IEC 61000-4-15:2010/COR1:2012
(Corrigendum)Corrigendum 1 - Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) - Part 4-15: Testing and measurement techniques - Flickermeter - Functional and design specifications
Corrigendum 1 - Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) - Part 4-15: Testing and measurement techniques - Flickermeter - Functional and design specifications
Corrigendum 1 - Compatibilité électromagnétique (CEM) - Partie 4-15: Techniques d'essai et de mesure - Flickermètre - Spécifications fonctionnelles et de conception
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
IEC 61000-4-15 CEI 61000-4-15
nd ième
(2 edition – 2010) (2 édition – 2010)
Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) – Compatibilité électromagnétique (CEM) –
Part 4-15: Testing and measurement Partie 4-15: Techniques d’essai et de mesure –
techniques – Flickermeter – Functional and Flickermètre – Spécifications fonctionnelles et
design specifications de conception
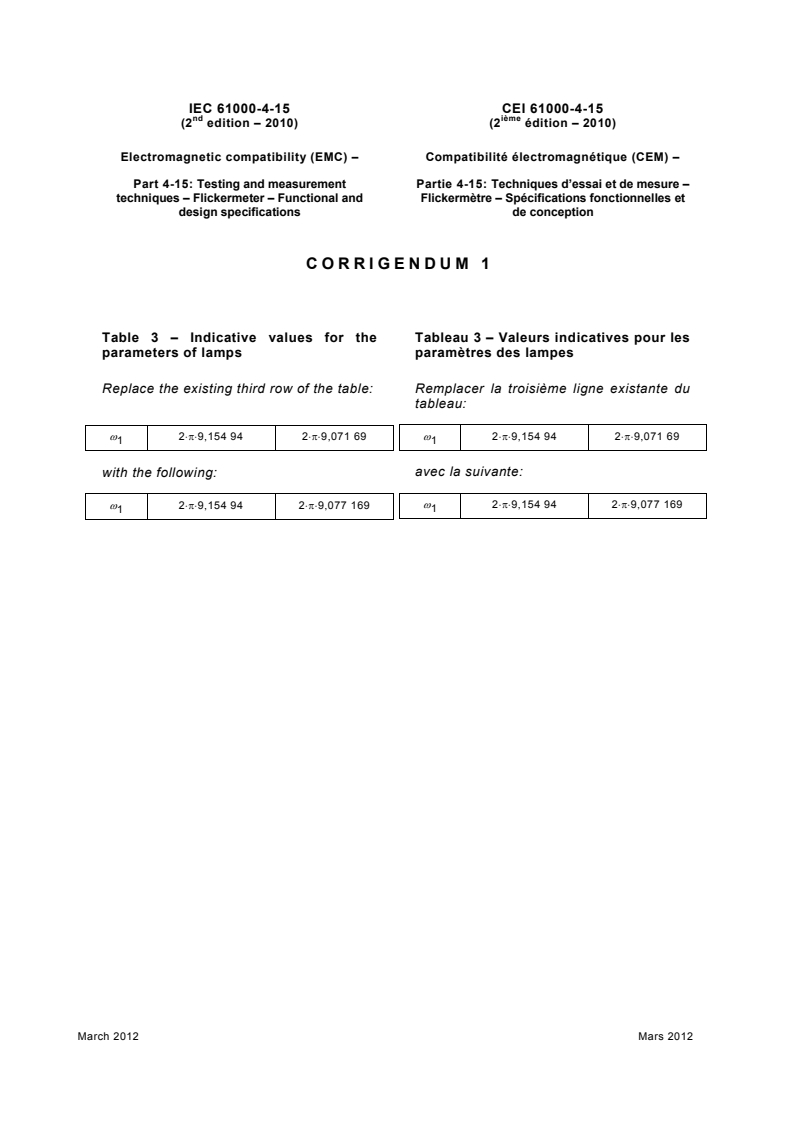
CORRIGENDUM 1
Table 3 – Indicative values for the Tablea
...
This May Also Interest You
- Standard10 pagesEnglish languagesale 15% off
- Standard11 pagesFrench languagesale 15% off
- Standard21 pagesEnglish and French languagesale 15% off
Considers immunity tests for electric and/or electronic equipment (apparatus and system) in its electromagnetic environment. Only conducted phenomena are considered, including immunity tests for equipment connected to public and industrial networks. Establishes a reference for evaluating the immunity of electrical and electronic equipment when subjected to unbalanced power supply voltage. Applies to 50 Hz/60 Hz three-phase powered electrical and/or electronic equipment with rated line current up to 16 A per phase.
- Standard50 pagesEnglish languagesale 15% off
- Standard41 pagesEnglish and French languagesale 15% off
- Standard41 pagesEnglish and French languagesale 15% off
This part of IEC 61000 defines the immunity test methods and range of preferred test levels for electrical and electronic equipment connected to low-voltage power supply networks for voltage dips, short interruptions, and voltage variations. This standard applies to electrical and electronic equipment having a rated input current exceeding 16 A per phase. It covers equipment installed in residential areas as well as industrial machinery, specifically voltage dips and short interruptions for equipment connected to either 50 Hz or 60 Hz a.c. networks, including 1-phase and 3-phase mains. The object of this standard is to establish a common reference for evaluating the immunity of electrical and electronic equipment when subjected to voltage dips, short interruptions and voltage variations. The test method documented in this part of IEC 61000 describes a consistent method to assess the immunity of equipment or a system against a defined phenomenon. It has the status of a Basic EMC Publication in accordance with IEC Guide 107.
- Standard69 pagesEnglish languagesale 15% off
- Standard63 pagesEnglish and French languagesale 15% off
- Standard66 pagesEnglish and French languagesale 15% off
- Standard4 pagesEnglish languagesale 15% off
- Standard4 pagesFrench languagesale 15% off
- Standard8 pagesEnglish and French languagesale 15% off
IEC 61000-2-4:2024 is related to conducted disturbances in the frequency range from 0 kHz to 150 kHz. It gives compatibility levels in differential mode (L-L and L-N) for industrial locations, with a nominal voltage up to 35 kV and a nominal frequency of 50 Hz or 60 Hz.
NOTE 1 Industrial locations are defined in 3.1.8.
Power distribution systems on ships, aircraft, offshore platforms and railways are not included.
NOTE 2 See also Annex E. The compatibility levels specified in this document apply at the in-plant point of coupling (IPC). The level of the low-frequency disturbances at the terminals of equipment receiving its supply from the IPC is generally assumed to be similar to the disturbance level at the IPC itself. However, in some situations this is not the case, particularly when a long feeder is dedicated to the supply of a particular load, or when a disturbance is generated or amplified within the installation of which the equipment forms a part.
Compatibility levels are specified for the types of low-frequency electromagnetic disturbances expected at any in-plant point of coupling (IPC) within industrial locations, for guidance in the definition of:
a) limits for disturbance emissions in industrial power distribution systems (including the planning levels defined in 3.1.5);
NOTE 3 A very wide range of conditions is possible in the electromagnetic environments of industrial networks. These are approximated in this document by the three classes described in Clause 4. However, it is the responsibility of the operator of such a network to take account of the particular electromagnetic and economic conditions, including equipment characteristics, in setting the above-mentioned limits.
b) immunity levels for the equipment within these systems.
The disturbance phenomena considered are:
- voltage deviations;
- voltage dips and short interruptions;
- voltage imbalance;
- power-frequency variations;
- harmonics up to order 40;
- interharmonics up to the 40th harmonic;
- voltage components above the 40th harmonic up to 150 kHz;
- DC component;
- transient overvoltages.
The compatibility levels are given for different classes of environment determined by the characteristics of the supply network and loads.
NOTE 4 Compatibility levels at the point of common coupling (PCC) on public networks are specified in IEC 61000‑2‑2 for low-voltage networks and IEC 61000‑2‑12 for medium-voltage networks. IEC TR 61000‑3‑6 and IEC TR 61000‑3‑7 describe the approach of power distribution system operators to the limitation of emissions from installations and large loads.
This third edition cancels and replaces the second edition published in 2002. This edition constitutes a technical revision. This edition includes the following significant technical changes with respect to the previous edition:
a) introduction of new classes 2a, 2b and 2L (former class 2);
b) modification of existing compatibility levels for class 3;
c) addition of compatibility levels in the frequency range 2 kHz to 150 kHz;
d) addition of compatibility levels using a new quantity: partial weighted harmonic distortion (PWHD).
- Standard150 pagesEnglish languagesale 15% off
- Standard96 pagesEnglish and French languagesale 15% off
I
- Standard2 pagesEnglish and French languagesale 15% off
- Standard3 pagesEnglish and French languagesale 15% off
IEC 61000-4-11:2020 defines the immunity test methods and range of preferred test levels for electrical and electronic equipment connected to low-voltage power supply networks for voltage dips, short interruptions, and voltage variations. This document applies to electrical and electronic equipment having a rated input current not exceeding 16 A per phase, for connection to 50 Hz or 60 Hz AC networks. It does not apply to electrical and electronic equipment for connection to 400 Hz AC networks. Tests for these networks will be covered by future IEC documents. The object of this document is to establish a common reference for evaluating the immunity of electrical and electronic equipment when subjected to voltage dips, short interruptions and voltage variations.
NOTE 1 Voltage fluctuation immunity tests are covered by IEC 61000-4-14. The test method documented in this document describes a consistent method to assess the immunity of equipment or a system against a defined phenomenon.
NOTE 2 As described in IEC Guide 107, this is a basic EMC publication for use by product committees of the IEC. As also stated in Guide 107, the IEC product committees are responsible for determining whether this immunity test standard should be applied or not, and, if applied, they are responsible for defining the appropriate test levels. Technical committee 77 and its sub-committees are prepared to co-operate with product committees in the evaluation of the value of particular immunity tests for their products. This third edition cancels and replaces the second edition published in 2004 and Amendment 1:2017. This edition constitutes a technical revision. This edition includes the following significant technical changes with respect to the previous edition:
- rise time and fall time of transients are now defined terms in Clause 3;
- the origin of voltage dips and short interruptions is now stated in Clause 4.
The contents of the corrigendum of May 2020 and October 2022 have been included in this copy.
- Standard194 pagesEnglish languagesale 15% off
- Standard62 pagesEnglish and French languagesale 15% off
- Standard2 pagesEnglish languagesale 15% off
- Standard12 pagesEnglish and French languagesale 15% off






Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.
Loading comments...