ASTM C1556-11a
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determining the Apparent Chloride Diffusion Coefficient of Cementitious Mixtures by Bulk Diffusion
Standard Test Method for Determining the Apparent Chloride Diffusion Coefficient of Cementitious Mixtures by Bulk Diffusion
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
This test method is applicable to cementitious mixtures that have not been exposed to external chloride ions, other than the negligible quantity of chloride ion exposure from sample preparation using potable water, prior to the test.
The calculation procedure described in this test method is applicable only to laboratory test specimens exposed to a sodium chloride solution as described in this test method. This calculation procedure is not applicable to specimens exposed to chloride ions during cyclic wetting and drying.
Note 1—The diffusion of ionic species in concrete occurs within the fluid-filled pores, cracks and void spaces. The concentration and valence of other ionic species in the pore fluid also influence the rate of chloride diffusion, and therefore, the apparent diffusion coefficient as determined by this test procedure.
In most cases, the value of the apparent chloride diffusion coefficient for cementitious mixtures changes over time (See Note 2). Therefore, apparent diffusion coefficients obtained at early ages may not be representative of performance in service.
Note 2—The rate of change of the apparent diffusion coefficient for cementitious mixtures containing pozzolans or blast-furnace slag is typically different than that for mixtures containing only portland cement.
The apparent chloride diffusion coefficient is used in Fick's second law of diffusion to estimate chloride penetration into cementitious mixtures that are in a saturated condition.
The apparent chloride diffusion coefficient is commonly used in chloride ingress models based on Fick's second law of diffusion. The apparent diffusion coefficient determined by this method includes bound chloride, so proper use of the apparent chloride diffusion coefficient to predict chloride ingress requires consideration of chloride binding.
The resistance to chloride penetration is affected by such factors as the environment, finishing, mixture composition, workmanship, curing, and age.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the laboratory determination of the apparent chloride diffusion coefficient for hardened cementitious mixtures.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: C1556 − 11a
StandardTest Method for
Determining the Apparent Chloride Diffusion Coefficient of
1
Cementitious Mixtures by Bulk Diffusion
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C1556; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* 2.2 NORDTEST Standards:
NT BUILD 443Approved 1995-11, Concrete, Hardened:
1.1 This test method covers the laboratory determination of
3
Accelerated Chloride Penetration (in English)
the apparent chloride diffusion coefficient for hardened cemen-
titious mixtures.
3. Terminology
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
3.1 Definitions:
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
3.1.1 For definitions of terms used in this test method, refer
standard.
to Terminology C125.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
3.2.1 apparent chloride diffusion coeffıcient, D,n—a chlo-
a
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
ride transport parameter calculated from acid-soluble chloride
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
profile data obtained from saturated specimens exposed to
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
chloridesolutions,withoutcorrectionforchloridebinding,that
provides an indication of the ease of chloride penetration into
2. Referenced Documents
cementitious mixtures.
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
3.2.2 chloride binding, v—the chemical process by which
C31/C31MPractice for Making and Curing Concrete Test
chloride ion is removed from solution and incorporated into
Specimens in the Field
cementitious binder hydration products.
C42/C42MTest Method for Obtaining and Testing Drilled
3.2.2.1 Discussion—Chloride binding is primarily associ-
Cores and Sawed Beams of Concrete
ated with hydration products formed by the aluminate phase of
C125Terminology Relating to Concrete and Concrete Ag-
cement and mixtures containing ground granulated blast fur-
gregates
nace slag.
C192/C192MPractice for Making and Curing ConcreteTest
3.2.3 chloride penetration, v—the ingress of chloride ions
Specimens in the Laboratory
due to exposure to external sources.
C670Practice for Preparing Precision and Bias Statements
for Test Methods for Construction Materials 3.2.4 exposure liquid, n—the sodium chloride solution in
C1152/C1152MTest Method for Acid-Soluble Chloride in which test specimens are stored prior to obtaining a chloride
profile.
Mortar and Concrete
C1202Test Method for Electrical Indication of Concrete’s
3.2.5 exposure time, n—the time that the test specimen is
Ability to Resist Chloride Ion Penetration
stored in the solution containing chloride ion.
3.2.6 initial chloride-ion content, C ,n—the ratio of the
i
1
massofchlorideiontothemassofconcreteforatestspecimen
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C09 on
Concrete and ConcreteAggregatesand is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
that has not been exposed to external chloride sources.
C09.66 on Concrete’s Resistance to Fluid Penetration.
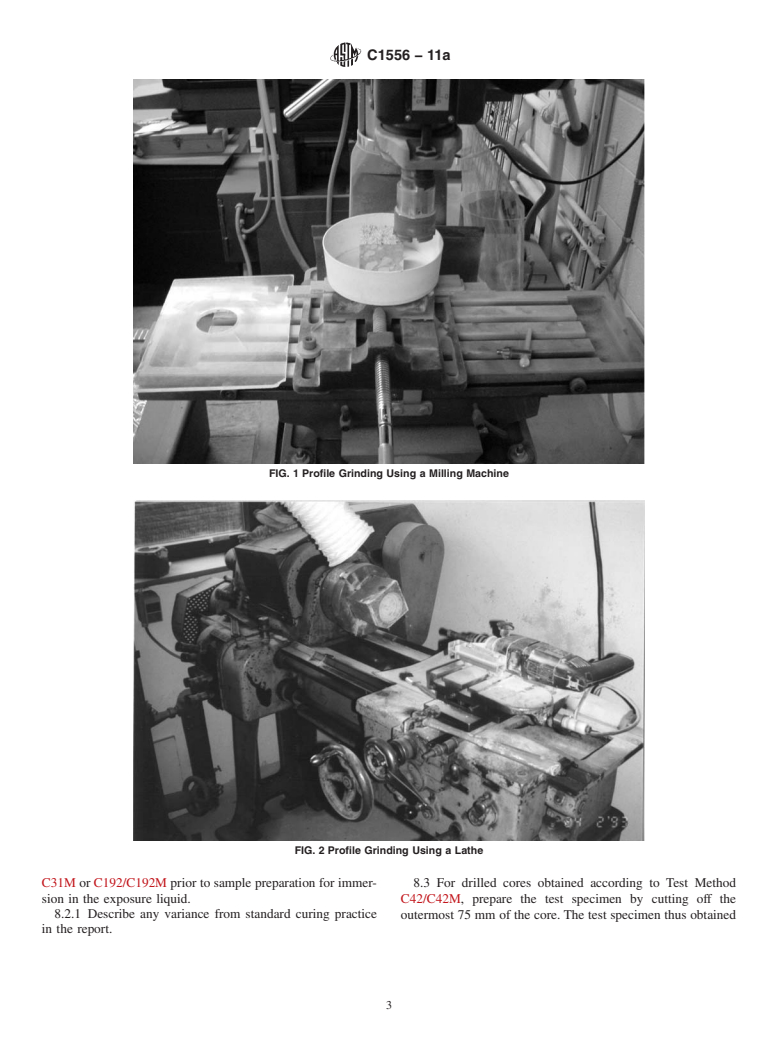
3.2.7 profile grinding, v—the process of grinding off and
Current edition approved Dec. 15, 2011. Published January 2012. Originally
approved in 2003. Last previous edition approved in 2011 as C1556 – 11. DOI: collectingapowdersampleinthinsuccessivelayersfromatest
10.1520/C1556-11A.
specimen using a dry process.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
3
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Published by NORDTEST, P.O. Box 116 FIN-02151 ESPOO Finland, Project
the ASTM website.
1154-94, e-mail: nordtest @vtt.fi, website: http://www.vtt.fi/nordtest
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C1556 − 11a
3.2.8 surface chloride content, C,n—thetheoreticalratioof 6. Apparatus
s
themassofchlorideiontothemassofconcreteattheinterface
6.1 Balance, accurate to at least 60.01 g.
between the exposure liquid and the test specimen.
6.2 Thermometer, accurate to at least 61.0 °C.
4. Summary of Test Method
6.3 Controlled Temperature Laboratory or Chamber. The
4.1 Obtain a representative sample of the cementitious laboratory or chamber shall maintain the temperature of a
mixturepriortoexposuretochlorideion.Separateeachsample
w
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:C1556–11 Designation: C1556 – 11a
Standard Test Method for
Determining the Apparent Chloride Diffusion Coefficient of
1
Cementitious Mixtures by Bulk Diffusion
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C1556; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*
1.1 Thistestmethodcoversthelaboratorydeterminationoftheapparentchloridediffusioncoefficientforhardenedcementitious
mixtures.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
C31/C31M Practice for Making and Curing Concrete Test Specimens in the Field
C42/C42M Test Method for Obtaining and Testing Drilled Cores and Sawed Beams of Concrete
C125 Terminology Relating to Concrete and Concrete Aggregates
C192/C192M Practice for Making and Curing Concrete Test Specimens in the Laboratory
C670 Practice for Preparing Precision and Bias Statements for Test Methods for Construction Materials
C1152/C1152M Test Method for Acid-Soluble Chloride in Mortar and Concrete
C1202 Test Method for Electrical Indication of Concrete’s Ability to Resist Chloride Ion Penetration
2.2 NORDTEST Standards:
3
NT BUILD 443, Approved 1995-11, Concrete, Hardened: Accelerated Chloride Penetration (in English)
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 For definitions of terms used in this test method, refer to Terminology C125.
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.2.1 apparent chloride diffusion coeffıcient, D , n—a chloride transport parameter calculated from acid-soluble chloride profile
a
data obtained from saturated specimens exposed to chloride solutions, without correction for chloride binding, that provides an
indication of the ease of chloride penetration into cementitious mixtures.
3.2.2 chloride binding, v—the chemical process by which chloride ion is removed from solution and incorporated into
cementitious binder hydration products.
3.2.2.1 Discussion—Chloride binding is primarily associated with hydration products formed by the aluminate phase of cement
and mixtures containing ground granulated blast furnace slag.
3.2.3 chloride penetration, v—the ingress of chloride ions due to exposure to external sources.
3.2.4 exposure liquid, n—the sodium chloride solution in which test specimens are stored prior to obtaining a chloride profile.
3.2.5 exposure time, n—the time that the test specimen is stored in the solution containing chloride ion.
3.2.6 initial chloride-ion content, C , n—the ratio of the mass of chloride ion to the mass of concrete for a test specimen that
i
has not been exposed to external chloride sources.
3.2.7 profile grinding, v—the process of grinding off and collecting a powder sample in thin successive layers from a test
specimen using a dry process.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee C09 on Concrete and ConcreteAggregates and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C09.66 on
Concrete’s Resistance to Fluid Penetration.
Current edition approved Oct.Dec. 15, 2011. Published November 2011.January 2012. Originally approved in 2003. Last previous edition approved in 20042011 as
C1556–04.C1556–11. DOI: 10.1520/C1556-11a.
2
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
Published by NORDTEST, P.O. Box 116 FIN-02151 ESPOO Finland, Project 1154-94, e-mail: nordtest @vtt.fi, website: http://www.vtt.fi/nordtest
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C1556 – 11a
3.2.8 surface chloride content, C , n—the theoretical ratio of the mass of chloride ion to the mass of concrete at the interface
s
between the exposure liquid and the test
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.