ASTM D6586-03
(Practice)Standard Practice for the Prediction of Contaminant Adsorption On GAC In Aqueous Systems Using Rapid Small-Scale Column Tests
Standard Practice for the Prediction of Contaminant Adsorption On GAC In Aqueous Systems Using Rapid Small-Scale Column Tests
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
Granular activated carbon (GAC) is commonly used to remove contaminants from water. However if not used properly, GAC can not only be expensive but can at times be ineffective. The development of engineering data for the design of full-scale adsorbers often requires time-consuming and expensive pilot plant studies. This rapid standard practice has been developed to predict adsorption in large-scale adsorbers based upon results from small column testing. In contrast to pilot plant studies, the small-scale column test presented in this practice does not allow for a running evaluation of factors that may affect GAC performance over time. Such factors may include, for example, an increased removal of target compounds by bacterial colonizing GAC3 or long term fouling of GAC caused by inorganic compounds or background organic matter4 . Nevertheless, this practice offers more relevant operational data than isotherm testing without the principal drawbacks of pilot plant studies, namely time and expense; and unlike pilot plant studies, small scale studies can be performed in a laboratory using water sampled from a remote location.
This practice known as the rapid small-scale column test (RSSCT) uses empty bed contact time (EBCT) and hydraulic loading to describe the adsorption process. Mean carbon particle diameter is used to scale RSSCT results to predict the performance of a full-scale adsorber.
This practice can be used to compare the effectiveness of different activated carbons for the removal of contaminants from a common water stream.
SCOPE
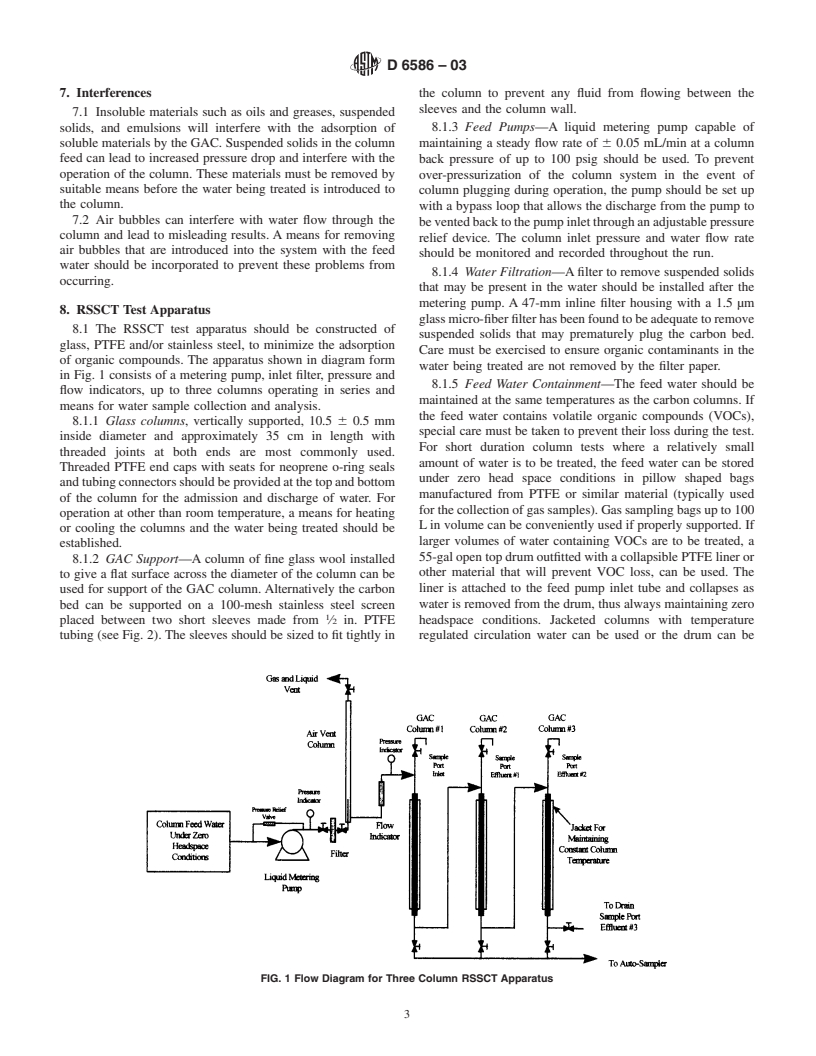
1.1 This practice covers a test method for the evaluation of granular activated carbon (GAC) for the adsorption of soluble pollutants from water. This practice can be used to estimate the operating capacities of virgin and reactivated granular activated carbons. The results obtained from the small-scale column testing can be used to predict the adsorption of target compounds on GAC in a large column or full scale adsorber application.
1.2 This practice can be applied to all types of water including synthetically contaminated water (prepared by spiking high purity water with selected contaminants), potable waters, industrial waste waters, sanitary wastes and effluent waters.
1.3 This practice is useful for the determination of breakthrough curves for specific contaminants in water, the determination of the lengths of the adsorbates mass transfer zones (MTZ) and the prediction of GAC usage rates for larger scale adsorbers.
1.4 The following safety caveat applies to the procedure section, Section 10, of this practice: This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D6586–03
Standard Practice for
the Prediction of Contaminant Adsorption On GAC In
1
Aqueous Systems Using Rapid Small-Scale Column Tests
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 6586; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope D 2862 Test Method Particle Size Distribution of Granular
Activated Carbon
1.1 This practice covers a test method for the evaluation of
granular activated carbon (GAC) for the adsorption of soluble
3. Terminology
pollutants from water.This practice can be used to estimate the
3.1 Definitions:
operating capacities of virgin and reactivated granular acti-
3.1.1 For definitions of terms in this practice relating to
vated carbons. The results obtained from the small-scale
activated carbon, refer to Terminology D 2652.
column testing can be used to predict the adsorption of target
3.1.2 For definitions of terms in this practice relating to
compounds on GAC in a large column or full scale adsorber
water, refer to Terminology D 1129.
application.
1.2 This practice can be applied to all types of water
4. Summary of Practice
including synthetically contaminated water (prepared by spik-
4.1 This practice consists of a method for the rapid deter-
ing high purity water with selected contaminants), potable
mination of breakthrough curves and the prediction of GAC
waters, industrial waste waters, sanitary wastes and effluent
usage rates for the removal of soluble contaminants from
waters.
water.This is accomplished by passing the contaminated water
1.3 This practice is useful for the determination of break-
at a constant controlled rate down flow through a bed of a
through curves for specific contaminants in water, the deter-
specially sized granular activated carbon until predetermined
mination of the lengths of the adsorbates mass transfer zones
levels of breakthrough have occurred.
(MTZ) and the prediction of GAC usage rates for larger scale
4.2 When the assumption is made that conditions of con-
adsorbers.
stant diffusivity exist within the GAC column, the break-
1.4 The following safety caveat applies to the procedure
through data obtained from the column test can be used to
section, Section 10, of this practice: This standard does not
estimate the size and operational conditions for a full-scale
purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated
carbon adsorber.
with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard
to establish appropriate safety and health practices and
5. Significance and Use
determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to
5.1 Granular activated carbon (GAC) is commonly used to
use.
remove contaminants from water. However if not used prop-
erly, GAC can not only be expensive but can at times be
2. Referenced Documents
2 ineffective.Thedevelopmentofengineeringdataforthedesign
2.1 ASTM Standards:
of full-scale adsorbers often requires time-consuming and
D 1129 Terminology Relating to Water
expensive pilot plant studies. This rapid standard practice has
D 1193 Specifications for Reagent Water
been developed to predict adsorption in large-scale adsorbers
D 2652 Terminology Relating to Activated Carbon
based upon results from small column testing. In contrast to
D 2854 Test MethodApparent Density ofActivated Carbon
pilot plant studies, the small-scale column test presented in this
D 2867 Test Method Moisture Content ofActivated Carbon
practice does not allow for a running evaluation of factors that
may affect GAC performance over time. Such factors may
include, for example, an increased removal of target com-
1
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D28 on Activated
3
pounds by bacterial colonizing GAC or long term fouling of
Carbon and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D28. 02 on Liquid PHase
Evaluation. GAC caused by inorganic compounds or background organic
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2003. Published November 2003. Originally
approved in 2000. Last previous edition approved in 2000 as D 6586–00.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
3
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Owen, D.M., Chowdhury, Z.K., Summers, R.S., Hooper, S.M., and Solarik, G.,
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on “Determination of Technology and Costs for GAC Treatment Using the ICR
the ASTM website. Methodology”AWWAGAC & MembraneWorkshop, March 1996, Cincinnati, OH.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United St
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.