ASTM D910-03a
(Specification)Standard Specification for Aviation Gasolines
Standard Specification for Aviation Gasolines
SCOPE
1.1 This specification is for the use of purchasing agencies in formulating specifications for purchases of aviation gasoline under contract.
1.2 This specification defines specific types of aviation gasolines for civil use. It does not include all gasolines satisfactory for reciprocating aviation engines. Certain equipment or conditions of use may permit a wider, or require a narrower, range of characteristics than is shown by this specification.
General Information
Relations
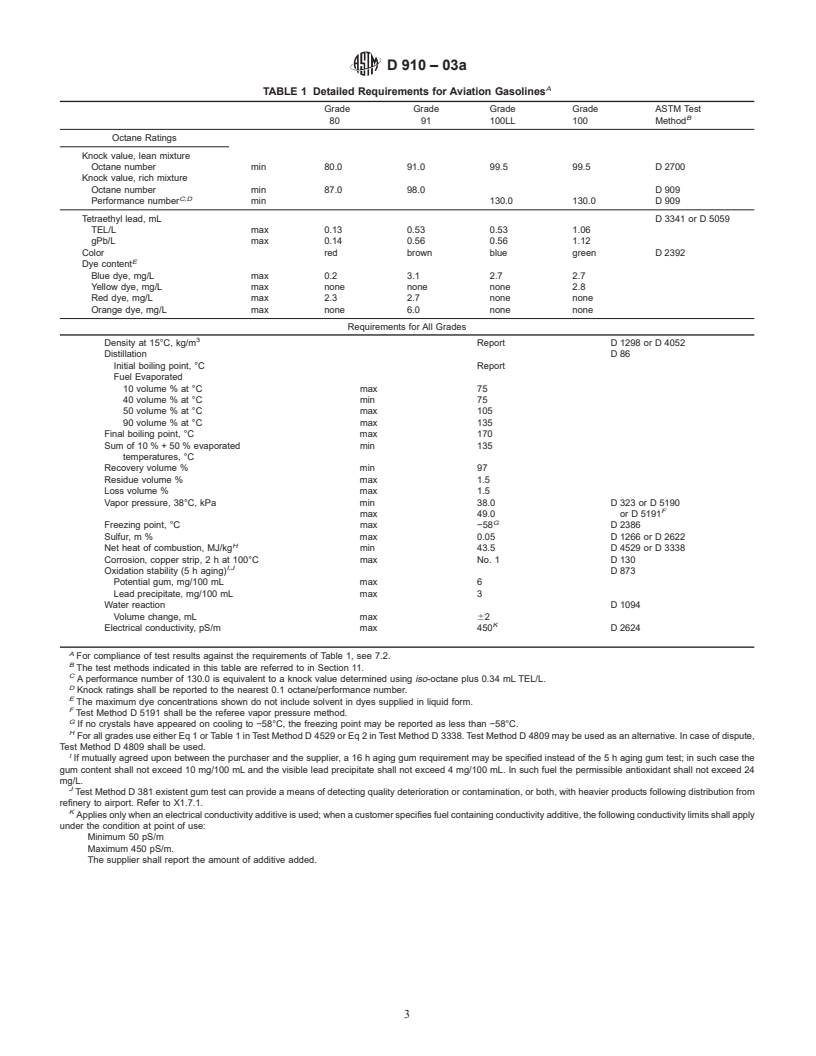
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
An American National Standard
Designation: D 910 – 03a
Standard Specification for
1
Aviation Gasolines
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 910; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope D 1266 Test Method for Sulfur in Petroleum Products
(Lamp Method)
1.1 This specification is intended primarily for use by
D 1298 Practice for Density, Relative Density (Specific
purchasing agencies in formulating specifications for purchases
Gravity), or API Gravity of Crude Petroleum and Liquid
of aviation gasoline under contract.
Petroleum Products by Hydrometer Method
1.2 This specification defines specific types of aviation
D 2386 Test Method for Freezing Point of Aviation Fuels
gasolines for civil use. It does not include all gasolines
D 2392 Test Method for Color of Dyed Aviation Gasolines
satisfactory for reciprocating aviation engines. Certain equip-
D 2622 Test Method for Sulfur in Petroleum Products by
ment or conditions of use may permit a wider, or require a
Wavelength Dispersive X-Ray Fluorescence Spectrometry
narrower, range of characteristics than is shown by this
D 2624 Test Method for Electrical Conductivity of Aviation
specification.
and Distillate Fuels
2. Referenced Documents D 2700 Test Method for Motor Octane Number of Spark-
2
Ignition Engine Fuel
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D 3338 Test Method for Estimation of Net Heat of Com-
D 86 Test Method for Distillation of Petroleum Products at
bustion of Aviation Fuels
Atmospheric Pressure
D 3341 Test Method for Lead in Gasoline–Iodine
D 93 Test Methods for Flash-Point by Pensky-Martens
Monochloride Method
Closed Cup Tester
D 4052 Test Method for Density and Relative Density of
D 130 Test Method for Detection of Copper Corrosion from
Liquids by Digital Density Meter
Petroleum Products by the Copper Strip Tarnish Test
D 4057 Practice for Manual Sampling of Petroleum and
D 323 Test Method for Vapor Pressure of Petroleum Prod-
Petroleum Products
ucts (Reid Method)
D 4171 Specification for Fuel System Icing Inhibitors
D 357 Method of Test for Knock Characteristics of Motor
3
D 4306 Practice for Aviation Fuel Sample Containers for
Fuels Below 100 Octane Number by the Motor Method
Tests Affected by Trace Contamination
D 381 Test Method for Gum Content in Fuels by Jet
D 4529 Test Method for Estimation of Net Heat of Com-
Evaporation
bustion of Aviation Fuels
D 614 Method of Test for Knock Characteristics of Aviation
3
D 4809 Test Method for Heat of Combustion of Liquid
Fuels by the Aviation Method
Hydrocarbon Fuels by Bomb Calorimeter (Precision
D 873 Test Method for Oxidation Stability of Aviation Fuels
Method)
(Potential Residue Method)
D 4865 Guide for the Generation and Dissipation of Static
D 909 Test Method for Knock Characteristics of Aviation
Electricity in Petroleum Fuel Systems
Gasolines by the Supercharge Method
D 5006 Test Method for Measurement of Fuel System Icing
D 1094 Test Method for Water Reaction of Aviation Fuels
Inhibitors (Ether Type) in Aviation Fuels
D 5059 Test Methods for Lead in Gasoline by X-Ray
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on
Spectroscopy
Petroleum Products and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
D 5190 Test Method for Vapor Pressure of Petroleum Prod-
D02.J0 on Aviation Fuels.
ucts (Automatic Method)
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2003. Published January 2004. Originally
approved in 1947 (replacing former D 615). Last previous edition approved in 2003 D 5191 Test Method for Vapor Pressure of Petroleum Prod-
as D 910–03.
ucts (Mini Method)
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
D 6469 Guide for Microbial Contamination in Fuels and
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Fuel Systems
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website.
3
Withdrawn.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D 910 – 03a
E 29 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to 6.2.1 Tetraethyl Lead, shall be added in the form of an
Determine Conformance with Specifications antiknock mixture containing not less than 61m%of tetraethyl
lead and sufficient ethylene dibromide to provide two bromine
3. Terminology atoms per atom of lead. The balance shall contain no added
ingredients other than kerosine, an approved oxidation inhibi-
3.1 Definitions:
to
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.