ASTM D1871-04(2010)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Adhesion Between Tire Bead Wire and Rubber
Standard Test Method for Adhesion Between Tire Bead Wire and Rubber
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
To contribute to the mechanical properties required in a product, tire bead wire must have good adhesion to the rubber matrix. This allows the rubber to absorb part of the energy, distributing it uniformly between the reinforcing material and the rubber compound. This test method is considered satisfactory for acceptance testing of commercial shipments of wire since it has been used extensively in the trade for this purpose. This test method may be used for purchase specification requirements or manufacturing control of bead wire.
If there are differences of practical significance between reported test results for two laboratories (or more), comparative tests should be performed to determine if there is a statistical bias between them, using competent statistical assistance. As a minimum, test samples should be used that are as homogeneous as possible, that are drawn from the material from which the disparate test results were obtained, and that are randomly assigned in equal numbers to each laboratory for testing. Other materials with established test values may be used for this purpose. The test results from the two laboratories should be compared using a statistical test for unpaired data, at a probability level chosen prior to the testing series. If a bias is found, either its cause must be found and corrected, or future test results for that material must be adjusted in consideration of the known bias.
The characteristics of single filament steel wires that affect the adhesion property are wire diameter, coating composition, and coating mass. The storage conditions, age, and vulcanization conditions of the rubber compound will affect the test results and must be specified by the supplier of the rubber compound.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method cover procedures for testing the strength of adhesion of single-filament wire to vulcanized rubber compounds. The method applies to, but is not limited to, wire made from brass, bronze, or zinc coated steel wire. The adhesion strength is expressed as the magnitude of the pull-out force for the single filament of wire.
1.2 This test method is applicable to single-filament wires used in reinforced rubber products as single filaments and is normally used to evaluate the adhesion of samples of wire to a standard rubber applied under specified conditions. It is primarily used to evaluate tire bead wire and may be applied, with modifications and by agreement between supplier and customer, to various wire types used in rubber product reinforcing.
1.3 This test method is written in SI units.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. See 6.5.1.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D1871 − 04(Reapproved 2010)
Standard Test Method for
Adhesion Between Tire Bead Wire and Rubber
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D1871; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope D4392 Terminology for Statistically Related Terms (With-
drawn 1993)
1.1 This test method cover procedures for testing the
D6477 Terminology Relating toTire Cord, BeadWire, Hose
strength of adhesion of single-filament wire to vulcanized
Reinforcing Wire, and Fabrics
rubbercompounds.Themethodappliesto,butisnotlimitedto,
E456 Terminology Relating to Quality and Statistics
wire made from brass, bronze, or zinc coated steel wire. The
adhesion strength is expressed as the magnitude of the pull-out
3. Terminology
force for the single filament of wire.
3.1 Definitions:
1.2 This test method is applicable to single-filament wires
3.1.1 Fordefinitionsoftermsrelatingtotirecord,beadwire,
used in reinforced rubber products as single filaments and is
hose wire, and tire cord fabrics, refer to Terminology D6477
normally used to evaluate the adhesion of samples of wire to a
3.1.1.1 The following terms are relevant to this standard:
standard rubber applied under specified conditions. It is pri-
adhesion, curing, holland cloth, hose reinforcing wire, mill
marilyusedtoevaluatetirebeadwireandmaybeapplied,with
grain, rubber, rubber compound, as used in the manufacture of
modifications and by agreement between supplier and
rubber articles, tire bead, tire bead wire, and vulcanization.
customer, to various wire types used in rubber product rein-
3.1.2 For definitions of terms relating to rubber, refer to
forcing.
Terminology D1566
1.3 This test method is written in SI units.
3.1.3 For definitions of terms relating to testing and statis-
tical concepts, refer to Terminology D4392 or
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
E456D4392E456.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
3.1.4 For definitions of other terms related to textiles, refer
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
to Terminology D123.
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. See 6.5.1.
4. Summary of Test Methods
2. Referenced Documents
4.1 The wires are vulcanized into a block or pad of rubber
and the force necessary to pull the wires out of the rubber is
2.1 ASTM Standards:
measured. The direction of pull-out is axial, that is, along the
D76 Specification for Tensile Testing Machines for Textiles
wire.
D123 Terminology Relating to Textiles
D1566 Terminology Relating to Rubber
5. Significance and Use
D2906 Practice for Statements on Precision and Bias for
5.1 To contribute to the mechanical properties required in a
Textiles (Withdrawn 2008)
D3182 PracticeforRubber—Materials,Equipment,andPro- product, tire bead wire must have good adhesion to the rubber
matrix. This allows the rubber to absorb part of the energy,
cedures for Mixing Standard Compounds and Preparing
Standard Vulcanized Sheets distributing it uniformly between the reinforcing material and
the rubber compound. This test method is considered satisfac-
tory for acceptance testing of commercial shipments of wire
Thistest method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D13 on Textiles
since it has been used extensively in the trade for this purpose.
and are the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D13.19 on Industrial Fibers and
Metallic Reinforcements.
This test method may be used for purchase specification
Current edition approved Jan. 1, 2010. Published February 2010. Originallyap-
requirements or manufacturing control of bead wire.
proved in 1961. Last previous edition approved in 2004 D1871 – 04. DOI:
5.1.1 If there are differences of practical significance be-
10.1520/D1871-04R10.
tween reported test results for two laboratories (or more),
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
comparative tests should be performed to determine if there is
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
a statistical bias between them, using competent statistical
the ASTM website.
assistance.As a minimum, test samples should be used that are
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
www.astm.org. as homogeneous as possible, that are drawn from the material
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
D1871 − 04 (2010)
from which the disparate test results were obtained, and that 6.2 Tensile Testing Machine, CRE (Constant-Rate-of-
are randomly assigned in equal numbers to each laboratory for Extension)type,ofsuchcapacityoftheloadcellinusethatthe
testing. Other materials with established test values may be maximum force required to pull out the wires shall not exceed
used for this purpose.The test results from the two laboratories 85 % nor be less than 15 % of the rated capacity. The rate of
should be compared using a statistical test for unpaired data, at travel of the power actuated grip shall be 50 6 5 mm/min, or
a probability level chosen prior to the testing series. If a bias is up to 1506 15 mm/min by agreement between the purchaser
found, either its cause must be found and corrected, or future and the seller. The specifications and methods of calibration
test results for that material must be adjusted in consideration and verification shall conform to Specification D76.
of the known bias. 4
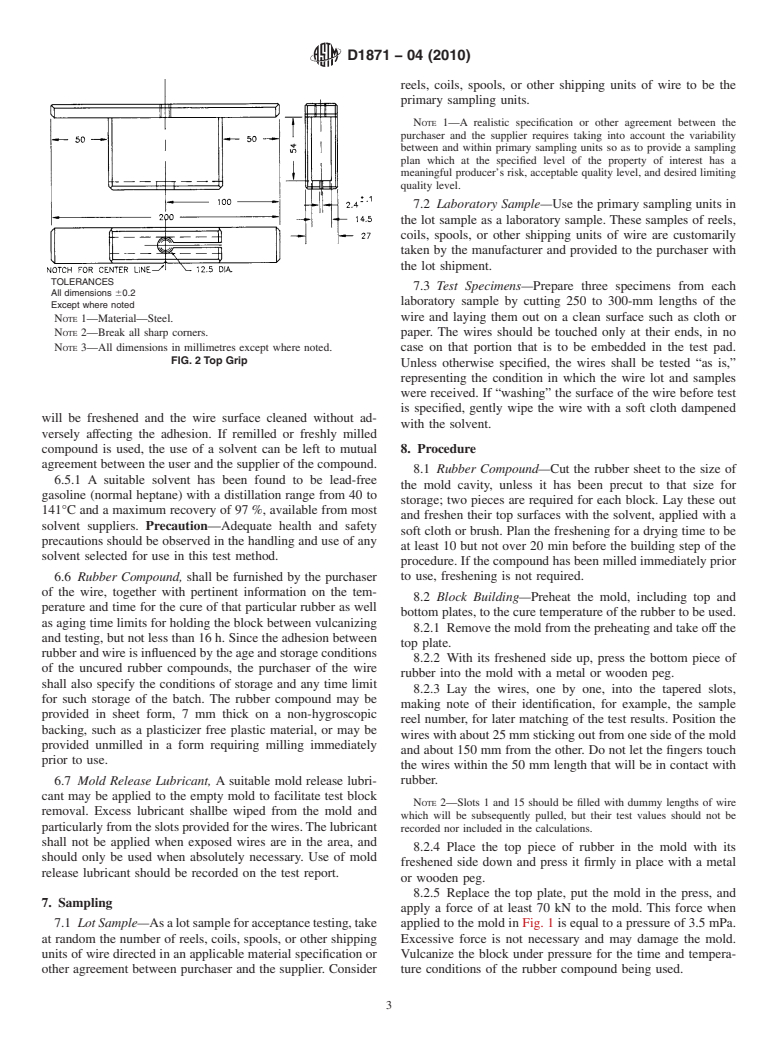
6.3 Top Grip, designed as shown in Fig. 2 shall be a special
5.2 The characteristics of single filament steel wires that holder made for the vulcanized block sample. The bottom grip
affect the adhesion property are wire diameter, coating may be any type clamp of sufficient capacity to handle the
composition, and coating mass. The storage conditions, age, specimen and designed to prevent its slippage in the grip or to
and vulcanization conditions of the rubber compound will prevent premature filament breakage.
affect the test results and must be specified by the supplier of
6.4 Vulcanizing Press, large enough to accommodate the
the rubber compound.
mold, and capable of exerting at least 70 kN total force on the
mold. Electrical or steam heat for the top and bottom platens
6. Apparatus and Materials
shall be provided, of sufficient capacity for maintaining the
6.1 Mold, designed as shown in Fig. 1 for a 12.5-mm thick mold components at a temperature within 3°C of the require-
block of rubber, 200 mm long, and 50 mm wide, with 15
ments for the rubber compound being used.
beveled slots across the width of the mold spaced 12.5 mm
6.5 Solvent, used for the preparation of the rubber and wire
apart at the middle of the mold thickness, and with top and
in this test method shall be such that the surface of the rubber
bottom plates for the mold. If more than five wires break when
testing with the standard mold, the purchaser and the supplier
Series 2710 screw action grips, Series 2716 wedge action grips from Instron
may agree to use a mold cavity that is less than 50 mm wide.
Corp., 2500 Washington St., Canton, MA 02021, and Scott A420 clamps from
GCA/Precision Scientific, 3737 W. Cortland St., Chicago, IL 60647, have been
found practical for testing single filament wire.
Suitable vulcanizing presses are manufactured by Given P-H-I, Pasadena
Presses, 1100 John Reed Court, City of Industry, CA 91745.
Suitable molds and block holder are available from Bartell Machinery Systems
Corp, Rome, NY 13440.
TOLERANCES
All dimensions 60.2
Angular6 ⁄2 °
Except where noted
NOTE 1—Material—Steel.
NOTE 2—Break all sharp corners.
NOTE 3—All dimensions in millimetres except where noted.
FIG. 1 Mold with Top and Bottom Plates
D1871 − 04 (2010)
reels, coils, spools, or other shipping units of wire to be the
primary sampling units.
NOTE 1—A realistic specification or other agreement between the
purchaser and the supplier requires taking into account the variability
between and within primary sampling units so as to provide a sampling
plan which at the specified level of the property of interest has a
meaningful producer’s risk, acceptable quality level, and desired limiting
quality level.
7.2 Laboratory Sample—Use the primary sampling units in
the lot sample as a laboratory sample. These samples of reels,
coils, spools, or other shipping units of wire are customarily
taken by the manufacturer and provided to the purchaser with
the lot shipment.
TOLERANCES
7.3 Test Specimens—Prepare three specimens from each
All dimensions 60.2
laboratory sample by cutting 250 to 300-mm lengths of the
Except where noted
wire and laying them out on a clean surface such as cloth or
NOTE 1—Material—Steel.
NOTE 2—Break all sharp corners. paper. The wires should be touched only at their ends, in no
NOTE 3—All dimensions in millimetres except where noted. case on that portion that is to be embedded in the test pad.
FIG. 2 Top Grip
Unless otherwise specified, the wires shall be tested “as is,”
representing the condition in which the wire lot and samples
were received. If “washing” the surface of the wire before test
is specified, gently wipe the wire with a soft cloth dampened
will be freshened and the wire surface cleaned without ad-
with the solvent.
versely affecting the adhesion. If remilled or freshly milled
compound is used, the use of a solvent can be left to mutual 8. Procedure
agreement between the user and the supplier of the compound.
8.1 Rubber Compound—Cut the rubber sheet to the size of
6.5.1 A suitable solvent has been found to be lead-free
the mold cavity, unless it has been precut to that size for
gasoline (normal heptane) with a distillation range from 40 to
storage; two pieces are required for each block. Lay these out
141°C and a maximum recove
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.