ASTM D3273-21
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Resistance to Growth of Mold on the Surface of Interior Coatings in an Environmental Chamber
Standard Test Method for Resistance to Growth of Mold on the Surface of Interior Coatings in an Environmental Chamber
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
3.1 An accelerated test for determining the resistance of interior coatings to mold growth is useful in estimating the performance of coatings designed for use in interior environments that promote mold growth and in evaluating compounds that may inhibit such growth and the aggregate levels for their use (see also Note 1).
3.2 This test method should preferably be used by persons who have had basic microbiological training.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method describes the use of an environmental chamber and operating conditions to evaluate the relative resistance of interior coatings to surface fungal growth in a severe interior environment during a 4-week period.
1.2 This test method can be used to evaluate the comparative resistance of interior coatings to accelerated mold growth. Performance at a certain rating does not imply any specific period of time for a fungal free coating. However, a better rated coating nearly always performs better in actual end use.
Note 1: This test method is intended for the accelerated evaluation of an interior coatings’ resistance to fungal defacement. Use of this test method for evaluating exterior coatings’ performance has not been validated, nor have the limitations for such use been determined. If this test method is to be used for the testing of an exterior coating system, a precautionary statement regarding interpretation of results as being outside of the scope of this test method must be included in the test report. Any accelerated weathering (leaching, weathering machine exposure, etc.) should be reported and should also bear reference to the fact that it is beyond the current scope of this test method.
1.3 Temperature and humidity must be effectively controlled within the relatively narrow limits specified in order for the chamber to function reproducibly during the short test period. Severity and rate of mold growth on a film is a function of the moisture content of both the film and the substrate. A relative humidity of >93 % at a temperature of 32.5 ± 1 °C (90 ± 2 °F ) is necessary to initiate and maintain mold growth and for test panels to develop rapidly and maintain an adequate moisture level to support mold growth.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D3273 − 21
Standard Test Method for
Resistance to Growth of Mold on the Surface of Interior
1
Coatings in an Environmental Chamber
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D3273; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.1 This test method describes the use of an environmental
1.6 This international standard was developed in accor-
chamber and operating conditions to evaluate the relative
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
resistance of interior coatings to surface fungal growth in a
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
severe interior environment during a 4-week period.
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
1.2 This test method can be used to evaluate the compara-
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
tive resistance of interior coatings to accelerated mold growth.
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Performance at a certain rating does not imply any specific
periodoftimeforafungalfreecoating.However,abetterrated
2. Referenced Documents
coating nearly always performs better in actual end use.
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
NOTE 1—This test method is intended for the accelerated evaluation of
E177Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in
an interior coatings’ resistance to fungal defacement. Use of this test
ASTM Test Methods
method for evaluating exterior coatings’ performance has not been
validated, nor have the limitations for such use been determined. If this
E691Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
test method is to be used for the testing of an exterior coating system, a
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
precautionary statement regarding interpretation of results as being
outsideofthescopeofthistestmethodmustbeincludedinthetestreport.
3. Significance and Use
Anyacceleratedweathering(leaching,weatheringmachineexposure,etc.)
should be reported and should also bear reference to the fact that it is
3.1 An accelerated test for determining the resistance of
beyond the current scope of this test method.
interior coatings to mold growth is useful in estimating the
1.3 Temperature and humidity must be effectively con- performance of coatings designed for use in interior environ-
trolled within the relatively narrow limits specified in order for ments that promote mold growth and in evaluating compounds
the chamber to function reproducibly during the short test that may inhibit such growth and the aggregate levels for their
period.Severityandrateofmoldgrowthonafilmisafunction use (see also Note 1).
of the moisture content of both the film and the substrate. A
3.2 This test method should preferably be used by persons
relativehumidityof>93%atatemperatureof32.5 61°C(90
who have had basic microbiological training.
6 2°F ) is necessary to initiate and maintain mold growth and
for test panels to develop rapidly and maintain an adequate
4. Apparatus
moisture level to support mold growth.
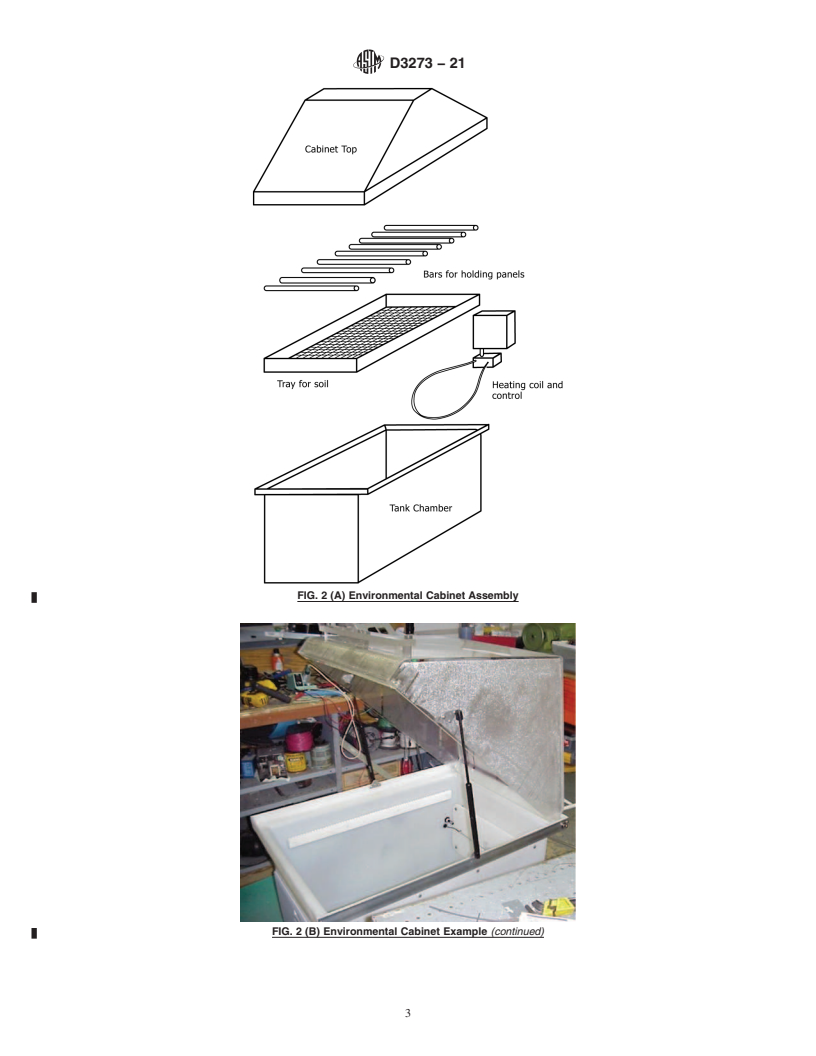
4.1 Environmental Chamber, capable of maintaining a rela-
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
tive humidity of >93% at a temperature of 32.5 6 1°C (90 6
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
2°F) while providing a continuous inoculation of the surface
only.
of the exposed test panels with mold spores. The chamber
3
could be a stand-alone unit that maintains the specified
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
temperature and humidity and can accommodate the sample
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
holding tank (Fig. 1) or an environmental room that fits one or
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
multiple sample holding tanks.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D01 on Paint
2
and Related Coatings, Materials, andApplications and is the direct responsibility of For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Subcommittee D01.28 on Biodeterioration. contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2021. Published December 2021. Originally Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D3273 − 16 D3273 − 21
Standard Test Method for
Resistance to Growth of Mold on the Surface of Interior
1
Coatings in an Environmental Chamber
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D3273; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method describes a small the use of an environmental chamber and theoperating conditions of operation to evaluate
reproducibly in a 4-week period the relative resistance of paint filmsinterior coatings to surface mold fungi, mildew fungal growth
in a severe interior environment. The apparatus is designed so it can be easily built or obtainedenvironment during by any
interested party and will duplicate results obtained in a large tropical chamber.a 4-week period.
1.2 This test method can be used to evaluate the comparative resistance of interior coatingcoatings to accelerated mildewmold
growth. Performance at a certain rating does not imply any specific period of time for a fungal free coating. However, a better rated
coating nearly always performs better in actual end use.
NOTE 1—This test method is intended for the accelerated evaluation of an interior coatings’ resistance to fungal defacement. Use of this test method for
evaluating exterior coatings’ performance has not been validated, nor have the limitations for such use been determined. If this test method is to be used
for the testing of an exterior coating system, a precautionary statement regarding interpretation of results as being outside of the scope of this test method
must be included. included in the test report. Any accelerated weathering (leaching, weathering machine exposure, etc.) should be reported and should
also bear reference to the fact that it is beyond the current scope of this test method.
1.3 Temperature and humidity must be effectively controlled within the relatively narrow limits specified in order for the chamber
to function reproducibly during the short test period. Severity and rate of mold growth on a film is a function of the moisture
content of both the film and the substrate. A relative humidity of 95 6 3 % >93 % at a temperature of 32.5 6 1°C1 °C (90 6
2°F2 °F ) is necessary to initiate and maintain mold growth and for test panels to develop rapidly and maintain an adequate
moisture level to support mold growth.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety safety, health, and healthenvironmental practices and determine the
applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D01 on Paint and Related Coatings, Materials, and Applications and is the direct responsibility of
Subcommittee D01.28 on Biodeterioration.
Current edition approved June 1, 2016Nov. 1, 2021. Published July 2016December 2021. Originally approved in 1973. Last previous edition approved in 20122016 as
ɛ1
D3273D3273 – 16. – 12 . DOI: 10.1520/D3273-16.10.1520/D3273-21.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D3273 − 21
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
E177 Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in ASTM Test Methods
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to Determine the Precision of a Test Method
3. Significance and Use
3.1 An accelerated test for determining the resistance of interior coatings to mold growth is useful in estimating the performance
of coatings designed for use in interior environments that promote mold growth and in evaluating compounds that may inhibit such
growth and the ag
...










Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.