ASTM E534-13
(Test Method)Standard Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Sodium Chloride
Standard Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Sodium Chloride
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
3.1 Sodium chloride occurs in nature. It is a necessary article of diet as well as the source for production of many sodium compounds and chlorine. The methods listed in 1.2 provide procedures for analyzing sodium chloride to determine if it is suitable for its intended use.
SCOPE
1.1 These test methods cover the chemical analyses usually required for sodium chloride.
1.2 The analytical procedures appear in the following sections:
Section
Sample Preparation
5 to 9
Moisture
10 to 16
Water Insolubles
17 to 24
Calcium and Magnesium
25 to 31
Sulfate
32 to 38
Reporting of Analyses
39 to 41
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.5 Review the current material safety data sheets (MSDS) for detailed information concerning toxicity, first-aid procedures, handling, and safety precautions.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: E534 − 13
Standard Test Methods for
1
Chemical Analysis of Sodium Chloride
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E534; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* 3. Significance and Use
1.1 These test methods cover the chemical analyses usually 3.1 Sodium chloride occurs in nature. It is a necessary
required for sodium chloride.
article of diet as well as the source for production of many
sodium compounds and chlorine. The methods listed in 1.2
1.2 The analytical procedures appear in the following sec-
provideproceduresforanalyzingsodiumchloridetodetermine
tions:
if it is suitable for its intended use.
Section
Sample Preparation 5 to 9
Moisture 10 to 16
4. Reagents
Water Insolubles 17 to 24
Calcium and Magnesium 25 to 31 4.1 Purity of Reagents—Unless otherwise indicated, it is
Sulfate 32 to 38
intended that all reagents should conform to the specifications
Reporting ofAnalyses 39 to 41
of the Committee on Analytical Reagents of the American
4
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
Chemical Society, where such specifications are available.
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
4.2 Purity of Water—Unless otherwise indicated, references
standard.
to water shall be understood to mean Type II or III reagent
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
water conforming to Specification D1193.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
SAMPLE PREPARATION
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
5. Scope
1.5 Review the current material safety data sheets (MSDS)
5.1 Thistestmethodcoverspreparationofasamplethatwill
for detailed information concerning toxicity, first-aid
be as representative as possible of the entire bulk quantity.The
procedures, handling, and safety precautions.
results of any analysis pertain only to the sample used.
2. Referenced Documents
6. Apparatus
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
6.1 Coarse Grinder.
D1193Specification for Reagent Water
6.2 High-Speed Blender.
E180Practice for Determining the Precision of ASTM
Methods for Analysis and Testing of Industrial and Spe-
6.3 Oven.
3
cialty Chemicals (Withdrawn 2009)
6.4 Riffle Sampler.
E200Practice for Preparation, Standardization, and Storage
of Standard and Reagent Solutions for ChemicalAnalysis
6.5 Scale.
7. Reagents
1
These test methods are under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D16 on
7.1 Hydrochloric Acid, Standard (1 meq/mL HCl)—Prepare
Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Related Chemicals and are under the direct responsi-
and standardize in accordance with Practice E200.
bility of Subcommittee D16.16 on Industrial and Specialty Product Standards.
Current edition approved June 1, 2013. Published September 2013. Originally
approved in 1975. Last previous edition approved in 2008 as E534–08. DOI:
10.1520/E0534-13.
2 4
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or Reagent Chemicals, American Chemical Society Specifications, American
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Chemical Society, Washington, DC. For suggestions on the testing of reagents not
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on listed by the American Chemical Society, see Analar Standards for Laboratory
the ASTM website. Chemicals, BDH Ltd., Poole, Dorset, U.K., and the United States Pharmacopeia
3
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on and National Formulary, U.S. Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. (USPC), Rockville,
www.astm.org. MD.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright ©ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E534 − 13
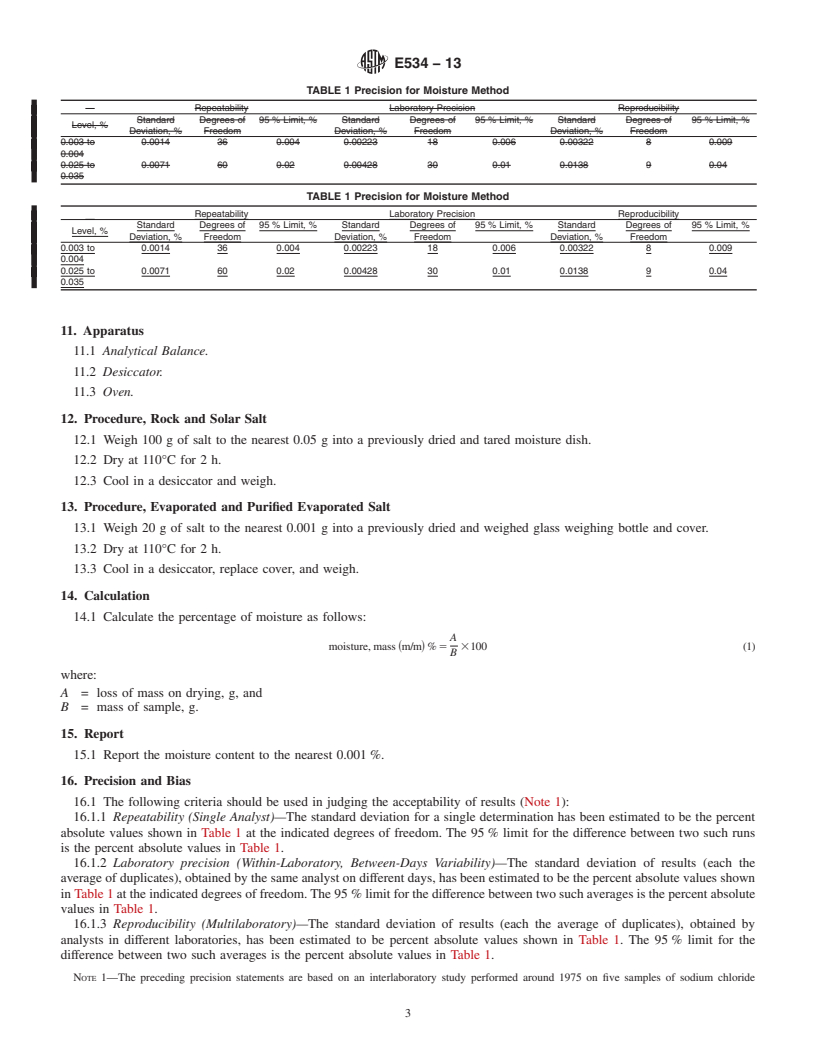
TABLE 1 Precision for Moisture Method
Repeatability Laboratory Precision Reproducibility
Standard Degrees of 95% Limit, % Standard Degrees of 95% Limit, % Standard Degrees of 95% Limit, %
Level, %
Deviation, % Freedom Deviation, % Freedom Deviation, % Freedom
0.003 to 0.0014 36 0.004 0.00223 18 0.006 0.00322 8 0.009
0.004
0.025 to 0.0071 60 0.02 0.00428 30 0.01 0.0138 9 0.04
0.035
8. Rock and Solar Salt Stock Solutions 12.3 Cool in a desiccator and weigh.
8.1 Mix and split sample to 500g, using the riffle sampler.
13. Procedure, Evaporated and Purified Evaporated Salt
8.2 If sample appears wet, dry at 110°C for 2h.
13.1 Weigh 20 g of salt to the nearest 0.001 g i
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: E534 − 08 E534 − 13
Standard Test Methods for
1
Chemical Analysis of Sodium Chloride
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E534; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*
1.1 These test methods cover the chemical analyses usually required for sodium chloride.
1.2 The analytical procedures appear in the following sections:
Section
Sample Preparation 5 to 9
Moisture 10 to 16
Water Insolubles 17 to 24
Calcium and Magnesium 25 to 31
Sulfate 32 to 38
Reporting of Analyses 39 to 41
Section
Sample Preparation 5 to 9
Moisture 10 to 16
Water Insolubles 17 to 24
Calcium and Magnesium 25 to 31
Sulfate 32 to 38
Reporting of Analyses 39 to 41
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
1.5 Review the current material safety data sheets (MSDS) for detailed information concerning toxicity, first-aid procedures,
handling, and safety precautions.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
E180 Practice for Determining the Precision of ASTM Methods for Analysis and Testing of Industrial and Specialty Chemicals
3
(Withdrawn 2009)
E200 Practice for Preparation, Standardization, and Storage of Standard and Reagent Solutions for Chemical Analysis
3. Significance and Use
3.1 Sodium chloride occurs in nature in almost unlimited quantities. nature. It is a necessary article of diet as well as the source
for production of many sodium compounds and chlorine. The methods listed in 1.2 provide procedures for analyzing sodium
chloride to determine if it is suitable for its intended use.
1
These test methods are under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E15 on Industrial and Specialty Chemicalsand are under the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
E15.02 on Product Standards.
Current edition approved Dec. 15, 2008June 1, 2013. Published January 2009September 2013. Originally approved in 1975. Last previous edition approved in 20032008
as E534 – 98E534 – 08.(2003). DOI: 10.1520/E0534-08.10.1520/E0534-13.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on www.astm.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E534 − 13
4. Reagents
4.1 Purity of Reagents—Unless otherwise indicated, it is intended that all reagents should conform to the specifications of the
4
Committee on Analytical Reagents of the American Chemical Society, where such specifications are available.
4.2 Purity of Water—Unless otherwise indicated, references to water shall be understood to mean Type II or III reagent water
conforming to Specification D1193.
SAMPLE PREPARATION
5. Scope
5.1 This test method covers preparation of a sample that will be as representative as possible of the entire bulk quantity. The
results of any analysis pertain only to the sample used.
6. Apparatus
6.1 Coarse Grinder.
6.2 High-Speed Blender.
6.3 Oven.
6.4 Riffle Sampler.
6.5 Scale.
7. Reagents
7.1 Hydrochloric Acid, Standard (1 meq/mL HCl)—Prepare and standardize in accordance with Practice E200.
8. Rock and Solar Salt Stock Solutions
8.1 Mix and split sample to 500 g, using the riffle sampler.
8.2 If sample appears wet, dry at 110°C for 2 h.
8.3 Grind the sample to −8 mesh in the coarse grinder.
8.4 Mix ground sample well and weigh out a 25.0-g representative portion for rock salt or 50.0 g for solar salt.
8.5 Place 200 mL of water in the high-speed blender and start at low speed.
8.6 Slowly add the salt sample to the high-speed blender and blend for 5 min.
8.7 Test for water insolubles as described in Sections 17
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.