ASTM D3664-04(2009)
(Specification)Standard Specification for Biaxially Oriented Polymeric Resin Film for Capacitors in Electrical Equipment
Standard Specification for Biaxially Oriented Polymeric Resin Film for Capacitors in Electrical Equipment
ABSTRACT
This specification covers two types and three grades of thin biaxially oriented polymeric resin film composed of polyethylene terephthalate (PET, Class A) or polypropylene (PP, Class B) for use in capacitors for electrical equipment. Type I has smooth surfaces, while Type II has at least one rough surface. Each of these types is further subdivided into the following grades: Grade 1, not pre-treated; Grade 2, one side pre-treated to facilitate the vacuum deposition of metal; and Grade 3, both side pre-treated. The physical, mechanical, and electrical requirements for which the polymer films shall be tested on for conformance are as follows: tensile strength and modulus, and break elongation; insulation resistance and conducting paths; permittivity, dissipation factor, and dielectric breakdown voltage; nominal thickness and width; density; melting point; shrinkage; tear and impact strength, and fold endurance; color or clarity; moisture absorption and permeability; oxygen index and permeability; resistance to corrosive agents; heat or solvent resistance, and hygroscopic coefficient of expansion; aqueous extract conductivity; and acidity. Thicknesses of the capacitor films shall be carried out by either the roll weight, ten-sheet stack, or gravimetric methods.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers thin biaxially oriented polymeric resin film for use in capacitors for electrical equipment. The material is biaxially oriented to improve the tensile properties in the machine (MD) and transverse (TD) directions.
1.2 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the test methods section of this specification. This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific warning statements see 9.3 and Table 1 footnote B.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are the standard. The values in parentheses are for information only.
Note 1—This standard resembles IEC 60674–3–2, Specification for plastic films for electrical use, in title only. The content is significantly different.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D3664 −04 (Reapproved 2009)
Standard Specification for
Biaxially Oriented Polymeric Resin Film for Capacitors in
Electrical Equipment
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D3664; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope lation (Withdrawn 2013)
D543Practices for Evaluating the Resistance of Plastics to
1.1 This specification covers thin biaxially oriented poly-
Chemical Reagents
meric resin film for use in capacitors for electrical equipment.
D570Test Method for Water Absorption of Plastics
The material is biaxially oriented to improve the tensile
D756Practice for Determination of Weight and Shape
propertiesinthemachine(MD)andtransverse(TD)directions.
ChangesofPlasticsUnderAcceleratedServiceConditions
1.2 ThevaluesstatedinSIunitsarethestandard.Thevalues (Withdrawn 1998)
D774/D774MTest Method for Bursting Strength of Paper
in parentheses are for information only.
NOTE 1—This standard resembles IEC 60674–3–2, Specification for
(Withdrawn 2010)
plastic films for electrical use, in title only. The content is significantly
D882Test Method for Tensile Properties of Thin Plastic
different.
Sheeting
1.3 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the D1004Test Method for Tear Resistance (Graves Tear) of
test methods section of this specification. This standard does
Plastic Film and Sheeting
not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any,
D1204Test Method for Linear Dimensional Changes of
associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this
Nonrigid Thermoplastic Sheeting or Film at Elevated
standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices
Temperature
and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior
D1434TestMethodforDeterminingGasPermeabilityChar-
to use. For specific warning statements see 9.3 and Table 1
acteristics of Plastic Film and Sheeting
footnote B.
D1435Practice for Outdoor Weathering of Plastics
D1505Test Method for Density of Plastics by the Density-
2. Referenced Documents
Gradient Technique
D2176Test Method for Folding Endurance of Paper by the
2.1 ASTM Standards:
M.I.T. Tester (Withdrawn 2010)
D149Test Method for Dielectric Breakdown Voltage and
D2305Test Methods for Polymeric Films Used for Electri-
DielectricStrengthofSolidElectricalInsulatingMaterials
cal Insulation
at Commercial Power Frequencies
D2863Test Method for Measuring the Minimum Oxygen
D150Test Methods forAC Loss Characteristics and Permit-
Concentration to Support Candle-Like Combustion of
tivity (Dielectric Constant) of Solid Electrical Insulation
Plastics (Oxygen Index)
D202Test Methods for Sampling and Testing Untreated
D3417Test Method for Enthalpies of Fusion and Crystalli-
Paper Used for Electrical Insulation
zation of Polymers by Differential Scanning Calorimetry
D257Test Methods for DC Resistance or Conductance of
(DSC) (Withdrawn 2004)
Insulating Materials
D3420Test Method for Pendulum Impact Resistance of
D374Test Methods for Thickness of Solid Electrical Insu-
Plastic Film
D3636Practice for Sampling and Judging Quality of Solid
Electrical Insulating Materials
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D09 on
D3755Test Method for Dielectric Breakdown Voltage and
Electrical and Electronic Insulating Materials and is the direct responsibility of
DielectricStrengthofSolidElectricalInsulatingMaterials
Subcommittee D09.07 on Flexible and Rigid Insulating Materials.
Under Direct-Voltage Stress
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2009. Published February 2010. Originally
approved in 1978. Last previous edition approved in 2004 as D3664-04. DOI: D3985Test Method for Oxygen Gas Transmission Rate
10.1520/D3664-04R09.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
the ASTM website. www.astm.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
D3664−04 (2009)
Through Plastic Film and Sheeting Using a Coulometric 3. Terminology
Sensor
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
D6054Practice for Conditioning Electrical Insulating Mate-
3.1.1 shiner, n—as related to dielectric films,aprotrusionof
rials for Testing (Withdrawn 2012)
material beyond the plane of either edge of the roll.
E96/E96MTest Methods for Water Vapor Transmission of
Materials
3.1.2 space factor, n— as related to dielectric films,a
E252Test Method for Thickness of Foil, Thin Sheet, and
measure of surface roughness of film expressed by the follow-
Film by Mass Measurement
ing equation:
2.2 IEC Standards:
Spacefactor 5100 T 2 T @T # (1)
@ #
b g g
IEC 60674–3–2Specification for plastic films for electrical
purposes—Part 3: Specifications for individual
where:
materials—Sheet 2: Requirements for balanced biaxially
T = bulking thickness determined using Test Methods
b
oriented polyethylene phthalate (PET) films used for
D374, and
electrical insulation
T = gravimetric thickness determined using Test Method
g
E252.
Available fromAmerican National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St.,
Space factor is expressed as %.
4th Floor, New York, NY 10036.
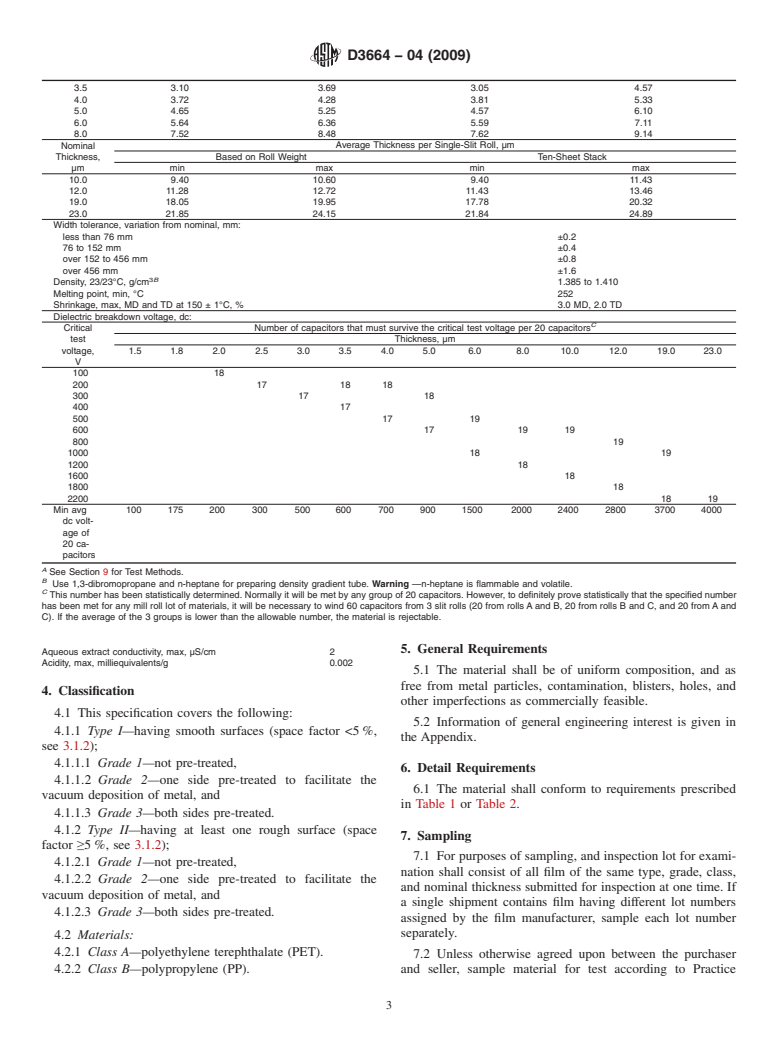
TABLE 1 Physical, Mechanical, and Electrical Requirements for Biaxially Oriented Polyethylene Terephthalate Capacitor Film (25.4 µm
A
or less in thickness)
Tensile Properties
Tensile strength modulus, and elongation, MD and TD:
Tensile Tensile
Nominal Break
Strength, Modulus
Thickness, Elongation,
min, MPA min, MPa
µm %min
MD and TD MD and TD
MD TD
1.5 110 40 20 2410
1.8 110 40 20 2410
2.0 110 . 30 2410
2.5 117 . 35 2410
3.0 131 . 35 2410
3.5 131 . 35 2716
4.0 131 45 2716
5.0 138 . 40 3103
6.0 138 . 40 3103
8.0 145 . 45 3103
10.0 145 . 50 3103
12.0 145 . 60 3103
19.0 145 . 60 2759
23.0 145 . 65 2759
Insulation resistance and conducting paths:
Nominal Thickness, µm Insulation Resistance, min MΩ at 125°C Conducting Paths, max No. per m
1.5 1000 .
1.8 1000 .
2.0 1000 .
2.5 850 .
3.0 850 .
3.5 850 128
4.0 825 107
5.0 825 86
6.0 800 64
8.0 600 53
10.0 600 43
12.0 600 22
19.0 500 11
23.0 400 11
Permittivity, 23°C, 50 % RH:
60 Hz 3.2±0.1
1 kHz 3.2±0.1
Dissipation factor, max 23°C: 60 Hz 1 kHz
2.0 to 4.0 µm thick 0.006 0.008
5.0 to 25.0 µm thick 0.004 0.006
Thickness, µm:
Nominal Average Thickness per Single-Slit Roll
Thickness, Based on Roll Weight Ten-Sheet Stack
µm min max min max
1.5 1.48 1.62 . .
1.8 1.61 1.89 . .
2.0 1.79 2.11 1.50 3.00
2.5 2.30 2.70 2.03 3.56
3.0 2.71 3.19 2.54 4.06
D3664−04 (2009)
3.5 3.10 3.69 3.05 4.57
4.0 3.72 4.28 3.81 5.33
5.0 4.65 5.25 4.57 6.10
6.0 5.64 6.36 5.59 7.11
8.0 7.52 8.48 7.62 9.14
Nominal Average Thickness per Single-Slit Roll, µm
Thickness, Based on Roll Weight Ten-Sheet Stack
µm min max min max
10.0 9.40 10.60 9.40 11.43
12.0 11.28 12.72 11.43 13.46
19.0 18.05 19.95 17.78 20.32
23.0 21.85 24.15 21.84 24.89
Width tolerance, variation from nominal, mm:
less than 76 mm ±0.2
76 to 152 mm ±0.4
over 152 to 456 mm ±0.8
over 456 mm ±1.6
3B
Density, 23/23°C, g/cm 1.385 to 1.410
Melting point, min, °C 252
Shrinkage, max, MD and TD at 150 ± 1°C, % 3.0 MD, 2.0 TD
Dielectric breakdown voltage, dc:
C
Critical Number of capacitors that must survive the critical test voltage per 20 capacitors
test Thickness, µm
voltage, 1.5 1.8 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0 5.0 6.0 8.0 10.0 12.0 19.0 23.0
V
100 18
200 17 18 18
300 17 18
400 17
500 17 19
600 17 19 19
800 19
1000 18 19
1200 18
1600 18
1800 18
2200 18 19
Min avg 100 175 200 300 500 600 700 900 1500 2000 2400 2800 3700 4000
dc volt-
age of
20 ca-
pacitors
A
See Section 9 for Test Methods.
B
Use 1,3-dibromopropane and n-heptane for preparing density gradient tube. Warning —n-heptane is flammable and volatile.
C
This number has been statistically determined. Normally it will be met by any group of 20 capacitors. However, to definitely prove statistically that the specified number
has been met for any mill roll lot of materials, it will be necessary to wind 60 capacitors from 3 slit rolls (20 from rolls A and B, 20 from rolls B and C, and 20 from A and
C). If the average of the 3 groups is lower than the allowable number, the material is rejectable.
5. General Requirements
Aqueous extract conductivity, max, µS/cm 2
Acidity, max, milliequivalents/g 0.002
5.1 The material shall be of uniform composition, and as
free from metal particles, contamination, blisters, holes, and
4. Classification
other imperfections as commercially feasible.
4.1 This specification covers the following:
5.2 Information of general engineering interest is given in
4.1.1 Type I—having smooth surfaces (space factor <5%,
the Appendix.
see 3.1.2);
4.1.1.1 Grade 1—not pre-treated,
6. Detail Requirements
4.1.1.2 Grade 2—one side pre-treated to facilitate the
6.1 The material shall conform to requirements prescribed
vacuum deposition of metal, and
in Table 1 or Table 2.
4.1.1.3 Grade 3—both sides pre-treated.
4.1.2 Type II—having at least one rough surface (space
7. Sampling
factor ≥5%, see 3.1.2);
7.1 For purposes of sampling, and inspection lot for exami-
4.1.2.1 Grade 1—not pre-treated,
nation shall consist of all film of the same type, grade, class,
4.1.2.2 Grade 2—one side pre-treated to facilitate the
and nominal thickness submitted for inspection at one time. If
vacuum deposition of metal, and
a single shipment contains film having different lot numbers
4.1.2.3 Grade 3—both sides pre-treated.
assigned by the film manufacturer, sample each lot number
separately.
4.2 Materials:
4.2.1 Class A—polyethylene terephthalate (PET).
7.2 Unless otherwise agreed upon between the purchaser
4.2.2 Class B—polypropylene (PP). and seller, sample material for test according to Practice
D3664−04 (2009)
TABLE 2 Physical, Mechanical, and Electrical Requirements for
aninitialjawseparationof50mm(2in.).Testa25-mm(1-in.)
Biaxially Oriented Polypropylene Capacitor Film (25.4 µm or less
width or the width as received
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.