ASTM E2712-22
(Test Method)Standard Test Methods for Bulge-Forming Superplastic Metallic Sheet
Standard Test Methods for Bulge-Forming Superplastic Metallic Sheet
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 When a superplastic material is regularly being used in industrial production, it is often convenient to use the bulge test to qualify a batch or heat lot to an acceptance criterion. Comparing these test methods with Test Method E2448, the bulge test does not require a machined test specimen, it is more convenient to perform, and it most closely simulates the multiaxial stresses and strains present in forming parts. These test methods do not measure the intrinsic superplastic properties of a material. Test Method E2448 should be used in that instance.
SCOPE
1.1 These test methods describe procedures for determining the biaxial formability of a test specimen of superplastic metallic sheet in a circular die.
1.2 The intent of these test methods are primarily to be used as tests of superplasticity as measured by the ability to form to a prescribed depth in a die cavity without rupturing. These test methods can also be used to generate material for the measurement of cavitation in the formed part. These can be used as go/no go criteria for qualification to a specification.
1.3 These test methods have been used successfully with aluminum alloys. The use of these test methods on other metals should be verified.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: E2712 − 22
Standard Test Methods for
1
Bulge-Forming Superplastic Metallic Sheet
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E2712; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 3. Terminology
1.1 These test methods describe procedures for determining 3.1 The terms specified temperature and indicated tempera-
the biaxial formability of a test specimen of superplastic ture are used as defined in Terminology E6.
metallic sheet in a circular die.
4. Summary of Test Method
1.2 Theintentofthesetestmethodsareprimarilytobeused
4.1 Twomethodsofbulgeformingareincludedinthesetest
as tests of superplasticity as measured by the ability to form to
methods.
a prescribed depth in a die cavity without rupturing.These test
4.1.1 IntheDomeRuptureTestmethod,thetestspecimenis
methodscanalsobeusedtogeneratematerialforthemeasure-
formed into a die of a fixed depth as prescribed in a specifi-
ment of cavitation in the formed part. These can be used as
cation. If it touches the base of the die without rupturing, then
go/no go criteria for qualification to a specification.
it is considered to have met the specification.
1.3 These test methods have been used successfully with
4.1.2 In the Cavitation Test method, the depth of the die is
aluminumalloys.Theuseofthesetestmethodsonothermetals
reducedsothatthematerialfillsthedie.Aportionexcisedfrom
should be verified.
the center of the formed part may be examined for internal
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
cavitation within the test specimen.
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
5. Significance and Use
standard.
5.1 When a superplastic material is regularly being used in
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
industrialproduction,itisoftenconvenienttousethebulgetest
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
to qualify a batch or heat lot to an acceptance criterion.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
Comparing these test methods with Test Method E2448, the
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
bulgetestdoesnotrequireamachinedtestspecimen,itismore
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
convenient to perform, and it most closely simulates the
1.6 This international standard was developed in accor-
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard- multiaxial stresses and strains present in forming parts. These
test methods do not measure the intrinsic superplastic proper-
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom- ties of a material. Test Method E2448 should be used in that
instance.
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
6. Apparatus
2. Referenced Documents
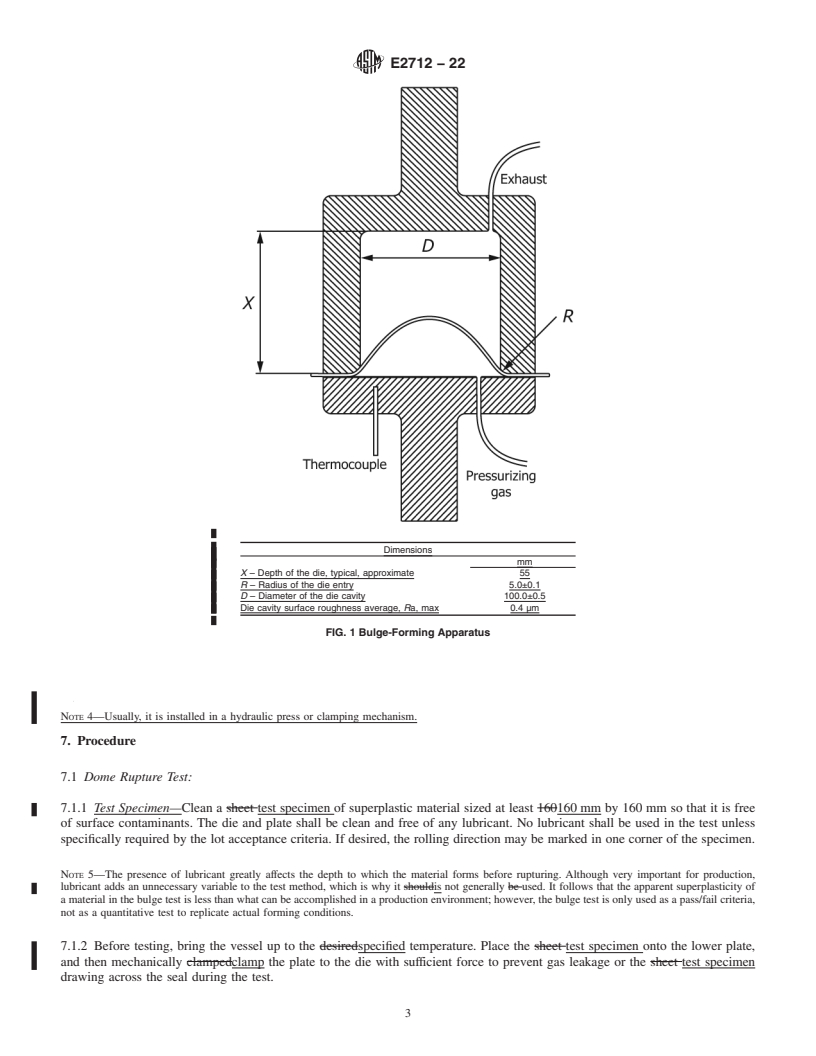
6.1 Thebulgetestconsistsofformingatestspecimeninthe
2
form of a sheet of material into a right circular cylindrical die
2.1 ASTM Standards:
E6Terminology Relating to Methods of MechanicalTesting using pressurized gas. The apparatus is shown in Fig. 1. The
diameter of the die cavity shall be 100 mm 6 0.5 mm, and the
E2448Test Method for Determining the Superplastic Prop-
erties of Metallic Sheet Materials specified depth of the vessel shall be suitably designed for the
pressure and temperature envisaged for the test. The surface
finish of the die cavity shall be Ra=0.4 µm maximum.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E28 on
Mechanical Testing and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E28.02 on 6.2 The depth of the die (X in Fig. 1), may be varied by
Ductility and Formability.
means of inserts or other methods to the depth set by the
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2022. Published December 2022. Originally
specification. For convenience, a series of inserts of different
approved in 2009. Last previous edition approved in 2015 as E2719–15. DOI:
heights may be installed in the die to provide different depths
10.1520/E2712-22.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
according to the bulge test requirements.
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on NOTE1—Adepthof55mmhasbeensuccessfullyusedonsuperplastic-
the ASTM website. forming (SPF) 5083 aluminum alloy.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: E2712 − 15 E2712 − 22
Standard Test Methods for
1
Bulge-Forming Superplastic Metallic Sheet
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E2712; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 These test methods describe procedures for determining the biaxial formability of a test specimen of superplastic metallic sheet
in a circular die.
1.2 The intent of these test methods are primarily to be used as tests of superplasticity as measured by the ability to form to a
prescribed depth in a die cavity without rupturing. These test methods can also be used to generate material for the measurement
of cavitation in the formed part. These can be used as go/no go criteria for qualification to a specification.
1.3 These test methods have been used successfully with aluminum alloys. The use of these test methods on other metals should
be verified.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of
the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of
regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
E6 Terminology Relating to Methods of Mechanical Testing
E2448 Test Method for Determining the Superplastic Properties of Metallic Sheet Materials
3. Terminology
3.1 The terms specified temperature and indicated temperature are used as defined in Terminology E6.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E28 on Mechanical Testing and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E28.02 on Ductility and
Formability.
Current edition approved May 1, 2015Nov. 1, 2022. Published July 2015December 2022. Originally approved in 2009. Last previous edition approved in 20092015 as
ε1
E2719–09–15. . DOI: 10.1520/E2712-15.10.1520/E2712-22.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E2712 − 22
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 Two methods of bulge forming are included in these test methods.
4.1.1 In the first test Dome Rupture Test method, the sheet test specimen is formed into a die of a fixed depth as prescribed in a
specification. If it touches the base of the die without rupturing, then it is considered to have met the specification.
4.1.2 In the second testCavitation Test method, the depth of the die is reduced so that the material fills the die. A portion excised
from the center of the formed part may be examined for internal cavitation within the sheet.test specimen.
5. Significance and Use
5.1 When a superplastic material is regularly being used in industrial production, it is often convenient to use the bulge test to
qualify a batch or heat lot to an acceptance criterion. Comparing these test methods with Test Method E2448, the bulge test does
not require a machined coupon, test specimen, it is more convenient to perform, and it most closely simulates the multiaxial
stresses and strains present in forming parts. These test methods do not measure the intrinsic superplastic properties of a material.
Test Method E2448 should be used in that instance.
6. Apparatus
6.1 The bulge test consists of forming a test specimen in the form
...










Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.