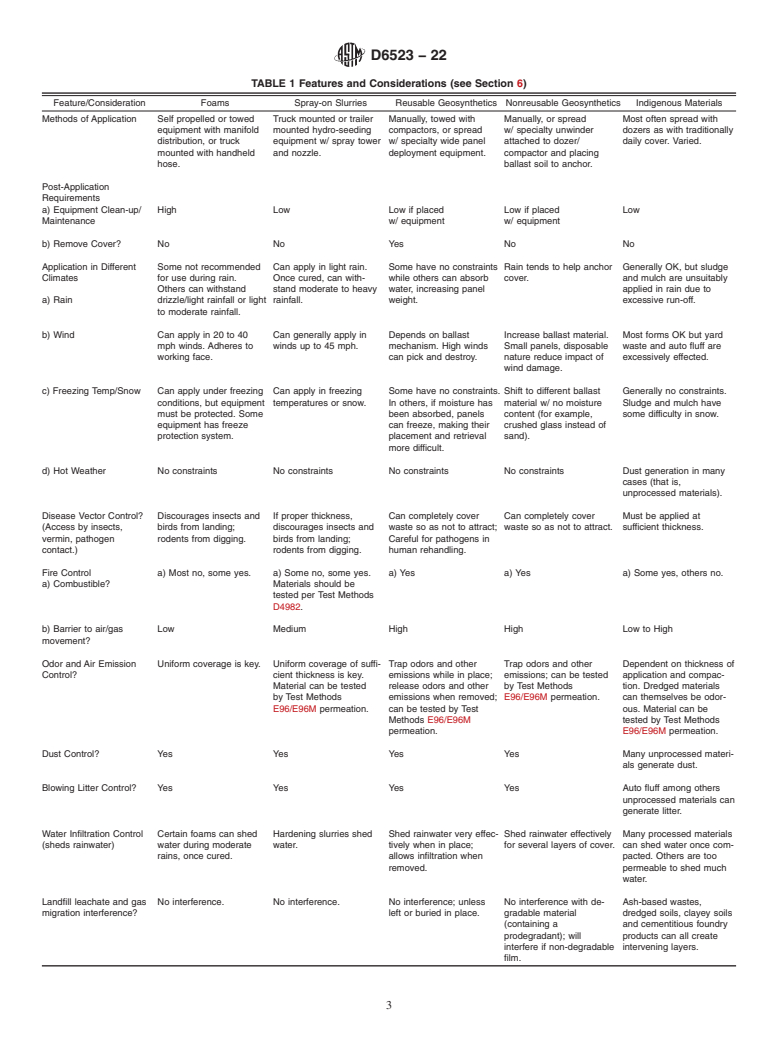
1.2 This guide assists in understanding different performance features of broad classifications of ADCs, and determining the extent and degree to which different ADCs are able to “control disease vectors, fires, odors, blowing litter, and scavenging, without presenting a threat to human health and the environment,” as intended by United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) regulations.
1.3 This guide is not intended to provide cost information regarding the various ADCs. As a standard guide, it does not dictate a protocol for the practice and testing of ADCs, but rather provides valuable information, guidance, and recommendations to interested parties concerning the many options available.
1.4 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.4.1 Exception—Metric units are used in 6.2.9.2.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D6523 −22
Standard Guide for
Evaluation and Selection of Alternative Daily Covers (ADCs)
1
for Sanitary Landfills
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6523; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
1.1 This guide is intended to assist specifiers and end users
D4982 Test Methods for Flammability Potential Screening
in assessing the different options available for sanitary landfill
Analysis of Waste
daily cover materials described as alternative (non-soil) daily
E96/E96M Test Methods for Gravimetric Determination of
covers (ADCs).Traditional daily cover consists of at least 6 in.
Water Vapor Transmission Rate of Materials
(15 cm) of soil spread over the working faces of sanitary
3
2.2 Other Standards:
landfills. Alternative systems are attractive to landfill opera-
Solid Waste Disposal Facility Criteria, USEPA, Technical
tions in order to conserve landfill disposal space, among other
Manual EPA 530-R-93-017, Cover Material
reasons.
Requirements, 40 CFR 258 21, Nov 1993
1.2 This guide assists in understanding different perfor-
“The Use of Alternative Materials for Daily Cover at
mance features of broad classifications of ADCs, and deter-
Municipal Solid Waste Landfills” EPA 600/R-93/172 PB
mining the extent and degree to which differentADCs are able
92-227197, July 1993
to “control disease vectors, fires, odors, blowing litter, and
Alternative Daily Cover Regulations, California Environ-
scavenging, without presenting a threat to human health and
mental Protection Agency, Title 27, Division 2, Subdivi-
the environment,” as intended by United States Environmental
sion 1, Chapter 3, Subchapter 4, Article 2, Section 20680
Protection Agency (USEPA) regulations.
CIWMB Daily Cover and Section 20690 CIWMB Alter-
native Daily Cover
1.3 This guide is not intended to provide cost information
regarding the various ADCs. As a standard guide, it does not
3. Terminology
dictate a protocol for the practice and testing of ADCs, but
3.1 Definitions:
rather provides valuable information, guidance, and recom-
3.1.1 alternative daily cover, n—an alternative to the tradi-
mendations to interested parties concerning the many options
tional 6 in. (15 cm) soil cover required by the USEPA for
available.
landfill working faces to “control disease vectors, fires, odors,
1.4 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
blowing litter, and scavenging, without presenting a threat to
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
human health and the environment.”
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
3.1.2 foam, n—a synthetic material sprayed and combined
and are not considered standard.
with air to form closed-cell air pockets.
1.4.1 Exception—Metric units are used in 6.2.9.2.
3.1.3 gas emissions, n—a release of landfill gas generated
1.5 This international standard was developed in accor-
within the waste mass into the atmosphere through cover
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
materials.
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
3.1.4 geosynthetic, n—a planar product manufactured from
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
polymeric material used with soil, rock, earth, or other geo-
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
technical engineering related material as an integral part of a
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
man-made project, structure, or system.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
1
This guide is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D35 on Geosynthetics contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D35.03 on Permeability and Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Filtration. the ASTM website.
3
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2022. Published December 2022. Originally AvailablefromU.S.GovernmentPrintingOfficeSuperintendentofDocuments,
ɛ1
approved in 2000. Last previous edition approved in 2014 as D6523 – 00 (2014) . 732 N. Capitol St., NW, Mail Stop: SDE, Washington, DC 20401, http://
DOI: 10.1520/D6523-22. www.access.gpo.gov.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 --------------------
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
´1
Designation: D6523 − 00 (Reapproved 2014) D6523 − 22
Standard Guide for
Evaluation and Selection of Alternative Daily Covers (ADCs)
1
for Sanitary Landfills
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6523; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1
ε NOTE—Units statement was inserted in Section 1.4 editorially in January 2014.
1. Scope
1.1 This guide is intended to assist specifiers and end users in assessing the different options available for sanitary landfill daily
cover materials described as alternative (non-soil) daily covers (ADCs). Traditional daily cover consists of at least 6 in. (15 cm)
of soil spread over the working faces of sanitary landfills. Alternative systems are attractive to landfill operations in order to
conserve landfill disposal space, among other reasons.
1.2 This guide assists in understanding different performance features of broad classifications of ADCs, and determining the extent
and degree to which different ADCs are able to “control disease vectors, fires, odors, blowing litter, and scavenging, without
presenting a threat to human health and the environment,” as intended by United States Environmental Protection Agency
(USEPA) regulations.
1.3 This guide is not intended to provide cost information regarding the various ADCs asADCs. As a standard guide, it does not
dictate a protocol for the practice and testing of ADCs, but rather provides valuable information, guidance, and recommendations
to interested parties concerning the many options available.
1.4 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.4.1 Exception—Metric units are used in 6.2.9.2.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D4982 Test Methods for Flammability Potential Screening Analysis of Waste
E96/E96M Test Methods for Gravimetric Determination of Water Vapor Transmission Rate of Materials
1
This guide is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D35 on Geosynthetics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D35.03 on Permeability and Filtration.
Current edition approved Jan. 1, 2014Dec. 1, 2022. Published January 2014December 2022. Originally approved in 2000. Last previous edition approved in 20092014
ɛ1
as D6523–00(2009).D6523 – 00 (2014) . DOI: 10.1520/D6523-00R14E01.10.1520/D6523-22.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D6523 − 22
3
2.2 Other StandardsStandards:
Solid Waste Disposal Facility Criteria, USEPA, Technical Manual EPA 530-R-93-017, Cover Material Requirements, 40 CFR
258 21, Nov 1993
“The Use of Alternative Materials for Daily Cover at Municipal Solid Waste Landfills” EPA 600/R-93/172 PB 92-22719792-
227197, July 1993
Alternative Daily Cover Regulations, California Environmental Protection Agency, Title 27, Division 2, Subdivision 1, Chapter
3, Subchapter 4, Article 2, Section 20680 CIWMB Daily Cover and Section 20690 CIWMB Alternative Daily Cover
3. Terminology
3.1 alternative daily cover, n—an alternative to the traditional 6-in. (15-cm) soil cover required by the USEPA for landfill working
faces to “control disease vectors, fires, odors, blowing litter, and scavenging, without presenting a threat to human health and the
environment.”
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 alternative daily cover, n—an alternative to the traditional 6 in. (15 cm) soil cover required by the USEPA for landfill
working faces to “control disease vectors, fires, odors, blowing litter, and scavenging, without presenting a threat to human health
and the environment.”
3.1
...










Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.