ASTM C1053-00(2005)
(Specification)Standard Specification for Borosilicate Glass Pipe and Fittings for Drain, Waste, and Vent (DWV) Applications
Standard Specification for Borosilicate Glass Pipe and Fittings for Drain, Waste, and Vent (DWV) Applications
ABSTRACT
This specification covers chemically resistant, low expansion, Type I, borosilicate glass, Class A, used to manufacture corrosion-resistant pipe and fittings for drain, waste, and vent service. The pipe and fittings covered by the specification are intended for chemical resistant service above and below grade under gravity flow or vacuum conditions. The pipe and fittings shall have beaded or plain ends. The chemical and physical requirements shall conform to the requirements specified.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers chemical resistant, low expansion, Type I, borosilicate glass, Class A (see Specification E438), used to manufacture corrosion-resistant pipe and fittings for drain, waste, and vent service.
1.2 The pipe and fittings covered by the specification are intended for chemical resistant service above and below grade under gravity flow or vacuum conditions.
1.3 The pipe and fittings shall have beaded or plain ends.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: C1053 – 00 (Reapproved 2005)
Standard Specification for
Borosilicate Glass Pipe and Fittings for Drain, Waste, and
Vent (DWV) Applications
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C1053; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope 3.1.6 Accessory items such as couplings, drains, adapters,
and cutters.
1.1 This specification covers chemically resistant, low ex-
pansion, Type I, borosilicate glass, Class A (see Specification
4. Materials and Manufacture
E438), used to manufacture corrosion-resistant pipe and fit-
4.1 The glass components shall represent good workman-
tings for drain, waste, and vent service.
ship as consistent with standard glass process capabilities.
1.2 The pipe and fittings covered by the specification are
intended for chemical resistant service above and below grade
5. Chemical Requirements Chemical Requirements
under gravity flow or vacuum conditions.
5.1 The chemical requirements shall be as described in
1.3 The pipe and fittings shall have beaded or plain ends.
Specification E438.
2. Referenced Documents
6. Physical Requirements
2.1 ASTM Standards:
6.1 The physical requirements shall be as described in
C600 Test Method of Thermal Shock Test on Glass Pipe
Specification E438.
C623 Test Method for Young’s Modulus, Shear Modulus,
6.2 Refer also toAnnexA1 for additional physical require-
and Poisson’s Ratio for Glass and Glass-Ceramics by
ments.
Resonance
C693 Test Method for Density of Glass by Buoyancy
7. Operating Temperatures
E438 Specification for Glasses in Laboratory Apparatus
7.1 Minimum Operating Temperature—The minimum rated
operating temperature for all sizes shall be −40°F (−40°C)
3. Ordering Information
provided the material being conveyed is fluid.
3.1 The minimum ordering information for material under
7.2 Maximum Operating Temperature—The maximum
this specification shall include the following information:
rated continuous operating temperature shall be 212°F
3.1.1 ASTM designation and date of issue,
(100°C).
3.1.2 Manufacturer’s catalog number or parts identification,
7.3 Thermal Shock Resistance—The maximum allowable
3.1.3 Quantity ordered,
temperature differential for installed systems shall be in accor-
3.1.4 Special test or certification requirements,
dance with Table 1 for the various pipe sizes. Maximum
3.1.5 Special packaging or marking, if required, and
temperature differential refers to an almost instantaneous
temperature change, such as low-pressure steam followed
This specification is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee C14 on Glass
directly by a flush of ice cold water, or the reverse. Maximum
and Glass
temperaturedifferentialpertainstoeitherinsideoroutsidepipe
Products and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C14.05 on Glass Pipe.
surfaces.
Current edition approved Sept. 1th, 2005. Published October 2005. Originally
7.3.1 Thermal shock resistance is not ordinarily tested. If
approved in 1985. Last previous edition approved in 2000 as C1053–00. DOI:
10.1520/C1053-00R05.
thermal shock resistance may be questioned, it shall be tested
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
in accordance with Method C600. If all pieces tested pass the
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
allowable temperature differential, the lot shall be accepted. If
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. one or more failures occur, a retest shall be made using a
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
C1053 – 00 (2005)
TABLE 1 Maximum Temperature Differential for Thermal Shock
Sudden Temperature
Pipe Size, in. (mm)
Difference, Max °F (°C)
1 ⁄2 –3 (38–76) 200 (93)
4 (102) 175 (78)
6 (152) 160 (71)
sample size twice that of the first test. If any failures occur on
the retest, the entire shipment shall be retested.
8. Pressure Rating
8.1 DWVpipingsystemsaredesignedforgravityflowonly.
Wall Thick-
A (OD) B (OD)
8.2 All pipe sizes are suitable for vacuum service. A
Size, in. ness, Length, ft
Diameter, in. Diameter, in.
in.
9. Dimensions and Permissible Variations
1 ⁄2 2.06 1.84 0.17 5 and 10
2 2.58 2.34 0.17 5 and 10
9.1 Beaded Flanges:
3 3.69 3.41 0.20 5 and 10
9.1.1 Flange Face Flatness—Maximum permissible devia-
4 4.84 4.53 0.27 5 and 10
tion from a flat plane across the face of a flange on all sizes 6 7.12 6.66 0.33 5 and 10
A
shall be ⁄16 in. (1.6 mm).
Length includes coupling allowance.
A
9.1.2 Flange Face Squareness—Flange faces of both pipe
Nominal OD Over EPS
and fittings shall be square to the pipe centerline within the
1 13
1 ⁄2 in. 2 ⁄16
limits prescribed in Table 2. 2in. 3 ⁄16
3in. 5
9.1.2.1 Squareness of straight pipe lengths shall be mea-
4in. 6 ⁄4
sured by placing the pipe on rollers, located approximately 2
6in. 8 ⁄16
in. (51 mm) from each end, and butting one end against a flat
A
Pipe with EPS (expanded polystyrene) covering for underground service;
plate perpendicular to the axis of the rollers. The pipe shall be
lengths of 5 ft only.
rotated and length variation read with a suitable mechanism, FIG. 1 Standard Specifications for Straight Lengths of Pipe
suchasadialindicator.Themaximumreadingshallnotexceed
that shown in Table 2 for the respective pipe size.
9.1.2.2 Pipe fittings shall be measured for flange squareness
byagagehavingflatplatesconstructedattheanglerequiredby
that fitting. One flange shall be firmly placed on one plate, and
any difference between the remaining flange face and the other
surface plate shall be measured with Feller gages. Differences
shallnotexceedtheamountshowninTable2fortherespective
fitting size.
A
A Dimension ,in.
9.1.3 Flange Dimensions and Specifications—Beaded
flange dimensions shall be as required by the manufacturer for Size 90° 60° 45° 22 ⁄2 °
1 1
the system.
1 ⁄232 ⁄2 2
1 3 1 1
23 ⁄4 2 ⁄4 2 ⁄4 2 ⁄4
9.2 Bow:
1 3 3
35 3 ⁄2 2 ⁄4 2 ⁄4
9.2.1 Bow for All Pipe Diameters—Bow shall be measured
1 1 1
47 4 ⁄2 3 ⁄4 3 ⁄4
by supporting the pipe in “V” blocks approximately 2 in. from
6— — 7 —
A
each end with a dial gage at midlength, rotating the pipe full
Dimensions to beaded flanges include coupling allowance.
360°.Thetotaldialdeflectiondividedbytwoisthemeasureof
FIG. 2 Elbows
bow, which shall not exceed 0.25% of the pipe length.
9.3 Dimensions of All Pipe and Fittings:
10. Inspection
9.3.1 Dimensional specifications for pipe and common fit-
tingsshallbeasshowninthemanufacturer’sliterature.Typical 10.1 Inspection of the material shall be made at the point of
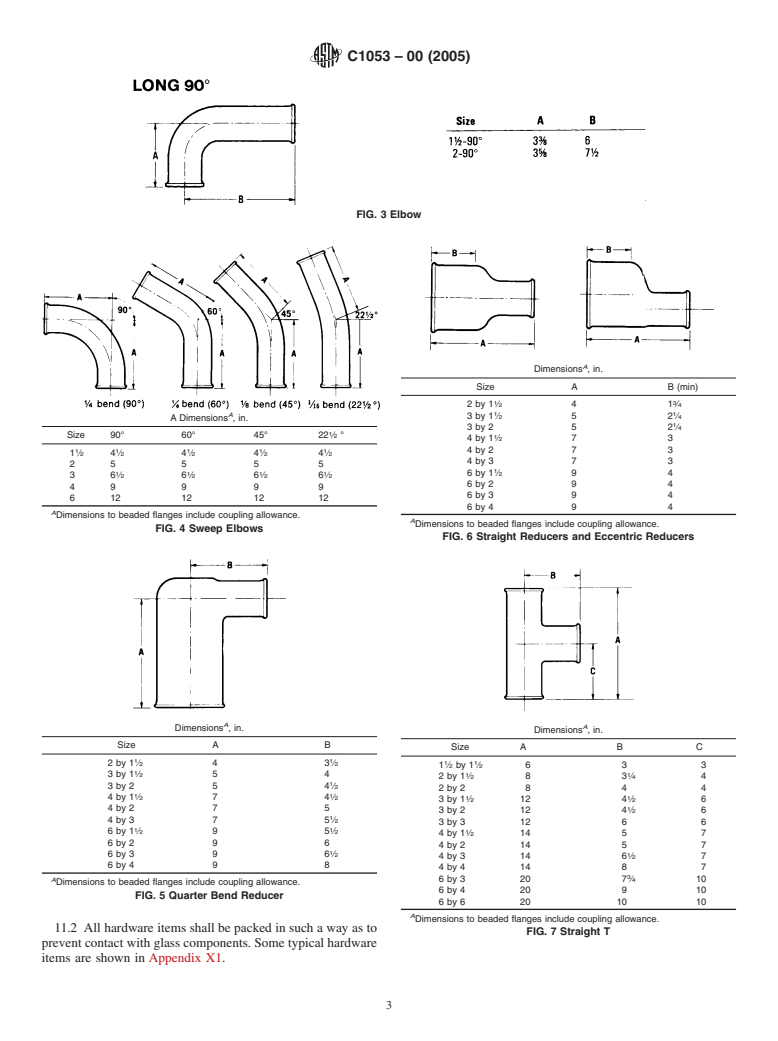
configurations are as illustrated in Figs. 1-45. deliveryunlessotherwiseagreeduponbythepurchaserandthe
seller.
TABLE 2 Flange Face Squareness
11. Packaging
Squareness
11.1 Pipe, fittings, and hardware shall be so packaged as to
Nominal Pipe Size, in. Measurement,
Max, in.
prevent damage during transportation and handling. Those
1 1
1 ⁄2 to 2 ⁄32 items packed in containers conforming to all construction
3 ⁄64
requirements of consolidated freight classification as to burst-
4 ⁄16
ingtests,sizelimit,andgrossmassshallbeconsideredasbeing
6 ⁄64
properly packed.
C1053 – 00 (2005)
FIG. 3 Elbow
A
Dimensions ,in.
Size A B (min)
1 3
2by1 ⁄2 41 ⁄4
1 1
A
3by1 ⁄2 52 ⁄4
A Dimensions ,in.
3by2 5 2 ⁄4
Size 90° 60° 45° 22 ⁄2 ° 1
4by1 ⁄2 73
1 1 1 1 1 4by2 7 3
1 ⁄2 4 ⁄2 4 ⁄2 4 ⁄2 4 ⁄2
4by3 7 3
25 5 5 5
1 1 1 1 6by1 ⁄2 94
36 ⁄2 6 ⁄2 6 ⁄2 6 ⁄2
6by2 9 4
49 9 9 9
6by3 9 4
612 12 12 12
6by4 9 4
A
Dimensions to beaded flanges include coupling allowance.
A
Dimensions to beaded flanges include coupling allowance.
FIG. 4 Sweep Elbows
FIG. 6 Straight Reducers and Eccentric Reducers
A
A
Dimensions ,in.
Dimensions ,in.
Size A B
Size A B C
1 1
2by1 ⁄2 43 ⁄2 1 1
1 ⁄2 by 1 ⁄263 3
3by1 ⁄2 54 1 1
2by1 ⁄2 83 ⁄4 4
3by2 5 4 ⁄2
2by2 8 4 4
1 1
4by1 ⁄2 74 ⁄2 1 1
3by1 ⁄2 12 4 ⁄2 6
4by2 7 5
3by2 12 4 ⁄2 6
4by3 7 5 ⁄2
3by3 12 6 6
1 1
6by1 ⁄2 95 ⁄2
4by1 ⁄2 14 5 7
6by2 9 6
4by2 14 5 7
6by3 9 6 ⁄2 1
4by3 14 6 ⁄2 7
6by4 9 8
4by4 14 8 7
A
6by3 20 7 ⁄4 10
Dimensions to beaded flanges include coupling allowance.
6by4 20 9 10
FIG. 5 Quarter Bend Reducer
6 by 6 20 10 10
A
Dimensions to beaded flanges include coupling allowance.
11.2 All hardware items shall be packed in such a way as to
FIG. 7 Straight T
preventcontactwithglasscomponents.Sometypicalhardware
items are shown in Appendix X1.
C1053 – 00 (2005)
FIG. 8 Test T with Clean-Out
A
Dimensions ,in.
Size A B C
1 1 1 3
1 ⁄2 by 1 ⁄2 6
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.