ASTM D7649-19
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determination of Trace Carbon Dioxide, Argon, Nitrogen, Oxygen and Water in Hydrogen Fuel by Jet Pulse Injection and Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometer Analysis (Withdrawn 2023)
Standard Test Method for Determination of Trace Carbon Dioxide, Argon, Nitrogen, Oxygen and Water in Hydrogen Fuel by Jet Pulse Injection and Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometer Analysis (Withdrawn 2023)
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 Low operating temperature fuel cells such as proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs) require high purity hydrogen for maximum performance. The following are the reported effects (SAE TIR J2719) of the compounds determined by this test method.
5.2 Carbon Dioxide (CO2), acts largely as a diluent; however, in the fuel cell environment, CO2 can be transformed into CO.
5.3 Water (H2O), is an inert impurity, as it does not affect the function of a fuel cell stack; however, it provides a transport mechanism for water-soluble contaminants, such as Na+ or K+. In addition, it may form ice on valve internal surface at cold weather or react exothermally with metal hydride used as hydrogen fuel storage.
5.4 Inert Gases (N2 and Ar), do not normally react with fuel cell components or fuel cell system and are considered diluents. Diluents can decrease fuel cell stack performance.
5.5 Oxygen (O2), in low concentrations is considered an inert impurity, as it does not adversely affect the function of a fuel cell stack; however, it is a safety concern for vehicle on board fuel storage as it can react violently with hydrogen to generate water and heat.
SCOPE
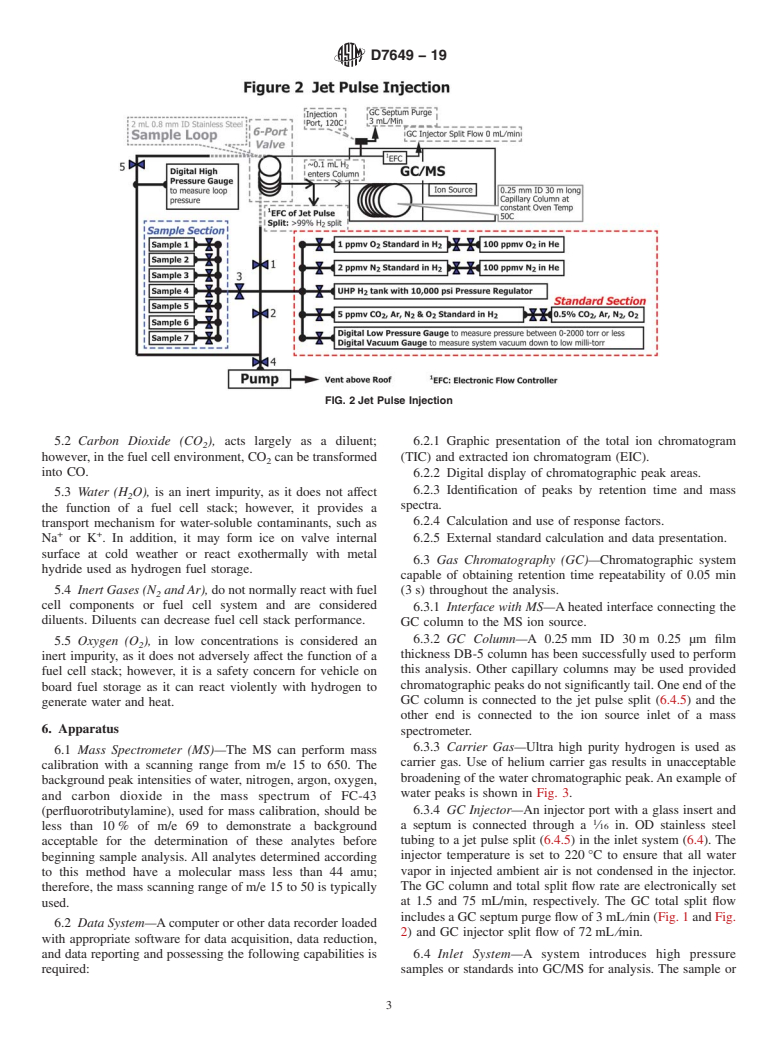
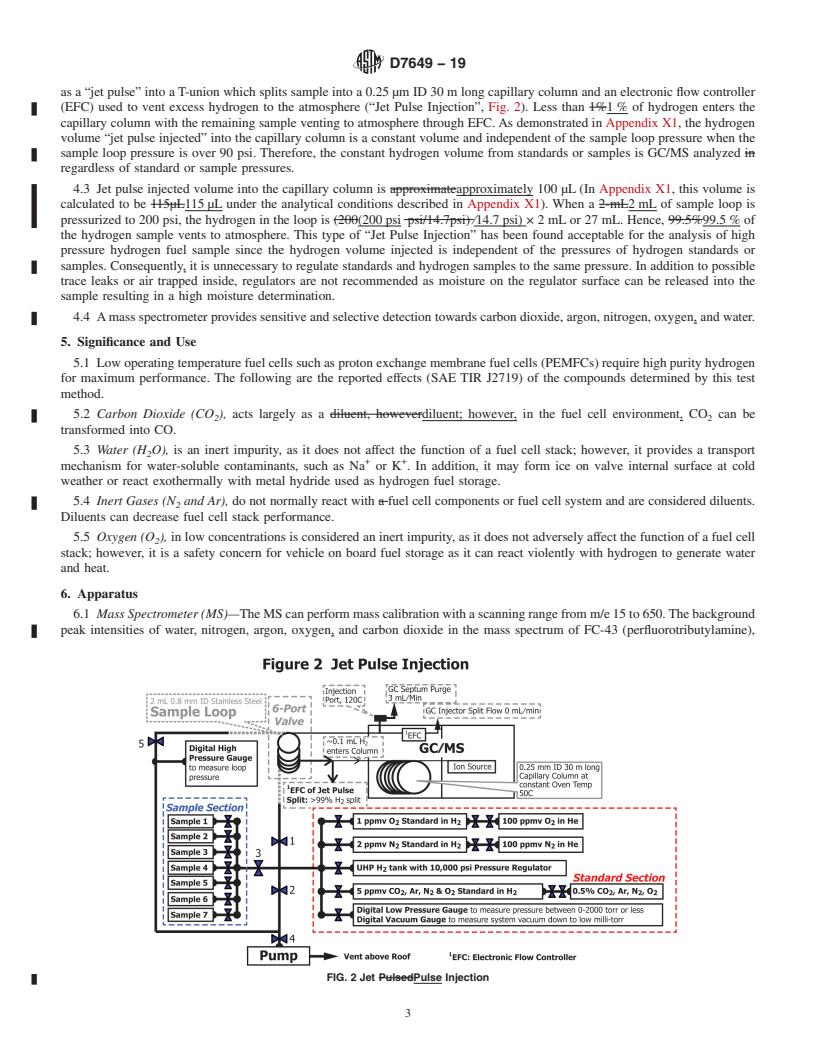
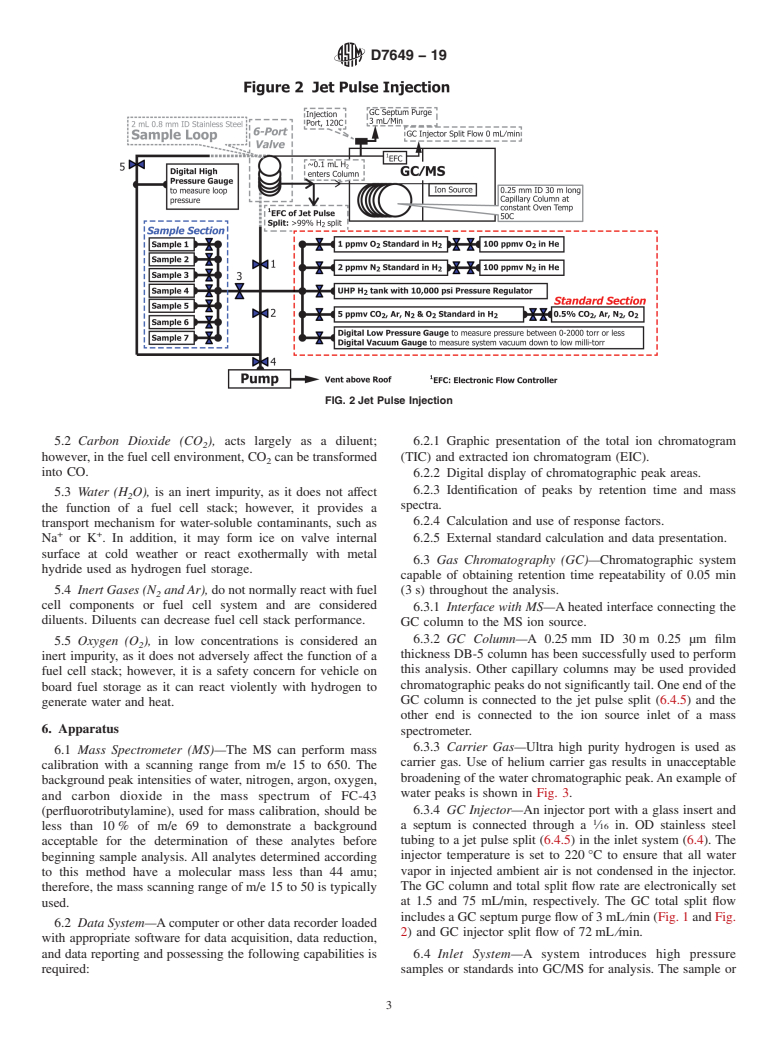
1.1 This test method describes a procedure primarily for the determination of carbon dioxide, argon, nitrogen, oxygen, and water in high pressure fuel cell grade hydrogen by gas chromatograph/mass spectrometer (GC/MS) with injection of sample at the same pressure as sample without pressure reduction, which is called “Jet Pulse Injection.” The procedures described in this method were designed to measure carbon dioxide at 0.5 micromole per mole (ppmv), Argon 1 ppmv, nitrogen 5 ppmv, oxygen 2 ppmv, and water 4 ppmv.
1.2 Units—The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses after SI units are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.3 The mention of trade names in standard does not constitute endorsement or recommendation for use. Other manufacturers of equipment or equipment models can be used.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
WITHDRAWN RATIONALE
This test method described a procedure primarily for the determination of carbon dioxide, argon, nitrogen, oxygen, and water in high pressure fuel cell grade hydrogen by gas chromatograph/mass spectrometer (GC/MS) with injection of sample at the same pressure as sample without pressure reduction, which is called “Jet Pulse Injection.”
Formerly under the jurisdiction of Committee D03 on Gaseous Fuels, this test method was withdrawn in November 2023. This standard is being withdrawn without replacement because there is no ILS.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D7649 − 19
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Trace Carbon Dioxide, Argon, Nitrogen,
Oxygen and Water in Hydrogen Fuel by Jet Pulse Injection
1
and Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometer Analysis
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7649; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope E177Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in
ASTM Test Methods
1.1 Thistestmethoddescribesaprocedureprimarilyforthe
E691Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
determination of carbon dioxide, argon, nitrogen, oxygen, and
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
water in high pressure fuel cell grade hydrogen by gas
3
2.2 Other Standards:
chromatograph/mass spectrometer (GC/MS) with injection of
SAE TIR J2719Information Report on the Development of
sample at the same pressure as sample without pressure
aHydrogenQualityGuidelineforFuelCellVehiclesApril
reduction,whichiscalled“JetPulseInjection.”Theprocedures
2008
described in this method were designed to measure carbon
dioxide at 0.5micromole per mole (ppmv), Argon 1 ppmv,
3. Terminology
nitrogen 5 ppmv, oxygen 2 ppmv, and water 4 ppmv.
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
1.2 Units—The values stated in SI units are to be regarded
3.1.1 absolute pressure, n—pressure measured with refer-
as standard. The values given in parentheses after SI units are
ence to absolute zero pressure, usually expressed as kPa, mm
providedforinformationonlyandarenotconsideredstandard.
Hg, bar or psi.
1.3 The mention of trade names in standard does not
constitute endorsement or recommendation for use. Other 3.1.1.1 Discussion—All the pressures mentioned in this
manufacturersofequipmentorequipmentmodelscanbeused. method are absolute pressure.
3.1.2 constituent, n—a component (or compound) found
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
within a hydrogen fuel mixture.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
3.1.3 contaminant, n—impurity that adversely affects the
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter- componentswithinthefuelcellsystemorthehydrogenstorage
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
system by reacting with its components.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accor-
3.1.3.1 Discussion—An adverse effect can be reversible or
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
irreversible.
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
3.1.4 dynamic calibration, n—calibration of an analytical
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
system using calibration gas standard generated by diluting
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
knownconcentrationcompressedgasstandardswithhydrogen,
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
as used in this method for carbon dioxide, argon, nitrogen, and
oxygen (7.3 and 7.4).
2. Referenced Documents
3.1.5 extracted ion chromatogram (EIC), n—a GC/MS
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
chromatogram where a selected ion is plotted to determine the
compound(s) of interest.
1
3.1.6 fuel cell grade hydrogen, n—hydrogen satisfying the
ThistestmethodisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeD03onGaseous
Fuels and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D03.14 on Hydrogen and
specifications in SAE TIR J2719.
Fuel Cells.
3.1.7 hydrogen fuel, n—hydrogen to be tested without
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2019. Published February 2020. Originally
approved in 2010. Last previous edition approved in 2017 as D7649–10(2017). compositional change due to sample introduction, etc.
DOI: 10.1520/D7649-19.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
3
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on AvailablefromSAEInternational(SAE),400CommonwealthDr.,Warrendale,
the ASTM website. PA 15096, http://www.sae.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D7649 − 19
3.1.8 jet pulse injection, n—high pressure hydrogen fuel inAppendixX1,thehydrogenvolume“jetpulseinjected”into
sample is introduced instantaneously at the same pressure into the capillary column is a constant volume and independent
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D7649 − 10 (Reapproved 2017) D7649 − 19
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Trace Carbon Dioxide, Argon, Nitrogen,
Oxygen and Water in Hydrogen Fuel by Jet Pulse Injection
1
and Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometer Analysis
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7649; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method describes a procedure primarily for the determination of carbon dioxide, argon, nitrogen, oxygen, and water
in high pressure fuel cell grade hydrogen by gas chromatograph/mass spectrometer (GC/MS) with injection of sample at the same
pressure as sample without pressure reduction, which is called “Jet Pulse Injection”.Injection.” The procedures described in this
method were designed to measure carbon dioxide at 0.5micromole0.5 micromole per mole (ppmv), Argon 1 ppmv, nitrogen 5
ppmv and ppmv, oxygen 2 ppmv, and water 4 ppmv.
1.2 Units—The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. The values stated in inch-pound given in parentheses
after SI units are provided for information only. only and are not considered standard.
1.3 The mention of trade names in standard does not constitute endorsement or recommendation for use. Other manufacturers
of equipment or equipment models can be used.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of
regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
E177 Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in ASTM Test Methods
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to Determine the Precision of a Test Method
3
2.2 Other Standards:
SAE TIR J2719 Information Report on the Development of a Hydrogen Quality Guideline for Fuel Cell Vehicles April 2008
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.1.1 absolute pressure—pressure, n—pressure measured with reference to absolute zero pressure, usually expressed as kPa,
mm Hg, bar or psi. All the pressures mentioned in this method are absolute pressure.
3.1.1.1 Discussion—
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D03 on Gaseous Fuels and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D03.14 on Hydrogen and Fuel
Cells.
Current edition approved April 1, 2017Dec. 1, 2019. Published April 2017February 2020. Originally approved in 2010. Last previous edition approved in 20102017 as
D7649D7649 – 10-10.(2017). DOI: 10.1520/D7649–10R17.10.1520/D7649-19.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
Available from SAE International (SAE), 400 Commonwealth Dr., Warrendale, PA 15096-0001, http://aerospace.sae.org.15096, http://www.sae.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D7649 − 19
All the pressures mentioned in this method are absolute pressure.
3.1.2 constituent—constituent, n—Aa component (or compound) found within a hydrogen fuel mixture.
3.1.3 contaminant—contaminant, n—impurity that adversely affects the components within the fuel cell system or the hydrogen
storage system by reacting with its components. An adverse effect can be reversible or irreversible.
3.1.3.1 Discussion—
An adverse effect can be reversible or irreversible.
3.1.4 dynami
...
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D7649 − 19
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Trace Carbon Dioxide, Argon, Nitrogen,
Oxygen and Water in Hydrogen Fuel by Jet Pulse Injection
1
and Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometer Analysis
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7649; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope E177 Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in
ASTM Test Methods
1.1 This test method describes a procedure primarily for the
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
determination of carbon dioxide, argon, nitrogen, oxygen, and
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
water in high pressure fuel cell grade hydrogen by gas
3
2.2 Other Standards:
chromatograph/mass spectrometer (GC/MS) with injection of
SAE TIR J2719 Information Report on the Development of
sample at the same pressure as sample without pressure
a Hydrogen Quality Guideline for Fuel Cell Vehicles April
reduction, which is called “Jet Pulse Injection.” The procedures
2008
described in this method were designed to measure carbon
dioxide at 0.5 micromole per mole (ppmv), Argon 1 ppmv,
3. Terminology
nitrogen 5 ppmv, oxygen 2 ppmv, and water 4 ppmv.
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
1.2 Units—The values stated in SI units are to be regarded
3.1.1 absolute pressure, n—pressure measured with refer-
as standard. The values given in parentheses after SI units are
ence to absolute zero pressure, usually expressed as kPa, mm
provided for information only and are not considered standard.
Hg, bar or psi.
1.3 The mention of trade names in standard does not
constitute endorsement or recommendation for use. Other 3.1.1.1 Discussion—All the pressures mentioned in this
manufacturers of equipment or equipment models can be used. method are absolute pressure.
3.1.2 constituent, n—a component (or compound) found
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
within a hydrogen fuel mixture.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro- 3.1.3 contaminant, n—impurity that adversely affects the
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
components within the fuel cell system or the hydrogen storage
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. system by reacting with its components.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accor-
3.1.3.1 Discussion—An adverse effect can be reversible or
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
irreversible.
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
3.1.4 dynamic calibration, n—calibration of an analytical
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
system using calibration gas standard generated by diluting
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
known concentration compressed gas standards with hydrogen,
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
as used in this method for carbon dioxide, argon, nitrogen, and
oxygen (7.3 and 7.4).
2. Referenced Documents
3.1.5 extracted ion chromatogram (EIC), n—a GC/MS
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
chromatogram where a selected ion is plotted to determine the
compound(s) of interest.
1
3.1.6 fuel cell grade hydrogen, n—hydrogen satisfying the
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D03 on Gaseous
Fuels and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D03.14 on Hydrogen and
specifications in SAE TIR J2719.
Fuel Cells.
3.1.7 hydrogen fuel, n—hydrogen to be tested without
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2019. Published February 2020. Originally
approved in 2010. Last previous edition approved in 2017 as D7649 – 10(2017). compositional change due to sample introduction, etc.
DOI: 10.1520/D7649-19.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
3
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available from SAE International (SAE), 400 Commonwealth Dr., Warrendale,
the ASTM website. PA 15096, http://www.sae.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D7649 − 19
3.1.8 jet pulse injection, n—high pressure hydrogen fuel in Appendix X1, the hydrogen volume “jet pulse injected” into
sample is introduced instantaneously at the same pressure into
the capillary column is a constant volume and independent of
GC/MS.
the sample loop pressure when the sample loop pre
...










Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.