ASTM D5200-92(1997)e1
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determination of Weight Percent Volatile Content of Solvent-Borne Paints in Aerosol Cans
Standard Test Method for Determination of Weight Percent Volatile Content of Solvent-Borne Paints in Aerosol Cans
SCOPE
1.1 This test method is for the determination of the weight percent volatile organic compounds of solvent-borne paints in aerosol cans. It offers a unique way to obtain paint specimens from aerosol cans.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. A specific hazard statement is given in Note 1.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
e1
Designation: D 5200 – 92 (Reapproved 1997)
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR TESTING AND MATERIALS
100 Barr Harbor Dr., West Conshohocken, PA 19428
Reprinted from the Annual Book of ASTM Standards. Copyright ASTM
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Weight Percent Volatile Content of Solvent-
Borne Paints in Aerosol Cans
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 5200; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
e NOTE—Editorial changes were made in the footnotes in September 1997.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method is for the determination of the weight
percent volatile organic compounds of solvent-borne paints in
aerosol cans. It offers a unique way to obtain paint specimens
from aerosol cans.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. A specific hazard
statement is given in Note 1.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
E 145 Specification for Gravity-Convection and Forced-
Ventilation Ovens
E 180 Practice for Determining the Precision of ASTM
Methods for Analysis and Testing of Industrial Chemicals
2.2 Other Standard:
Method 35 Determination of Percent Volatile Organic Com-
pounds (VOC) in Solvent Based Aerosol Paints
3. Summary of Test Method
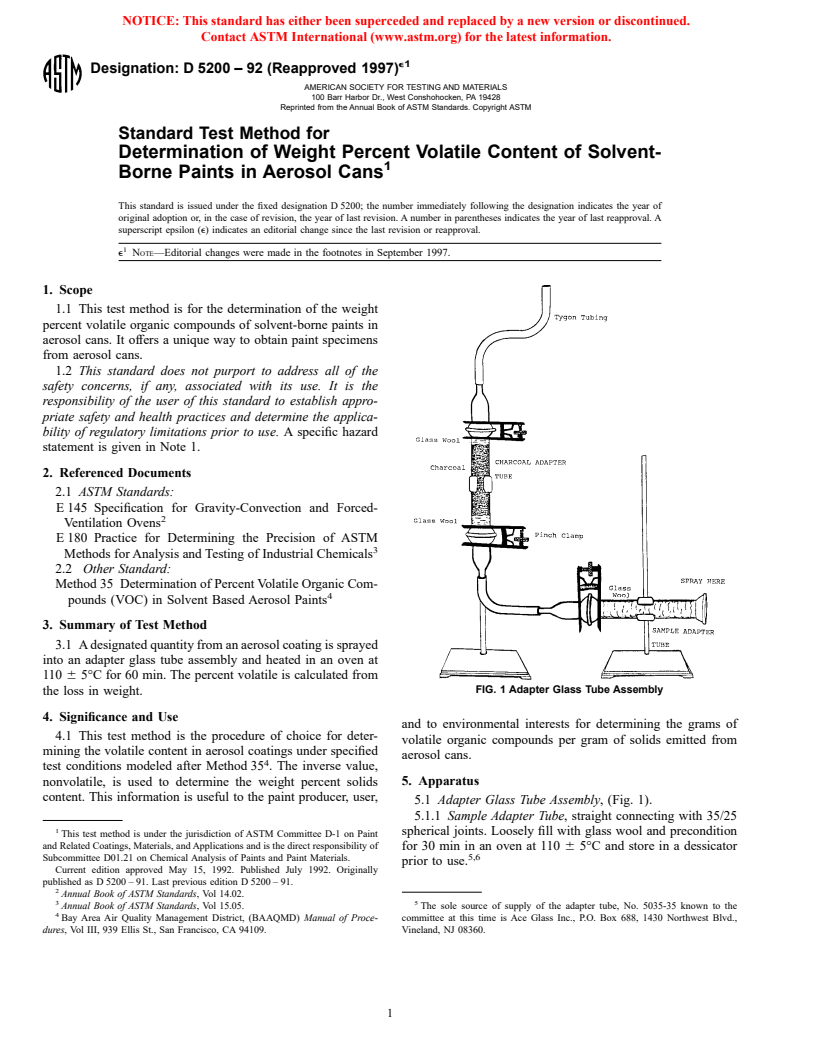
3.1 A designated quantity from an aerosol coating is sprayed
into an adapter glass tube assembly and heated in an oven at
110 6 5°C for 60 min. The percent volatile is calculated from
FIG. 1 Adapter Glass Tube Assembly
the loss in weight.
4. Significance and Use
and to environmental interests for determining the grams of
4.1 This test method is the procedure of choice for deter-
volatile organic compounds per gram of solids emitted from
mining the volatile content in aerosol coatings under specified
aerosol cans.
test conditions modeled after Method 35 . The inverse value,
5. Apparatus
nonvolatile, is used to determine the weight percent solids
content. This information is useful to the paint producer, user,
5.1 Adapter Glass Tube Assembly, (Fig. 1).
5.1.1 Sample Adapter Tube, straight connecting with 35/25
spherical joints. Loosely fill with glass wool and precondition
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D-1 on Paint
and Related Coatings, Materials, and Applications and is the direct responsibility of for 30 min in an oven at 110 6 5°C and store in a dessicator
,
5 6
Subcommittee D01.21 on Chemical Analysis of Paints and Paint Materials.
prior to use.
Current edition approved May 15, 1992. Published July 1992. Originally
published as D 5200 – 91. Last previous edition D 5200 – 91.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 14.02.
3 5
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 15.05. The sole source of supply of the adapter tube, No. 5035-35 known to the
Bay Area Air Quality Management District, (BAAQMD) Manual of Proce- committee at this time is Ace Glass Inc., P.O. Box 688, 1430 Northwest Blvd.,
dures, Vol III, 939 Ellis St., San Francisco, CA 94109. Vineland, NJ 08360.
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
D 5200
6.5 Weigh the aerosol can with the actuator to the nearest
0.01 g. Spray 3 to5gof aerosol into the adapter tube assembly,
spreading out the coating by moving the extension tube around
the wall of the adapter tube. The spraying is done with the
vacuum on.
6.6 Obtain the specimen weight by difference by weighing
the aerosol can again to 0.01 g after spraying out the specimen.
6.7 Place the sample adapter tube in the drying oven for 60
min at 110 6 5°C.
NOTE 1—Warning: Provide adequate ventilation, consistent with ac-
FIG. 2 Aerosol Can on Eberbach Shaker
cepted laboratory practice, to prevent solvent vapors from accumulating to
a dangerous level.
5.1.2 Charcoal Adapter Tube, straight connecting with
6.8 Remove the adapter tubes from the oven, place imme-
35/25 spherical joints. Fill with activated charcoal and plug
diately in a dessicator, cool to ambient temperature, and weigh
both ends with glass wool. This tube is used to prevent the
to 0.01 g.
,
6 7
solvent vapors from contaminating the vacuum pump.
6,8
7. Calculations
5.1.3 Adapters, connecting hose with 35/25 socket joints.
,
6 9
...






Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.