ASTM D1189-61(1973)
(Test Method)Method of Test for Vacuum Distillation of Liquid and Semi-Solid Asphaltic Materials to Obtain a Residue of Specified Penetration (Withdrawn 1979)
Method of Test for Vacuum Distillation of Liquid and Semi-Solid Asphaltic Materials to Obtain a Residue of Specified Penetration (Withdrawn 1979)
General Information
Standards Content (Sample)
~~r~ Designation: D 1189 - 61 (Reapproved 1973)
Standard Test Method for
VACUUM DISTILLATION OF LIQUID AND SEMI
SOLID ASPHALTIC MATERIALS TO OBTAIN A
RESIDUE OF SPECIFIED PENETRATION 1
This Standard is issued under the fixed designation D 1189; the number immediately following the designation indicates the
year of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of
last reapproval.
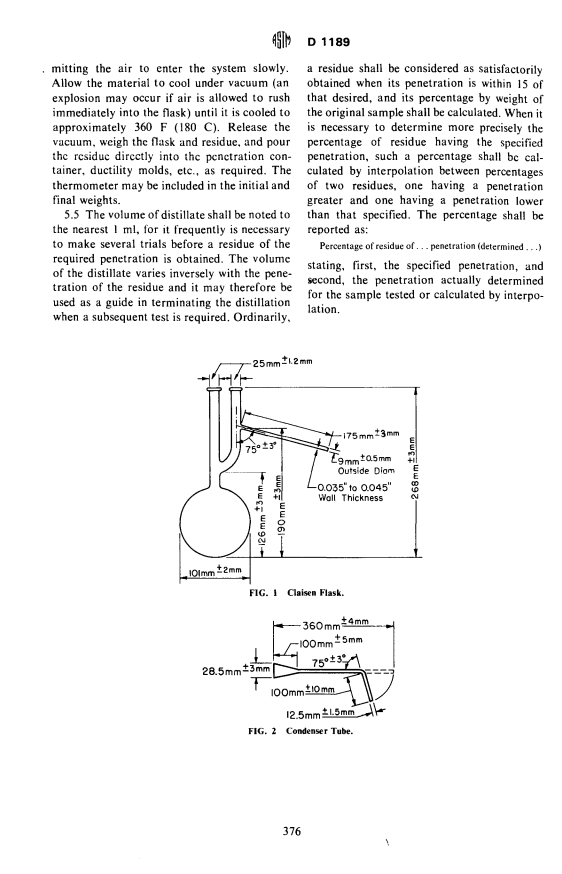
1. Scope Outside diameter of small end 12.5 ± 1.5 mm
28.5 ± 3.0 mm
Outside diameter of large end
1.1 This method of test covers the determi
Length 360.0 ± 4.0 mm
Length of tapered part 100.0 ± 5.0 mm
nation, by vacuum <;Iistillation and with the
elimination of oxidation effects, ofthe quantity
The condenser tube shall be as shown in Fig. 2,
of asphaltic residue of specified penetration.
with a 75-deg angle smooth bend toward the
When the penetration of the residue is not
and with approximately a 100-mm
outlet,
otherwise stated, it shall be understood to be
straight section at the outlet.
100. The residue obtained is available for tests
2.3 Shield-A galvanized il'Qn shield, lined
as desired.
with VB-in. (3.2-mm) asbestos, fitted with
N OTE I-The test results on the residue may be
transparent covered windows, of the form and
affected by nonasphaltic materials present in the
dimensions shown in Fig. 3, to protect the flask
asphalt.
from air currents and to prevent radiation. The
NOTE 2-This method is not intended to replace
ASTM Method D 243, Test for Residue of Specified
cover (top) may be of Transite board made in
Penetration', which introduces oxidation effects.
two parts, or it may be of galvanized iron lined
with VB-in. asbestos.
2. Apparatus
2.4 Receiver-Graduated cylinder, of uni
2.1 Flask-A standard 500-ml Claisen dis
form diameter, with a pressed or molded base
tilling flask, constructed of heat-resistant
and the lip on the top closed so as to make
glass,' as shown in Fig. I and conforming to
possible an airtight deal with a rubber stopper.
the following dimensions:
The over-all height shall be not less than 248
Diameter of bulb, outside lOl ± 2.0mm
mm (9% in.) nor more than 260 mm (10 V4 in.).
Diameter of necks outside 25 ± 1.2mm
Diameter of tubulature, outside 9 ± 0.5 mm The cylinder shall be graduated in I-ml divi
Height of flask, outside 268 ± 3.0mm
sions to contain 100 ml, and the graduated
Vertical distance from bottom of 126±3mm
portion shall be not less than 177.8 mm (7 in.)
bulb, outside, to horizontal tan
gent at junction of necks, outside nor more than 203.2 mm (8 in.) in length. Each
Vertical distance from bottom of 190±3mm
fifth graduation shall be distinguished by a
bulb, outside, to horizontal tan
longer line, and the graduations shall be num-
gent at junction of neck and tubu
lature, inside
Length of tubulature 175 ± 3 mm
Angle oftubulature 75 ± 3 deg
I This method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Com
Thickness of tubulature wall 0.035 to 0.045 in.
mittee D-4 on Road and Paving Materials and is the
(0.89 to 1.14 mm)
direct responsibility of Subcommittee D04.46 on Durability
Tests.
2.2 Condenser Tube-A suitable form of
Current edition approved Sept. 18. 1961. Originally
issued 1952. Replaces D 1189 - 52 (1955).
tapered glass condenser tube constructed of
2 Apnual Book of ASTM Standards, Part 15.
heat-resistant glass' and having the following
, Borosilicate glass has been found satisfactory for this
purpose.
dimensions:
374
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
01189
bered from the bottom up at intervals of 10 ml. eter, vacuum source, etc. shall be connected
The graduations shall not be in error by more into the system as shown in Fig. 4. To prevent
than I ml at any point on the scale. Immedi air leakage into the system, %-in. hose clamps
may be used at all the rubber tubing glass
ately above the lOO-ml graduation line, ap
proximately 45 mm of chemically resistant connection points. All glass items should be
glass tubing, 7 mm in outside diameter, shall well annealed and of uniform and heavy wall
be sealed in to provide a vacuum connection. thickness in order to avoid danger of collapse
2.5 Thermometer-An ASTM High Distil under vacuum.
Thermometer having a range from 30 to
lation
5. Procedure
760 F (-2 to +400 C), as specified, and
conforming to the requirements for Thermom 5.1 Charge the tared flask with 200 ± 0.1 g
eter SF or SC, respectively, as prescribed in of the material to be tested and insert the
ASTM Specification E -I for ASTM thermometer. Place the flask in the assembly,
tighten the connections, and apply the vacuum.
Thermometers. •
2.6 Manometer-A suitable laboratory ma (If trouble is encountered in foaming, heating
nometer or gage for measuring the pressure ()f to 190 F (90 C) before applying the vacuum
the system at the receiver to within I mm Hg. will be of assistance.) Apply heat slowly. Care
2.7 Va
...








Disqus seems to be taking longer than usual. Reload?