ASTM F1316-18(2023)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Measuring the Transmissivity of Transparent Parts
Standard Test Method for Measuring the Transmissivity of Transparent Parts
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 Significance—This test method provides a means to measure the transmissivity of parts in the field (already installed on aircraft) and of large, thick or curved parts physically difficult to measure using Test Method D1003.
5.2 Use—This test method is acceptable for use on any transparent part. It is primarily intended for use on large, curved, or thick parts either pre- or post-installation (for example, windscreens on aircraft).
SCOPE
1.1 This test method describes an apparatus and procedure that is suitable for measuring the transmissivity of large, thick, or curved transparent parts including parts already installed. This test method is limited to transparencies that are relatively neutral with respect to wavelength (not highly colored).
1.2 Since the transmissivity (transmission coefficient) is a ratio of two luminance values, it has no units. The units of luminance recorded in the intermediate steps of this test method are not critical; any recognized units of luminance (for example, foot-lamberts or candelas per square metre) are acceptable for use, as long as use is consistent.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: F1316 − 18 (Reapproved 2023)
Standard Test Method for
Measuring the Transmissivity of Transparent Parts
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F1316; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
INTRODUCTION
Test Method D1003 has received wide acceptance as a test method to measure luminous
transmissivity in transparent materials. However, because Test Method D1003 requires critical
alignment of equipment on both sides of the transparency, it is not suited to measuring the
transmissivity of large, curved parts or parts that are installed. In addition, Test Method D1003
measures the luminous transmissivity of the material in a direction perpendicular to the surface of the
material. For the majority of aircraft windscreens, the pilot is not viewing through the transparency
perpendicular to the surface. Since the transmissivity varies as a function of viewing angle the values
of transmissivity measured perpendicular to the surface do not indicate what the pilot will see when
viewing through the windscreen.
For the above reasons this test method has been developed to allow the measurement of
transmissivity of a transparent part at any angle. Since the relative alignment of the equipment items
on either side of the transparency is not critical, this test method can also be used on large, thick, or
curved parts and parts that are already installed.
1. Scope mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
1.1 This test method describes an apparatus and procedure
that is suitable for measuring the transmissivity of large, thick,
2. Referenced Documents
or curved transparent parts including parts already installed.
This test method is limited to transparencies that are relatively 2.1 ASTM Standards:
neutral with respect to wavelength (not highly colored). D1003 Test Method for Haze and Luminous Transmittance
of Transparent Plastics
1.2 Since the transmissivity (transmission coefficient) is a
ratio of two luminance values, it has no units. The units of
3. Terminology
luminance recorded in the intermediate steps of this test
method are not critical; any recognized units of luminance (for 3.1 Definitions:
example, foot-lamberts or candelas per square metre) are 3.1.1 black reference, n—a light-absorbing, black material,
acceptable for use, as long as use is consistent. such as black velvet flocking.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the 3.1.2 photometer, n—a device that measures luminance as
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the defined by the spectral sensitivity of the photopic curve.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
3.1.3 Photopic curve, n—the photopic curve is the spectral
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
sensitivity of the eye for daytime conditions as Committee
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
Internationale d’Elairage (CIE) 1931 standard observer.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
3.1.4 regulated light source, n—a light source with elec-
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
tronic feedback to ensure that its illuminance remains constant
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
over time.
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
3.1.5 transmission coeffıcient, n—same as transmissivity.
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F07 on
Aerospace and Aircraft and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F07.08 on
Transparent Enclosures and Materials. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved May 1, 2023. Published June 2023. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
approved in 1990. Last previous edition approved in 2018 as F1316 – 18. DOI: Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
10.1520/F1316-18R23. the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
F1316 − 18 (2023)
3.1.6 transmissivity, n—the transmissivity of a transparent reflecting surface illuminated by sunlight instead of a powered
medium is the ratio of the luminance of an object measured light source. Care must be taken that the luminance of the
through the medium to the luminance of the object measured reflective surface does not change during the reading.
directly.
6.4 Black Reference—Use a shaded, light-absorbing black
material such as velvet to increase the accuracy of the
4. Summary of Test Method
measurement. This reference must have about the same area as
4.1 A regulated light source with a relatively large, diffusely
the light source or reflective material used for the light reading
radiating surface area is placed on one side of a transparent part
since the photometer must also measure the apparent lumi-
to be measured. A black, light-absorbing reference surface is
nance of the black reference.
placed next to the light source. A photometer is used to
7. Test Specimen
measure the luminance of the light source and black reference
directly and through the transparency. The light source reading
7.1 Clean the part to be measured, using any acceptable
measured through the transparency minus the black reference
procedure, to remove any surface contaminants with the
reading through the transparency is divided by the light source
potential to contribute to the loss of transmissivity. No special
measured directly minus the black reference measured directly
conditioning other than cleaning is required.
(see Eq 1). This ratio is the transmission coefficient of the
8. Calibration and Standardization
transparency. The black reference surface is used to correct the
measurement from the effects of light scatter due to haze and
8.1 The photometer is to have the same spectral sensitivity
from reflections.
as the eye but since the measurement involves the division of
two quantities measured by the photometer it is not necessary
5. Significance and Use
that the photometer be calibrated in absolute luminance units.
5.1 Significance—This test method provides a means to
9. Procedure
measure the transmissivity of parts in the field (already
installed on aircraft) and of large, thick or curved parts 9.1 Place the light source (or white-reflective surface) on
physically difficult to measure using Test Method D1003. one side of the transparency such that is can be viewed from
the other side of the transparency. Place the transparency at the
5.2 Use—This test method is acceptable for use on any
desired angle for measurement. The distance from the light
transparent part. It is primarily intended for use on large,
source to the transparency is not critical but must be greater
curved, or thick parts either pre- or post-installation (for
than 30 cm (11.8 in.) to prevent erroneous readings due to light
example, windscreens on aircraft).
scatter and reflections. The distance from the light source to the
photometer is also not critical, but is to be short enough so that
6. Apparatus
the photometer measurement field easily falls within the
6.1 Test Environment—It is preferable to carry out this test
emitting area of the light source. The distance from the
method in a light-controlled environment although this is not
transparency to the photometer is not critical, as the smallest
absolutely necessary. To do so, shade the transparency from
permitted distance is 0 cm. Place the black reference adjacent
direct sunlight falling on the surface and place a light-
to the light source so that it is also visible through the
absorbing black cloth in the appropriate reflection geometry
transparency. Place the light-absorbing cloth next to the trans-
with respect to the transparency to reduce reflections.
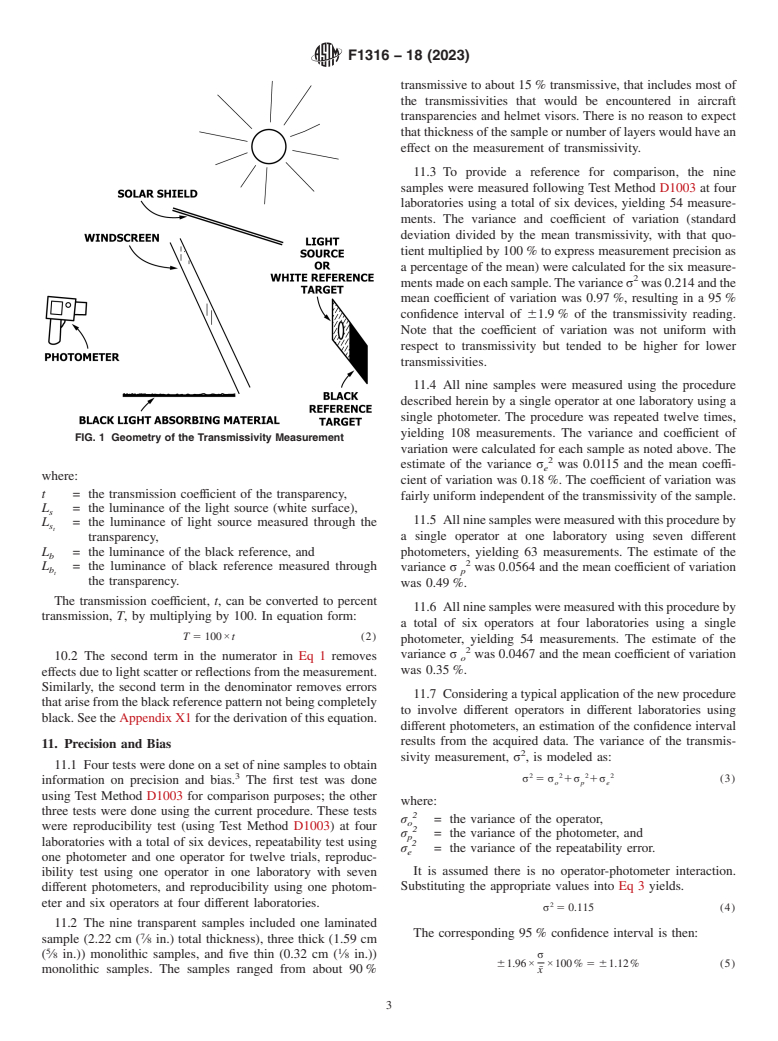
parency on the opposite side from the light source (see Fig. 1).
6.2 Photometer—Use any properly calibrated photometer
9.2 If the transparency is subject to direct sunlight, use a
for this measurement. The photometer is to have a measure-
solar shield to shade the area of the transparency (see Fig. 1).
ment field that is smaller than the regulated light source to
ensure accurate readings. It is recommended that a small, 9.3 The photometer is then used to measure the luminance
of the light source and the black reference. These readings are
portable photometer with a 1° measurement field (or less) be
used. designated L and L respectively. The light source and black
s b
reference are then measured again but this time viewing
6.3 Light Source—Regulate the light source to ensure that it
through the transparency. These readings are L and L
s b
does not change luminance during the reading period. The light t t
respectively. Make both the direct measurements and the
source is to have a relatively large, diffusely emitting surface
measurements through the transparency from about the same
area to permit easy measurement when using the photometer.
distance and angle from the light source.
The spectral distribution of the light source is not critical unless
the transparency under test has significant spectral peaks or
10. Calculation
voids. For daylight measurements it is
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.