ASTM F2213-04
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Measurement of Magnetically Induced Torque on Passive Implants in the Magnetic Resonance Environment
Standard Test Method for Measurement of Magnetically Induced Torque on Passive Implants in the Magnetic Resonance Environment
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the measurement of the magnetically induced torque produced by the static magnetic field in the magnetic resonance environment on medical devices and the comparison of that torque to the equivalent torque applied by the gravitational force to the implant.
1.2 This test method does not address other possible safety issues which include but are not limited to issues of magnetically induced force due to spatial gradients in the static magnetic field, RF heating, induced heating, acoustic noise, interaction among devices, and the functionality of the device and the MR system.
1.3 The torque considered here is the magneto-static torque due to the interaction of the MRI static magnetic field with the magnetization in the implant. The dynamic torque due to interaction of the static field with eddy currents induced in a rotating device is not addressed in this test method. Currents in lead wires may induce a torque as well.
1.4 The sensitivity of the torque measurement apparatus must be greater than 1/10 the "gravity torque," the product of the device's maximum linear dimension and its weight.
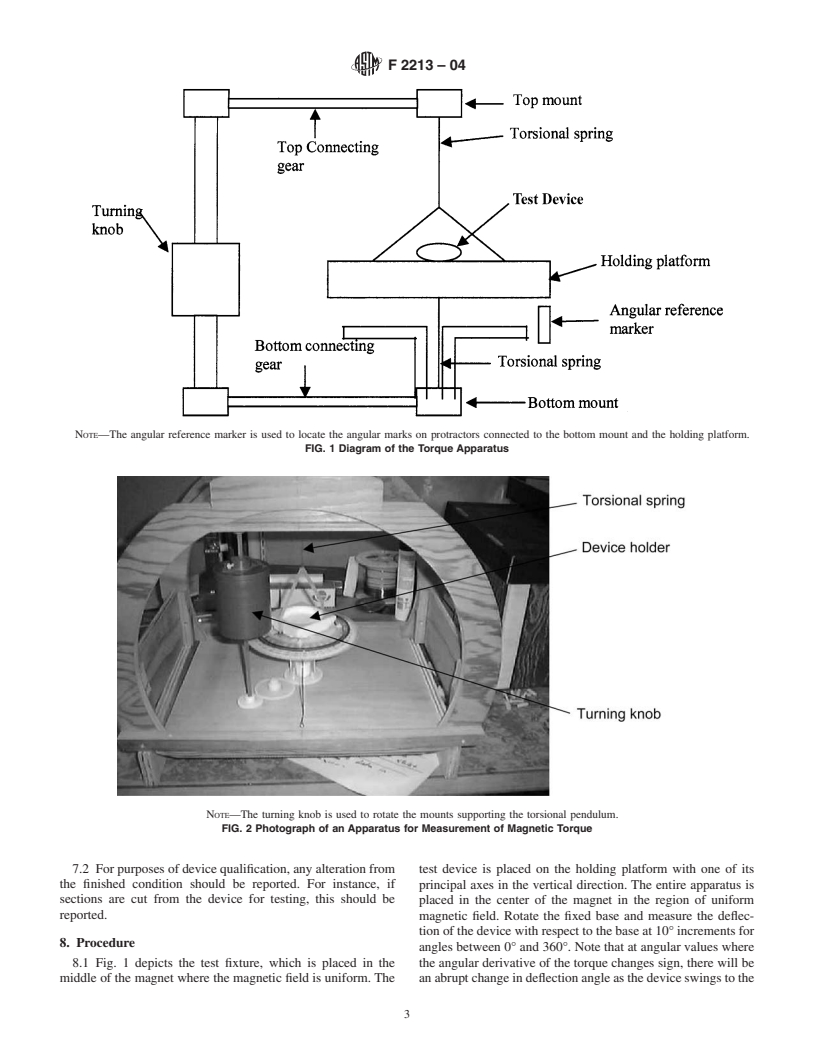
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: F 2213 – 04
Standard Test Method for
Measurement of Magnetically Induced Torque on Medical
1
Devices in the Magnetic Resonance Environment
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F 2213; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope F 2052 Test Method for Measurement of Magnetically In-
duced Displacement Force on Medical Devices in the
1.1 This test method covers the measurement of the mag-
Magnetic Resonance Environment
netically induced torque produced by the static magnetic field
F 2119 Test Method for Evaluation of MR Image Artifacts
inthemagneticresonanceenvironmentonmedicaldevicesand
from Passive Implants
the comparison of that torque to the equivalent torque applied
F 2182 Test Method for Measurement of Radio Frequency
by the gravitational force to the implant.
Induced Heating Near Passive Implants During Magnetic
1.2 This test method does not address other possible safety
Resonance Imaging
issues which include but are not limited to issues of magneti-
2.2 IEC Standard:
cally induced force due to spatial gradients in the static
60601-2-33 Ed. 2.0 Medical Electrical Equipment—Part 2:
magnetic field, RF heating, induced heating, acoustic noise,
Particular Requirements for the Safety of Magnetic Reso-
interaction among devices, and the functionality of the device
3
nance Equipment for Medical Diagnosis, 2002
and the MR system.
1.3 The torque considered here is the magneto-static torque
3. Terminology
due to the interaction of the MRI static magnetic field with the
3.1 Definitions—For the purposes of this test method, the
magnetization in the implant. The dynamic torque due to
definitions in 3.1.1-3.1.18 shall apply:
interaction of the static field with eddy currents induced in a
3.1.1 diamagnetic material—a material whose relative per-
rotating device is not addressed in this test method. Currents in
meability is less than unity.
lead wires may induce a torque as well.
3.1.2 ferromagnetic material—a material whose magnetic
1.4 The sensitivity of the torque measurement apparatus
1 moments are ordered and parallel producing magnetization in
mustbegreaterthan ⁄10the“gravitytorque,”theproductofthe
one direction.
device’s maximum linear dimension and its weight.
3.1.3 magnetic induction or magnetic flux density (B in
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
T)—that magnetic vector quantity which at any point in a
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
magnetic field is measured either by the mechanical force
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
experiencedbyanelementofelectriccurrentatthepoint,orby
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
the electromotive force induced in an elementary loop during
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
any change in flux linkages with the loop at the point. The
2. Referenced Documents magnetic induction is frequently referred to as the magnetic
2
field. B isthestaticfieldinanMRsystem.Plaintypeindicates
0
2.1 ASTM Standards:
a scalar (for example, B) and bold type indicates a vector (for
A 340 Terminology of Symbols and Definitions Relating to
example,B).
Magnetic Testing
3.1.4 magnetic field strength (H in A/m)—strength of the
F 1542 Specification for the Requirements and Disclosure
applied magnetic field.
of Self-Closing Aneurysm Clips
3.1.5 magnetic resonance (MR)—resonant absorption of
electromagnetic energy by an ensemble of atomic particle
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee F04 on Medical situated in a magnetic field.
and Surgical Materials and Devices and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
3.1.6 magnetic resonance diagnostic device—a device in-
F04.15 on Material Test Methods.
tended for general diagnostic use to present images which
Current edition approved Jan. 1, 2004. Published February 2004. Originally
approved in 2002. Last previous edition approved in 2002 as F 2213 – 02.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
3
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available from the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), 3 rue de
the ASTM website. Varembe, Case postale 131, CH-1211, Geneva 20, Switzerland.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
F2213–04
reflectthespatialdistributionormagneticresonancespectra,or measurement of
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.