ASTM F788-13(2018)
(Specification)Standard Specification for Surface Discontinuities of Bolts, Screws, and Studs, Inch and Metric Series
Standard Specification for Surface Discontinuities of Bolts, Screws, and Studs, Inch and Metric Series
ABSTRACT
This specification establishes allowable limits for the various types of surface discontinuities that may occur during the manufacture and processing of bolts, screws, and studs, including heat-treated machine screws, tapping screws, and sems. Types of surface discontinuities are: crack; burst; seam; fold; thread lap; void; tool marks; and gouge and nick. These surface discontinuities shall be inspected in accordance with the specified requirements.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification establishes allowable limits for the various types of surface discontinuities that may occur during the manufacture and processing of bolts, screws, and studs, including heat-treated machine screws, tapping screws, and sems (the washers of screw-washer assemblies are excluded). This specification covers metric series products with nominal diameters of 4 mm and larger and with specified minimum tensile strengths of 420 MPa and higher; and inch series products with nominal diameters of No. 5 (0.1250 in.) and larger and with specified minimum tensile strengths of 60 000 psi and higher.
1.2 When the engineering requirements of the application necessitate control of surface discontinuities on bolts, screws, or studs, the purchaser shall specify conformance to ASTM Specification F788, in the original inquiry and purchase order.
1.2.1 When the engineering requirements of the application necessitate that surface discontinuities on bolts, screws, and studs be controlled within limits closer than those specified in this specification, the purchaser shall specify the applicable limits in the original inquiry and purchase order.
1.3 The allowable limits established in this specification for metric bolts, screws, and studs with nominal diameters from 4 to 24 mm inclusive, are essentially identical with requirements given in ISO 6157/I. There are no ISO standards for surface discontinuities on any inch-series products.
1.4 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:F788 −13 (Reapproved 2018)
Standard Specification for
Surface Discontinuities of Bolts, Screws, and Studs, Inch
1
and Metric Series
ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationF788;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginal
adoptionor,inthecaseofrevision,theyearoflastrevision.Anumberinparenthesesindicatestheyearoflastreapproval.Asuperscript
epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope* ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
1.1 This specification establishes allowable limits for the
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
various types of surface discontinuities that may occur during
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
the manufacture and processing of bolts, screws, and studs,
including heat-treated machine screws, tapping screws, and
2. Referenced Documents
sems (the washers of screw-washer assemblies are excluded).
2
This specification covers metric series products with nominal 2.1 ASTM Standards:
diameters of 4 mm and larger and with specified minimum E340Practice for Macroetching Metals and Alloys
tensile strengths of 420 MPa and higher; and inch series F1470Practice for Fastener Sampling for Specified Me-
products with nominal diameters of No. 5 (0.1250 in.) and chanical Properties and Performance Inspection
larger and with specified minimum tensile strengths of 60000 F1789Terminology for F16 Mechanical Fasteners
3
psi and higher.
2.2 ISO Standard:
ISO6157⁄IFasteners, Surface Discontinuities on Bolts,
1.2 When the engineering requirements of the application
Screws and Studs
necessitate control of surface discontinuities on bolts, screws,
or studs, the purchaser shall specify conformance to ASTM
3. Ordering Information
Specification F788, in the original inquiry and purchase order.
1.2.1 When the engineering requirements of the application
3.1 Orders for bolts, screws, and studs requiring disconti-
necessitate that surface discontinuities on bolts, screws, and
nuity control shall include the following:
studs be controlled within limits closer than those specified in
3.1.1 ASTM designation and date of issue of this specifica-
this specification, the purchaser shall specify the applicable
tion.
limits in the original inquiry and purchase order.
3.1.2 Special requirements, for example, closer discontinu-
ity limits (1.2.1) and inspection sampling plan (6.2).
1.3 The allowable limits established in this specification for
metric bolts, screws, and studs with nominal diameters from 4
4. Types of Surface Discontinuities (see Terminology
to 24 mm inclusive, are essentially identical with requirements
given in ISO6157⁄I. There are no ISO standards for surface F1789 for definitions not provided)
discontinuities on any inch-series products.
4.1 Crack
1.4 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units 4.1.1 Quench Cracks—Typical quench cracks are shown in
Fig. 1. Limits are specified in 5.2.
are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in
4.1.2 Forging Cracks—Typical forging cracks are shown in
each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each
Fig. 2. Limits are specified in 5.3.
system shall be used independently of the other. Combining
values from the two systems may result in non-conformance
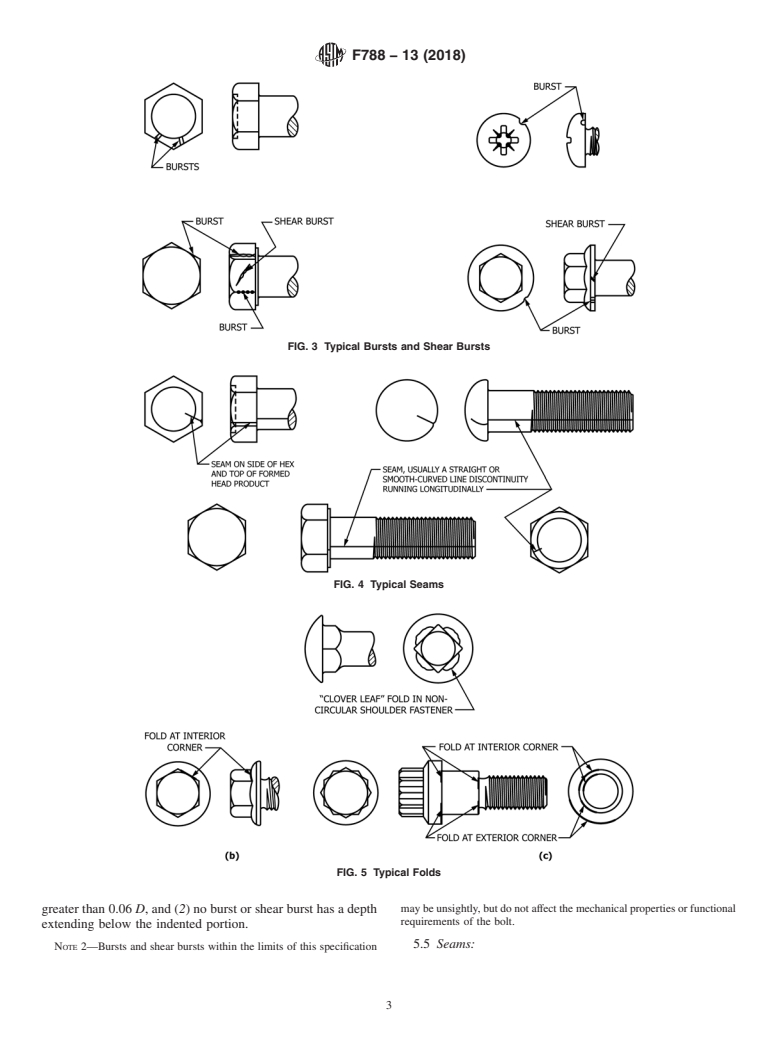
4.2 Burst—Typical bursts are shown in Fig. 3. Limits are
with the standard.
specified in 5.4.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accor-
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F16 on contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Fasteners and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F16.93 on Quality Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Assurance Provisions for Fasteners. the ASTM website.
3
Current edition approved Sept. 1, 2018. Published September 2018. Originally Available from International Organization for Standardization (ISO), ISO
approved in 1982. Last previous edition approved in 2013 as F788–13. DOI: Central Secretariat, BIBC II, Chemin de Blandonnet 8, CP 401, 1214 Vernier,
10.1520/F0788-13R18. Geneva, Switzerland, http://www.iso.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
F788−13 (2018)
FIG. 1 Typical Quench Cracks
5. Allowable Limits
5.1 Letter Definitions—Throughout the following
requirements, D designates the nominal size (bas
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: F788 − 13 F788 − 13 (Reapproved 2018)
Standard Specification for
Surface Discontinuities of Bolts, Screws, and Studs, Inch
1
and Metric Series
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F788; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of original
adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A superscript
epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope*
1.1 This specification establishes allowable limits for the various types of surface discontinuities that may occur during the
manufacture and processing of bolts, screws, and studs, including heat-treated machine screws, tapping screws, and sems (the
washers of screw-washer assemblies are excluded). This specification covers metric series products with nominal diameters of 4
mm and larger and with specified minimum tensile strengths of 420 MPa and higher; and inch series products with nominal
diameters of No. 5 (0.1250 in.) and larger and with specified minimum tensile strengths of 60 000 psi and higher.
1.2 When the engineering requirements of the application necessitate control of surface discontinuities on bolts, screws, or
studs, the purchaser shall specify conformance to ASTM Specification F788, in the original inquiry and purchase order.
1.2.1 When the engineering requirements of the application necessitate that surface discontinuities on bolts, screws, and studs
be controlled within limits closer than those specified in this specification, the purchaser shall specify the applicable limits in the
original inquiry and purchase order.
1.3 The allowable limits established in this specification for metric bolts, screws, and studs with nominal diameters from 4 to
24 mm inclusive, are essentially identical with requirements given in ISO 6157 ⁄I. There are no ISO standards for surface
discontinuities on any inch-series products.
1.4 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each
system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the
two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
E340 Practice for Macroetching Metals and Alloys
F1470 Practice for Fastener Sampling for Specified Mechanical Properties and Performance Inspection
F1789 Terminology for F16 Mechanical Fasteners
3
2.2 ISO Standard:
ISO 6157 ⁄I Fasteners, Surface Discontinuities on Bolts, Screws and Studs
3. Ordering Information
3.1 Orders for bolts, screws, and studs requiring discontinuity control shall include the following:
3.1.1 ASTM designation and date of issue of this specification.
3.1.2 Special requirements, for example, closer discontinuity limits (1.2.1) and inspection sampling plan (6.2).
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F16 on Fasteners and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F16.93 on Quality Assurance
Provisions for Fasteners.
Current edition approved April 1, 2013Sept. 1, 2018. Published April 2013September 2018. Originally approved in 1982. Last previous edition approved in 20122013 as
F788 – 12.F788 – 13. DOI: 10.1520/F0788-13.10.1520/F0788-13R18.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
Available from American National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St., 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.International Organization for
Standardization (ISO), ISO Central Secretariat, BIBC II, Chemin de Blandonnet 8, CP 401, 1214 Vernier, Geneva, Switzerland, http://www.iso.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
F788 − 13 (2018)
4
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.