ASTM A439/A439M-15
(Specification)Standard Specification for Austenitic Ductile Iron Castings
Standard Specification for Austenitic Ductile Iron Castings
ABSTRACT
This specification covers austenitic ductile iron castings used for their resistance to heat, corrosion and wear. The castings shall be melt processed using cupolas, air furnaces, electric furnaces or crucible furnaces. The iron castings shall undergo magnetic permeability test. Samples taken from test coupons, broken test specimens, or castings shall conform to the required chemical compositions of carbon, silicon, manganese, phosphorus, nickel and chromium. Mechanical tests shall be performed wherein the iron casting specimens shall conform to the required values of tensile strength, yield strength, elongation and Brinell hardness.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers austenitic ductile iron castings, which are used primarily for their resistance to heat, corrosion, and wear, and for other special purposes.
1.2 Austenitic ductile iron, also known as austenitic nodular iron or austenitic spheroidal iron, is characterized by having its graphite substantially in a spheroidal form and substantially free of flake graphite. It contains some carbides and sufficient alloy content to produce an austenitic structure.
1.3 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard.
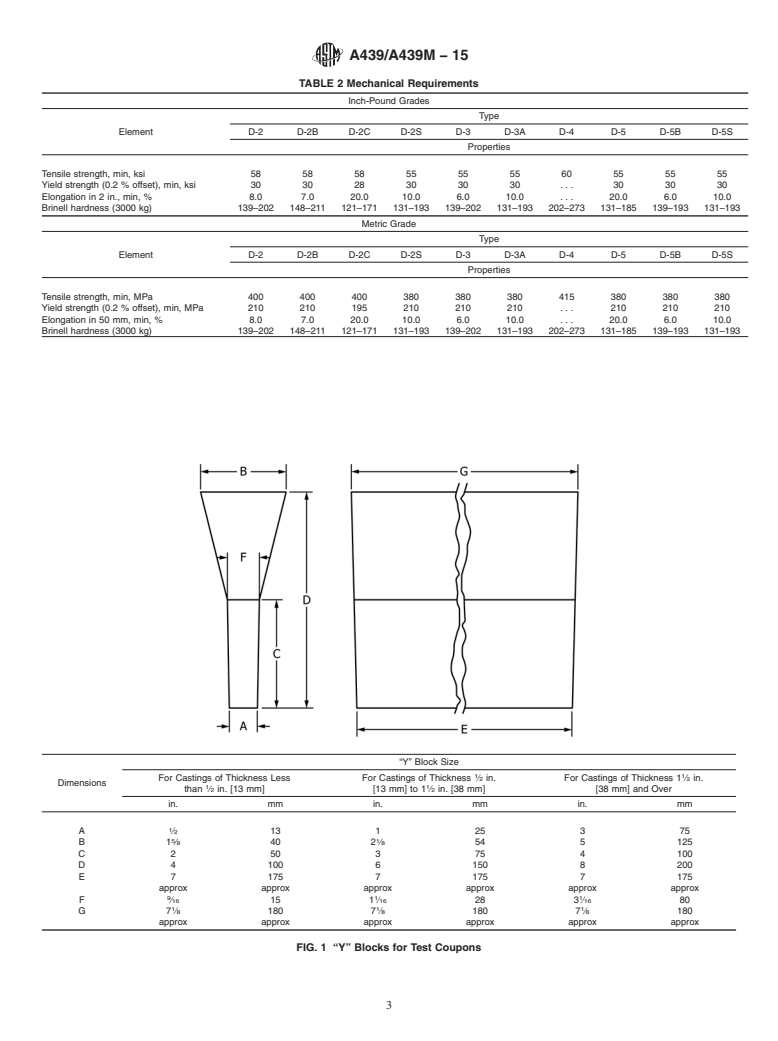
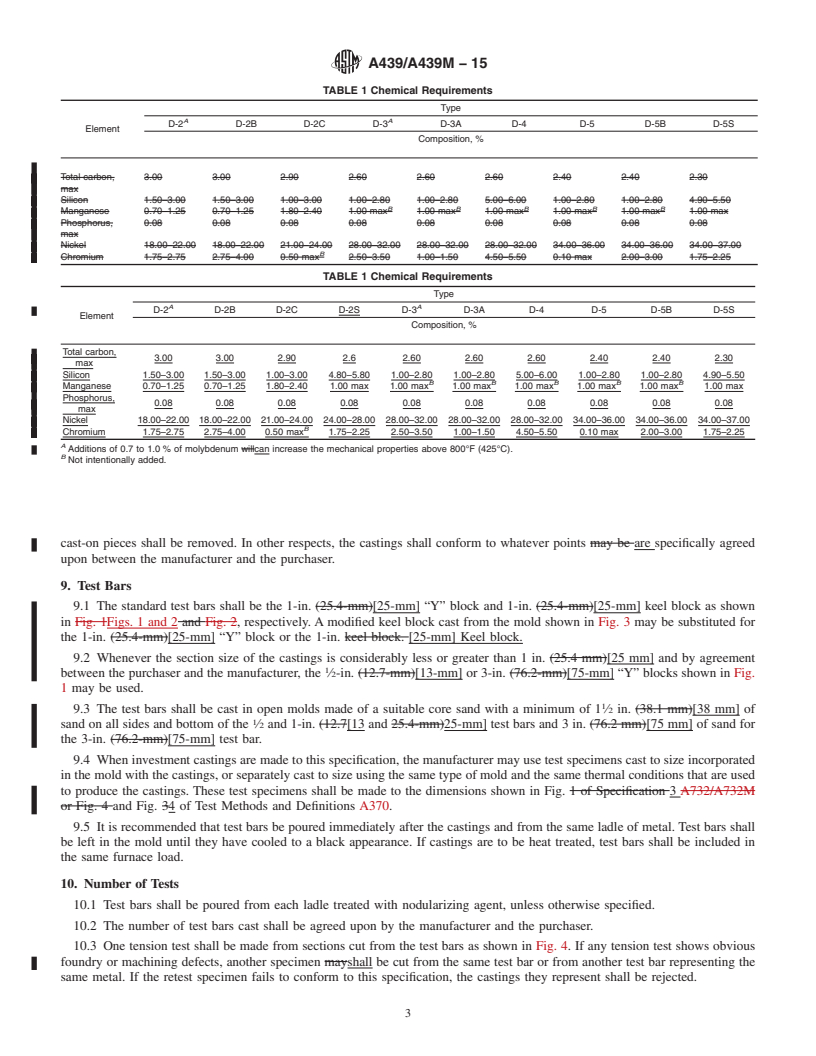
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: A439/A439M −15
Standard Specification for
1
Austenitic Ductile Iron Castings
This standard is issued under the fixed designationA439/A439M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope 3. Ordering Information
3.1 Orders for material to this specification shall include the
1.1 This specification covers austenitic ductile iron castings,
following information:
which are used primarily for their resistance to heat, corrosion,
3.1.1 ASTM designation,
and wear, and for other special purposes.
3.1.2 Type of austenitic ductile iron required (see 6.1),
1.2 Austenitic ductile iron, also known as austenitic nodular
3.1.3 Heat treatment options (see 4.3 – 4.6),
iron or austenitic spheroidal iron, is characterized by having its
3.1.4 If repair of castings is permitted (see 4.7),
graphite substantially in a spheroidal form and substantially
3.1.5 Size and number of test bars required (see 9.1 – 9.4
free of flake graphite. It contains some carbides and sufficient
and 10.1),
alloy content to produce an austenitic structure.
3.1.6 Special tests, if required (see 12.1),
1.3 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units 3.1.7 Certification, if required (see 14.1), and
are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in 3.1.8 Different preparation for delivery requirements, if
each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each needed (see 15.1).
system shall be used independently of the other. Combining
values from the two systems may result in non-conformance
4. Manufacture
with the standard.
4.1 Melting may be done in any furnaces that produce
castings meeting the chemical and mechanical requirements
2. Referenced Documents
outlined in this specification. These include cupolas, air
2
furnaces, electric furnaces, crucible furnaces, and so forth.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
Nodularizing and inoculation practice shall be optional with
A247 Test Method for Evaluating the Microstructure of
the foundry to produce a microstructure in accordance with 1.2
Graphite in Iron Castings
and Test Method A247.
A370 Test Methods and Definitions for Mechanical Testing
of Steel Products
4.2 Austenitic ductile iron castings may be supplied in
E8 Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials
either the as-cast or the heat-treated condition.
E10 Test Method for Brinell Hardness of Metallic Materials
3 4.3 By agreement between the manufacturer and the
E30 Methods for Chemical Analysis of Ferroalloys
purchaser, the castings may be stress relieved by heating to
E59 Practice for Sampling Steel and Iron for Determination
3 1150 to 1200°F [620 to 650°C] for not less than 1 h and not for
of Chemical Composition
more than 2 h per inch [25 mm] of thickness in the thickest
E351 Test Methods for ChemicalAnalysis of Cast Iron—All
section. Heating and cooling shall be uniform and shall not be
Types
more than 400°F/h [220°C/h] for castings less than 1 inch
[25 mm] in maximum thickness and shall be not more than
400°F/h [220°C/h] divided by the maximum section thickness
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee A04 on Iron
in inches [25 mm] for thicker castings. During the cooling
Castings and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee A04.02 on Malleable and
cycle, castings may be cooled in still air after the temperature
Ductile Iron Castings.
has dropped to 600°F [310°C].
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2015. Published December 2015. Originally
approved in 1960. Last previous edition approved in 2009 as A439 – 83 (2009).
4.4 By agreement between the manufacturer and the
DOI: 10.1520/A0439_A0439M-15.
2
purchaser, the castings may be in-mold stress relieved by
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
allowing castings to cool slowly in the mold at a rate not
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
exceeding 400°F/h [220°C/h]. Once the temperature has
the ASTM website.
3
dropped below 600°F [310°C], castings can be removed from
Withdrawn. The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced
on www.astm.org. the mold and cooled in still air.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
A439/A439M − 15
4.5 Whenever dimensional changes in high-temperature 6.4 The chemical analysis for total carbon shall be made o
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: A439 − 83 (Reapproved 2009) A439/A439M − 15
Standard Specification for
1
Austenitic Ductile Iron Castings
This standard is issued under the fixed designation A439;A439/A439M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the
year of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last
reapproval. A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope
1.1 This specification covers austenitic ductile iron castings, which are used primarily for their resistance to heat, corrosion, and
wear, and for other special purposes.
1.2 Austenitic ductile iron, also known as austenitic nodular iron or austenitic spheroidal iron, is characterized by having its
graphite substantially in a spheroidal form and substantially free of flake graphite. It contains some carbides and sufficient alloy
content to produce an austenitic structure.
1.3 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values given in
parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered stated in each
system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the
two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
A247 Test Method for Evaluating the Microstructure of Graphite in Iron Castings
A370 Test Methods and Definitions for Mechanical Testing of Steel Products
A732/A732M Specification for Castings, Investment, Carbon and Low Alloy Steel for General Application, and Cobalt Alloy
for High Strength at Elevated Temperatures
E8 Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials
E10 Test Method for Brinell Hardness of Metallic Materials
3
E30 Methods for Chemical Analysis of Ferroalloys
3
E59 Practice for Sampling Steel and Iron for Determination of Chemical Composition
E351 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Cast Iron—All Types
3. Ordering Information
3.1 Orders for material to this specification shall include the following information:
3.1.1 ASTM designation,
3.1.2 Type of austenitic ductile iron required (see 6.1),
3.1.3 Heat treatment requiredoptions (see 4.24.3 – 4.44.6),
3.1.4 If repair of castings is permitted (see 4.54.7),
3.1.5 Size and number of test bars required (see 9.1 – 9.4 and 10.1),
3.1.6 Special tests, if required (see 12.1),
3.1.7 Certification, if required (see 14.1), and
3.1.8 Different preparation for delivery requirements, if needed (see 15.1).
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee A04 on Iron Castings and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee A04.02 on Malleable and Ductile
Iron Castings.
Current edition approved May 1, 2009Nov. 1, 2015. Published August 2009December 2015. Originally approved in 1960. Last previous edition approved in 20042009
as A439 - 83A439 – 83 (2009). (2004). DOI: 10.1520/A0439-83R09.10.1520/A0439_A0439M-15.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
Withdrawn. The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on www.astm.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
A439/A439M − 15
4. Manufacture
4.1 Melting may be done in any furnaces that produce castings meeting the chemical and mechanical requirements outlined in
this specification. These include cupolas, air furnaces, electric furnaces, crucible furnaces, etc. and so forth. Nodularizing and
inoculation practice shall be optional with the foundry to produce a microstructure in accordance with 1.2 and Test Method A247.
4.2 Austenitic ductile iron castings may be supplied in either the as-cast or the heat-treated condition.
4.3 By agreement between the manufacturer and the purchaser, the castings may be stress relieved by heating to 1150 to 1200°F
(621[620 to 650°C)650°C] for not less than 1 h nor and not for more than 2 h per inch [25 mm] of thickness in the thickest section.
Heating and cooling shall be uniform and shall not be more than 400°F (222°C)/h400°F/h [220°C/h] for cast
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.