ASTM D4986-03
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Horizontal Burning Characteristics of Cellular Polymeric Materials
Standard Test Method for Horizontal Burning Characteristics of Cellular Polymeric Materials
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
This test method provides a means of measuring the time and extent of burning for cellular polymeric materials. It also provides a means of measuring burning rates for materials that continue to burn past the specified gage marks.
This test method provides a means of comparing the burning characteristics of materials of like thickness density, cell size, and skin irregularities, including the effect of falling particles of cellular polymeric materials. It may be used for quality control, specification acceptance, and for research and development. Such materials may be filled or reinforced, rigid or flexible, cut or formed.
In this test method, the specimens are subjected to one or more specific sets of laboratory fire test exposure conditions. If different test conditions are substituted or if the anticipated end-use conditions are changed, it may not be possible from this test method to predict changes in the performance characteristics measured. Therefore, the results are strictly valid only for the fire test exposure conditions described in this procedure.
This test method is not intended to be a criterion for fire hazard. The fire hazard created by materials depends upon the form and end use of the material. Assessment of fire hazard includes, but is not limited to, many factors such as flame spread, burning rate, ease of ignition, fuel contribution, heat evolution, products of combustion, and others.
SCOPE
1.1 This fire-test-response test method describes a small-scale horizontally oriented burning test procedure for comparing the relative rate of burning and the extent and time of burning of cellular polymeric materials having a density less than 250 kg/m3.
1.2 The classification system described in the Appendix X1 is intended for quality assurance and the preselection of component materials for products.
1.3 This standard measures and describes the response of materials, products, or assemblies to heat and flame under controlled conditions, but does not by itself incorporate all factors required for fire hazard or fire risk assessment of the materials, products, or assemblies under actual fire conditions.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For a specific hazard statement, see Note 3.
Note 1—This test method and ISO 9772 are technically equivalent.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: D4986 – 03
Standard Test Method for
Horizontal Burning Characteristics of Cellular Polymeric
1
Materials
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D4986; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* (Square Opening Series) (Discontinued 2000) Replaced by
3
E 2016
1.1 This fire-test-response test method describes a small-
2.2 ISO Standard:
scale horizontally oriented burning test procedure for compar-
ISO 9772 Cellular Plastics—Determination of Horizontal
ing the relative rate of burning and the extent and time of
Burning Characteristics of Small Specimens Subjected to
burning of cellular polymeric materials having a density less
4
3
a Small Flame
than 250 kg/m .
1.2 The classification system described in theAppendix X1
3. Terminology
is intended for quality assurance and the preselection of
3.1 Definitions—Fordefinitionsoffire-relatedtermsusedin
component materials for products.
this test method, refer to Terminology E176.
1.3 This standard measures and describes the response of
3.2 afterflame time, n—the length of time for which a
materials, products, or assemblies to heat and flame under
material continues to flame, under specified conditions, after
controlled conditions, but does not by itself incorporate all
the ignition source has been removed.
factors required for fire hazard or fire risk assessment of the
3.3 afterglow time, n—the length of time for which a
materials, products, or assemblies under actual fire conditions.
materialcontinuestoglowunderspecifiedtestconditions,after
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
the ignition source has been removed or cessation of flaming,
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
or both.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
3.4 flame, vb—to undergo combustion in the gaseous phase
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
with emission of light.
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. For a specific
3.5 glow, n—visible light, other than from flaming, emitted
hazard statement, see Note 3.
by a solid undergoing combustion.
NOTE 1—This test method and ISO 9772 are technically equivalent.
4. Summary of Test Method
2. Referenced Documents
4.1 This test method for measuring the burning characteris-
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
tics of cellular polymeric materials employs a small standard
D4483 Practice for Evaluating Precision for Test Method
test specimen 50 by 150 mm. The specimen is supported
Standards in the Rubber and Carbon Black Manufacturing
horizontally. One end is exposed to a specified gas flame for 60
Industries
s and the extent of burning is measured.
D5025 Specification for Laboratory Burner Used for Small-
Scale Burning Tests on Plastic Materials 5. Significance and Use
E176 Terminology of Fire Standards
5.1 This test method provides a means of measuring the
E437 Specification for Industrial Wire Cloth and Screens
time and extent of burning for cellular polymeric materials. It
also provides a means of measuring burning rates for materials
that continue to burn past the specified gage marks.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D20 on Plastics
5.2 This test method provides a means of comparing the
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.30 on Thermal Properties.
Current edition approved May 10, 2003. Published July 2003. Originally burning characteristics of materials of like thickness density,
approved in 1989. Last previous edition approved in 1998 as D4986 – 98. DOI:
10.1520/D4986-03.
2 3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or Withdrawn. The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM on www.astm.org.
4
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available fromAmerican National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St.,
the ASTM website. 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D4986 – 03
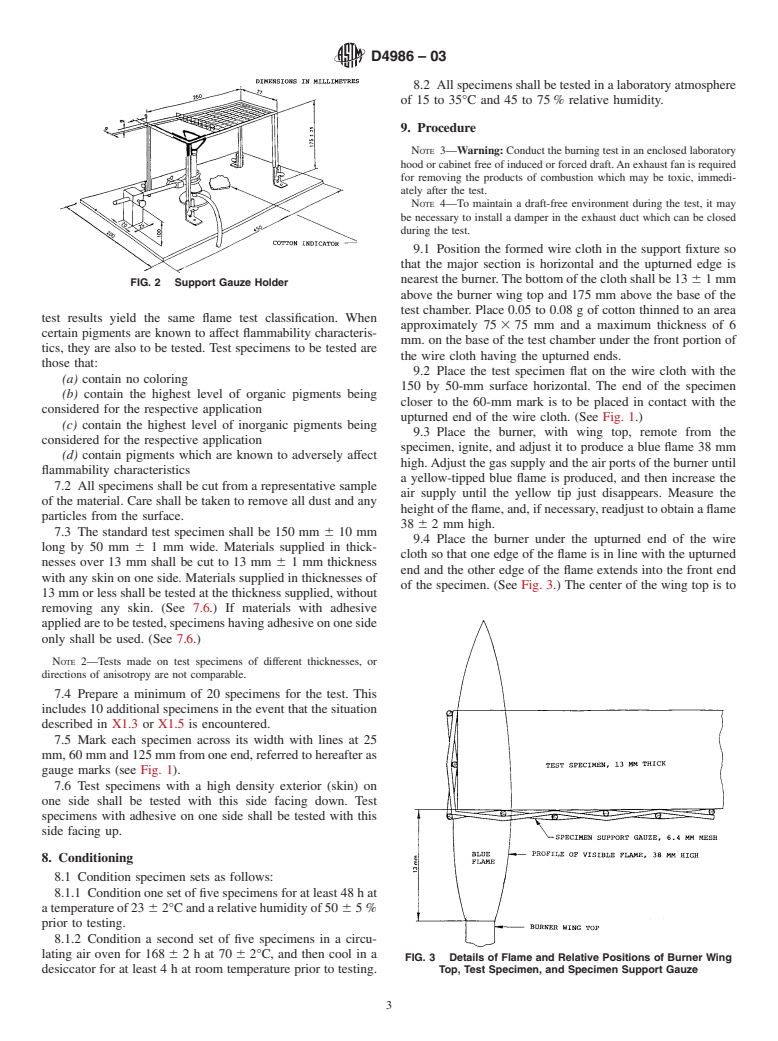
cell size, and skin irregularities, including the effect of falling 6.5 Wire Cloth—Low-carbon, plain, steel wire, 6.4-mm
particles of cellular polymeric materials. It may be used for mesh of 0.90 6 0.05-mm wire diameter. The cloth mesh and
quality control, specification acceptance, and for research and wire diameter shall be determined
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.