ASTM D4803-10
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Predicting Heat Buildup in PVC Building Products
Standard Test Method for Predicting Heat Buildup in PVC Building Products
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
Heat buildup in PVC exterior building products due to absorption of the energy from the sun may lead to distortion problems. Heat buildup is affected by the color, emittance, absorptance, and reflectance of a product. Generally, the darker the color of the product, the more energy is absorbed and the greater is the heat buildup. However, even with the same apparent color, the heat buildup may vary due to the specific pigment system involved. The greatest heat buildup generally occurs in the color black containing carbon black pigment. The black control sample used in this test method contains 2.5 parts of furnace black per 100 parts of PVC suspension resin. The maximum temperature rise above ambient temperature for this black is 90°F (50°C) for a 45° or horizontal surface when the sun is perpendicular to the surface and 74°F (41°C) for a vertical surface assuming that the measurements were done on a cloudless day with no wind and heavy insulation on the back of the specimen. See Appendix X1.
This test method allows the measurement of the temperature rise under a specific type heat lamp, relative to that of a black reference surface, thus predicting the heat buildup due to the sun's energy.
The test method allows prediction of heat buildup of various colors or pigment systems, or both.
This test method gives a relative heat buildup compared to black under certain defined severe conditions but does not predict actual application temperatures of the product. These will also depend on air temperature, incident angle of the sun, clouds, wind velocity, insulation, installation behind glass, etc.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers prediction of the heat buildup in rigid and flexible PVC building products above ambient air temperature, relative to black, which occurs due to absorption of the sun's energy.
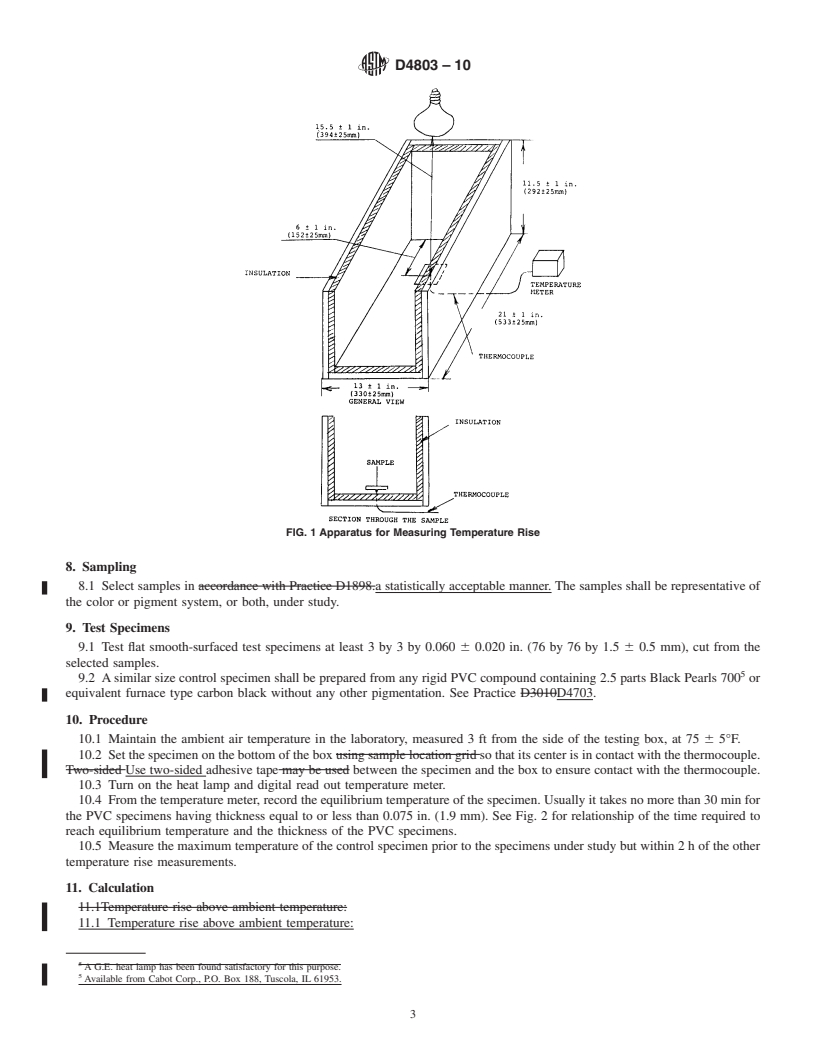
Note 1—This test method is expected to be applicable to all types of colored plastics. The responsible subcommittee intends to broaden the scope beyond PVC when data on other materials is submitted for review.
Note 2—There are no ISO standards covering the primary subject matter of this test method.
1.2 Rigid PVC exterior profile extrusions for assembled windows and doors are covered in Specification D4726.
1.3 Rigid PVC exterior profiles for fencing are covered in Specification F964.
1.4 Rigid PVC siding profiles are covered in Specification D3679.
1.5 Rigid PVC soffit profiles are covered in Specification D4477.
1.6 Rigid PVC and Rigid CPVC plastic building products compounds are covered in Specification D4216.
1.7 The text of this test method references notes and footnotes which provide explanatory material. These notes and footnotes (excluding those in tables and figures) shall not be considered as requirements of this test method.
1.8 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard.
1.9 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific safety hazard statements are given in Section 7.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D4803 − 10 An American National Standard
Standard Test Method for
1
Predicting Heat Buildup in PVC Building Products
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D4803; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* 2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
1.1 Thistestmethodcoverspredictionoftheheatbuildupin
D883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
rigid and flexible PVC building products above ambient air
D1600 Terminology forAbbreviatedTerms Relating to Plas-
temperature, relative to black, which occurs due to absorption
tics
of the sun’s energy.
D4703 Practice for Compression Molding Thermoplastic
NOTE 1—This test method is expected to be applicable to all types of
Materials into Test Specimens, Plaques, or Sheets
colored plastics. The responsible subcommittee intends to broaden the
D3679 Specification for Rigid Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC)
scope beyond PVC when data on other materials is submitted for review.
Siding
NOTE 2—There are no ISO standards covering the primary subject
D4216 Specification for Rigid Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC)
matter of this test method.
and Related PVC and Chlorinated Poly(Vinyl Chloride)
1.2 Rigid PVC exterior profile extrusions for assembled
(CPVC) Building Products Compounds
windows and doors are covered in Specification D4726.
D4477 Specification for Rigid (Unplasticized) Poly(Vinyl
Chloride) (PVC) Soffit
1.3 Rigid PVC exterior profiles for fencing are covered in
D4726 Specification for Rigid Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC)
Specification F964.
Exterior-Profile Extrusions Used forAssembled Windows
1.4 Rigid PVC siding profiles are covered in Specification
and Doors
D3679. E631 Terminology of Building Constructions
F964 Specification for Rigid Poly (Vinyl Chloride) (PVC)
1.5 Rigid PVC soffit profiles are covered in Specification
Exterior Profiles Used for Fencing and Railing
D4477.
3. Terminology
1.6 Rigid PVC and Rigid CPVC plastic building products
compounds are covered in Specification D4216. 3.1 Definitions—Definitions are in accordance with Termi-
nologies D883 or E631 and abbreviations with Terminology
1.7 The text of this test method references notes and
D1600 unless otherwise indicated.
footnotes which provide explanatory material. These notes and
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
footnotes (excluding those in tables and figures) shall not be
3.2.1 heat buildup—the increase in temperature above that
considered as requirements of this test method.
of ambient air due to the amount of energy absorbed by a
1.8 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
specimen from the sun.
as the standard.
3.2.2 temperature rise—the increase in temperature above
1.9 This standard does not purport to address all of the
that of ambient (laboratory) air due to absorption of energy
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
from a heating lamp (source).
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
4. Summary of Test Method
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific safety
4.1 The PVC product (extruded product, injection molded
hazard statements are given in Section 7.
part, or compression molded) is cut apart to obtain a flat test
specimen at least 3 by 3 by 0.060 6 0.020 in. (76 by 76 by 1.5
6 0.5 mm).
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D20 on Plastics
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.24 on Plastic Building
2
Products. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2010. Published January 2011. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
ε1
approved in 1989. Last previous edition approved in 2002 as D4803 - 97 (2002) . Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
DOI: 10.1520/D4803-10. the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D4803 − 10
4.2 The test specimen is heated under the infrared reflective
heat lamp to determine the temperature rise above ambient
(laboratory) temperature relative to a black control sample.
4.3 The temperature rise data, obtained in the laboratory for
a given test specimen, is then used to predict the heat buildup,
which may occur outdoors due to the sun.
5. Significance and Use
5.1 Heat buildup in PVC exterior building produ
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
An American National Standard
´1
Designation:D4803–97 (Reapproved 2002) Designation:D4803–10
Standard Test Method for
1
Predicting Heat Buildup in PVC Building Products
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D4803; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1
´ NOTE—Footnote text inadvertently left out of Table 1 was reinserted editorially in March 2003.
1. Scope*
1.1 This test method covers prediction of the heat buildup in rigid and flexible PVC building products above ambient air
temperature, relative to black, which occurs due to absorption of the sun’s energy.
NOTE 1—This test method is expected to be applicable to all types of colored plastics. The responsible subcommittee intends to broaden the scope
beyond PVC when data on other materials is submitted for review.
NOTE 2—There are no ISO standards covering the primary subject matter of this test method.
1.2 Rigid PVC exterior profile extrusions for assembled windows and doors are covered in Specification D4726.
1.3 Rigid PVC exterior profiles for fencing are covered in Specification F964.
1.4 Rigid PVC siding profiles are covered in Specification D3679.
1.5 Rigid PVC soffit profiles are covered in Specification D4477.
1.6 Rigid PVC and Rigid CPVC plastic building products compounds are covered in Specification D4216.
1.7The1.7 The text of this test method references notes and footnotes which provide explanatory material. These notes and
footnotes (excluding those in tables and figures) shall not be considered as requirements of this test method.
1.8 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard.
1.9 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use. Specific safety hazard statements are given in Section 7.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
D1600 Terminology for Abbreviated Terms Relating to Plastics D1898Practice for Sampling Plastics
0
D3010Practice for Preparing Compression-Molded Test Sample Plaques of Rigid Poly(Vinyl Chloride) Compounds
4703 Practice for Compression Molding Thermoplastic Materials into Test Specimens, Plaques, or Sheets
D3679 Specification for Rigid Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Siding
D4216 Specification for Rigid Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) and Related PVC and Chlorinated Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (CPVC)
Building Products Compounds
D4477 Specification for Rigid (Unplasticized) Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Soffit
D4726 Specification for Rigid Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Exterior-Profile Extrusions Used for Assembled Windows and
Doors
E631 Terminology of Building Constructions
F964 Specification for Rigid Poly (Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Exterior Profiles Used for Fencing and Railing
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions—Definitions are in accordance with Terminologies D883 or E631 and abbreviations with Terminology D1600
unless otherwise indicated.
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D20 on Plastics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.24 on Plastic Building Products.
Current edition approved March 27, 2003. Published March 2003. Originally approved in 1989. Last previous edition approved in 1997 as D4803–97. DOI:
10.1520/D4803-97R02E01.
´1
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2010. Published January 2011. Originally approved in 1989. Last previous edition approved in 2002 as D4803 - 97 (2002) . DOI:
10.1520/D4803-10.
2
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D4803–10
3.2.1 heat buildup—the increase in temperature above that of ambient air due to the amount of energy absorbed by a specimen
from the sun.
3.2.2 temperature rise—the increase in temp
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.