ASTM D7650-21
(Practice)Standard Practice for Sampling of Particulate Matter in High Pressure Gaseous Fuels with an In-Stream Filter
Standard Practice for Sampling of Particulate Matter in High Pressure Gaseous Fuels with an In-Stream Filter
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 This sampling procedure is used to collect a particulate filter sample containing particulates 0.2 µm or larger in size to be used to measure the size and concentration of particulates in a gaseous fuel stream.
SCOPE
1.1 This practice is primarily for sampling particulates in gaseous fuels up to a nominal working pressure (NWP) of 70 MPa (10 152 psi) using an in-stream filter. This practice describes sampling apparatus design, operating procedures, and quality control procedures required to obtain the stated levels of precision and accuracy.
1.2 Units—The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses after SI units are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D7650 − 21
Standard Practice for
Sampling of Particulate Matter in High Pressure Gaseous
Fuels with an In-Stream Filter
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7650; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
4,5
1. Scope 2.3 CSA/ANSI/NGV Standards:
HGV 4.1Hydrogen Dispensing Systems
1.1 This practice is primarily for sampling particulates in
NGV 1Fueling Connection Devices
gaseous fuels up to a nominal working pressure (NWP) of 70
NGV 4.1Natural Gas Vehicle (NGV) Dispensing Systems
MPa (10152 psi) using an in-stream filter. This practice
2.4 SAE Standards:
describes sampling apparatus design, operating procedures,
SAE J2579 Standard for Fuel Systems in Fuel Cell and
and quality control procedures required to obtain the stated
Other Hydrogen Vehicles
levels of precision and accuracy.
SAE J2600Compressed Hydrogen Surface Vehicle Fueling
1.2 Units—The values stated in SI units are to be regarded
Connection Devices
as standard. The values given in parentheses after SI units are
SAE J2719Hydrogen Fuel Quality for Fuel Cell Vehicles
providedforinformationonlyandarenotconsideredstandard.
2.5 ISO Standard:
ISO 14687Hydrogen Fuel Quality— Product Specification
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
2.6 ASME Standard:
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
2.7 UN Global Technical Regulation:
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
No. 13Global Technical Regulation on Hydrogen and Fuel
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
Cell Vehicles
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
2.8 NIST Standard:
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
Handbook 44 Specifications,Tolerances, and OtherTechni-
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
cal Requirements for Weighing and Measuring Devices
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
3. Terminology
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
3.1 Definitions—For definitions of general terms used in
D03 Gaseous Fuels standards, refer to Terminology D4150.
2. Referenced Documents
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
2.1 ASTM Standards:
3.2.1 maximum allowable working pressure (MAWP),
D4150Terminology Relating to Gaseous Fuels
n—the maximum gauge pressure of the working fluid (gas or
D7651Test Method for Gravimetric Measurement of Par-
liquid)towhichapieceofprocessequipmentorsystemisrated
ticulate Concentration of Hydrogen Fuel
with consideration for initiating fault management above
2.2 NFPA Standard:
normal operation.
NFPA 2Hydrogen Technologies Code
Available from Canadian Standards Association (CSA), 178 Rexdale Blvd.,
Toronto, ON M9W 1R3, Canada, http://www.csagroup.org.
1 5
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D03 on Gaseous Available fromAmerican National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St.,
Fuels and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D03.14 on Hydrogen and 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
Fuel Cells. AvailablefromSAEInternational(SAE),400CommonwealthDr.,Warrendale,
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2021. Published January 2022. Originally PA 15096-0001, http://www.sae.org.
approved in 2010. Last previous edition approved in 2013 as D7650–13. DOI: Available from International Organization for Standardization (ISO), 1, ch. de
10.1520/D7650-21. la Voie-Creuse, CP 56, CH-1211 Geneva 20, Switzerland, http://www.iso.org.
2 8
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or Available from American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), ASME
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM International Headquarters, Two Park Ave., New York, NY 10016-5990, http://
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on www.asme.org.
the ASTM website. Available from UNECE, https://unece.org/.
3 10
Available from National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), 1 Batterymarch Available from National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), 100
Park, Quincy, MA 02169-7471, http://www.nfpa.org. Bureau Dr., Stop 1070, Gaithersburg, MD 20899-1070, http://www.nist.gov.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
D7650 − 21
3.2.2 nominal working pressure (service pressure, working instrumentation design of the two different sampling ap-
pressure), n—the gauge pressure that characterizes typical proaches. Both apparatuses have the following:
operation of a pressure vessel, container, or system. (1)Receptacle to attach to dispenser nozzle,
3.2.2.1 Discussion—For compressed hydrogen gas (2)Filter and filter holder,
containers, NWP is the container pressure, as specified by the (3) Pressure relief valve to protect against over-
manufacturer, at a uniform gas temperature of 15°C (59°F) pressurization,
and full gas content. (4)Control valves to regulate the gas,
(5)Pressuregaugetomonitorthepressureoftheapparatus,
3.2.3 pinhole, n—asmallholegeneratedduringsamplingof
and
particulates that can be identified by microscope.
(6)Check valves to prevent back flow of the gas from the
3.3 Abbreviations:
vent stack. If the apparatus has a tank, check valves should be
MAWP—Maximum Allowable Working Pressure
placed upstream of the tank to prevent any gas from the tank
PM—Particulate Matter
from flowing backwards across the filter.
NWP—Nominal Working Pressure
7.1.1 The requirements for these components and for com-
PPE—Personal Protective Equipment
ponents specific to sampling are discussed below. The design
PRD—Pressure Relief Device
of the apparatus can vary if the requirements below are met.
4. Summary of Practice
7.2 General Apparatus Requirements—See CSA HGV 4.1
for general information on hydrogen and NGV 4.1 for general
4.1 This practice provides a procedure for the sampling of
information on natural gas.
particulate matter (PM) contained in gaseous fuels primarily
7.2.1 All equipment shall be designed to the maximum
used in motor vehicles. It is designed to collect all particulates
allowable working pressure (MAWP) of the dispenser.
0.2µm or larger contained in a known amount of fuel at a
7.2.2 Allequipmentshallbedesignedtothemaximumpeak
station dispenser nozzle in a way that simulates a vehicle
flow rate of the dispenser. The peak flow rate for most
fueling event.
dispensers for passenger cars is typically 60 g/s.
4.1.1 The practice has two different approaches:
(1)The Tank Approach emulates a typical fueling by 7.2.3 All apparatus components shall be constructed with
collecting the gas, which passes across the filter, into a tank. materials compatible with the gaseous fuel being tested. High
(2)The Atmosphere Approach allows the gas to escape to pressure hydrogen may alter the mechanical properties of
atmosphere but sets a constant back pressure typically found common structural metal alloys. These effects are similar for
during a fueling. all relevant structural metals and alloys in that hydrogen
reduces the resistance to crack initiation and crack growth and
5. Significance and Use
reduces ductility. The reduction is dependent on several vari-
ablesbasedonthematerial,theenvironment,andthemechani-
5.1 This sampling procedure is used to collect a particulate
cal loading conditions. This can lead to failure or hydrogen
filter sample containing particulates 0.2µm or larger in size to
leaks. The sampling apparatus and all equipment used accord-
beusedtomeasurethesizeandconcentrationofparticulatesin
ing to this test method must be closely inspected for signs of
a gaseous fuel stream.
cracks or any other combination of signs of wear and damage.
6. Interferences
7.2.4 The apparatus shall be built to withstand gaseous fuel
temperatures ranging from −40°C to 50°C, except the tank
6.1 Dust and other environmental PM 10 µm or larger will
which should have a temperature range of −40°C to 85°C.
interfere with the accurate measurement of particulates;
therefore, every measure should be taken according to Section 7.2.5 Theequipmentshallbedesignedtooperateinambient
13 to prevent contamination of the apparatus and all conditions.
equipment, supplies, and gases used in these procedures.
7.2.6 Refer to Section 10 (Hazards) for more information
regarding safety requirements. A hazard analysis shall be
7. Apparatus Design
performed on the apparatus. This shall be available to share
7.1 Fig.1andFig.2belowshowarecommendedpipingand with dispenser manufacturers/operators.
FIG. 1 Piping and Instrumentation Diagram Sampling Using the Tank Approach
D7650 − 21
FIG. 2 Piping and Instrumentation Diagram Sampling Using the Atmosphere Approach
7.2.7 The flow path from the nozzle to the filter shall be andensuresitisnotrupturedduringahigh-pressurepulse.The
designed to minimize trapping particulates on any surface. inletandoutletadaptersshallhaveaprotectivecaptomaintain
7.2.8 All hose assemblies shall have an anti-whip that is the sample integrity and keep particulates from entering the
attached to a suitable anchor point during sampling to prevent filter holder during transport.
the hose from whipping should the connection become un-
7.4.1 Filter Holder Support—The filter holder support must
coupled.
be designed to securely hold the filter holder and dispenser
hose nozzle in a downward vertical position. The nozzle shall
7.3 Receptacle—The receptacles shall be designed in accor-
be held firmly and not move or shake during particulate
dance with SAE J2600 or ISO 17268 for hydrogen or NGV1
sampling.
for natural gas. Most receptacles have an integrated particulate
filter installed in them. Receptacles for testing purposes shall
7.5 Pressure Relief Device (PRD)—Theapparatusshouldbe
not contain a filter.
equipped with a PRD to avoid over-pressurization. The PRD,
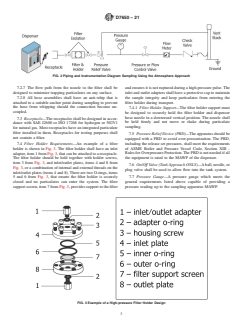
7.4 Filter Holder Requirements—An example of a filter includingthereleasesetpressures,shallmeettherequirements
holder is shown in Fig. 3. The filter holder shall have an inlet of ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code, Section XIII -
adapter,item1fromFig.3,thatcanbeattachedtoareceptacle. RulesforOverpressureProtection.ThePRDisnotneededifall
The filter holder should be held together with holder screws, the equipment is rated to the MAWP of the dispenser.
item 3 from Fig. 3, and inlet/outlet plates, items 4 and 8 from
7.6 On/Off Valve (Tank Approach ONLY)—Aball,needle,or
Fig. 3, or a combination of internal and external threads on the
plug valve shall be used to allow flow into the tank system.
inlet/outletplates(items4and8).TherearetwoO-rings,items
5 and 6 from Fig. 3, that ensure the filter holder is securely 7.7 Pressure Gauge—A pressure gauge which meets the
closed and no particulates can enter the system. The filter general requirements listed above capable of providing a
supportscreen,item7fromFig.3,providessupporttothefilter pressure reading up to the sampling apparatus MAWP.
FIG. 3 Example of a High-pressure Filter Holder Design
D7650 − 21
7.8 Pressure or Flow Control Valve (Atmosphere Approach 8.2 Anti-static Bags—Anti-static bags shall be used during
ONLY)—Apressure or flow control valve that can regulate the transport of the filter and filter holder. This will prevent any
pressure during sampling to 20MPa (2900psi). static buildup during transport and ensure that no particulates
will enter the filter holder.
7.9 Tank System (Tank Approach ONLY)—For systems
whichusetheTankApproach,thetankshallmeettheminimum 8.3 Glove Box (Option A)—Agloveboxisasealedchamber
requirements in one of the following standards: SAE J2579 or that, in this application, allows weight measurements to be
UN GTR 13. The high-pressure filter holder shall connect to taken without particulate contamination from ambient air.Two
thetankusingafuelinghosemadeofmaterialthatconformsto gloves are built into the front side of the glove box so that the
the general requirements listed in 7.2. Unless the tank is user can place their hands into the gloves and perform weight
Hazmat certified by local and government agencies, then it measurements, install filters, and assemble the filter holders.A
shall be exhausted completely before leaving the station. side evacuation port or antechamber should also be used to
minimize contamination of the glove box environment. The
7.10 Vent Stack—For systems which use theAtmosphere or
glove box must always be kept clean, and any visual PM must
Tank Approach, a portable vent stack or the refueling station
be removed immediately. The glove box should always have a
vent stack shall be connected after the outlet of the particulate
steady flow of clean, dry nitrogen. The temperature and
sampling holder for the atmosphere approach or used to
humidityshouldbekeptconsistentat21 62°Cand35 65%
exhaust the tank system; see 7.9.
relative humidity and should be monitored by a data logger or
7.10.1 Location of Vent Stack—Gaseousfuelmustbevented
other device installed in the glove box.
at a safe distance from personnel and equipment. The ventila-
tionoutletshouldbeataminimumdistancefromthesampling 8.4 Clean Room (Option B)—Analysis should occur in a
andthegroundascalculatedusingNFPA2,Chapter7.3.2.3.1.1 climate-controlled, draft-free room constantly under positive
tables based on the diameter of the vent stack. The vent stack pressure. The relative humidity must be maintained at 35 6
should be placed clear of any overhead or nearby objects that 5% and the temperature must be maintained at 21 6 2°C. If
may trap gas. Depending on the ambient and gas conditions, thetemperatureorhumidityfallsoutofrange,noweighingcan
the gaseous fuel may not always flow upward. Ensure that occur for 24h. Before entering the clean room, the analyst
venting is performed in accordance with applicable national, must step on "sticky" floor mats to remove any PM from the
regional, and local laws and regulations. It is recommended to bottomsofshoes.TheroommusthaveaHEPAairfilteronthe
set the vent downwind of the dispenser and sampling event. inlet air system to remove particulates from the air.
7.11 Grounding—All components of the apparatus shall
9. Reagents and Materials
alw
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D7650 − 13 D7650 − 21
Standard Test Method Practice for
Sampling of Particulate Matter in High Pressure Hydrogen
used as a Gaseous FuelGaseous Fuels with an In-Stream
Filter
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7650; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method practice is primarily for sampling particulates in hydrogen fuel used in hydrogen fuel cell vehicles or gaseous
hydrogen powered internal combustion vehicle engines up to pressures gaseous fuels up to a nominal working pressure (NWP)
of 70 MPa (700 bars)(10 152 psi) using an in-stream filter. This test method practice describes sampling apparatus design,
operating procedures, and quality control procedures required to obtain the stated levels of precision and accuracy.
1.2 Units—The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this The
values given in parentheses after SI units are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.2.1 Exception—In 7.1 and 10.1.1 the values stated in psi are for information only.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of
the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of
regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D4150 Terminology Relating to Gaseous Fuels
D7651 Test Method for Gravimetric Measurement of Particulate Concentration of Hydrogen Fuel
2.2 NFPA Standard:
NFPA 2 Hydrogen Technologies Code
This test method practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D03 on Gaseous Fuels and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D03.14 on Hydrogen
and Fuel Cells.
Current edition approved May 1, 2013Dec. 1, 2021. Published June 2013January 2022. Originally approved in 2010. Last previous edition approved in 20102013 as
D7650D7650 – 13.–10. DOI: 10.1520/D7650–13.10.1520/D7650-21.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Available from National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), 1 Batterymarch Park, Quincy, MA 02169-7471, http://www.nfpa.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
D7650 − 21
4,5
2.3 CSA/ANSI/NGV Standards:
HGV 4.1 Hydrogen Dispensing Systems
NGV 1 Fueling Connection Devices
NGV 4.1 Natural Gas Vehicle (NGV) Dispensing Systems
2.4 SAE Standards:
SAE J2719J2579 Hydrogen Fuel Quality Standard for Fuel Cell Systems in Fuel Cell and Other Hydrogen Vehicles
SAE J2600 Compressed Hydrogen Surface Vehicle RefuelingFueling Connection Devices
SAE J2719 Hydrogen Fuel Quality for Fuel Cell Vehicles
2.5 ISO Standard:
ISO/CD 14687–2ISO 14687 Hydrogen fuel — Product Specification — Part 2: Proton exchange membrane (PEM) fuel cell
applications for road vehicles.Fuel Quality— Product Specification
2.6 EUASME Standard:
97/23/EC Pressure Equipment Directive of the EU set out the standards for the design and fabrication of pressure
equipmentBoiler and Pressure Vessel Code
2.7 DIN Standard:UN Global Technical Regulation:
DIN EN 12266-1No. 13 Industrial valves-Testing of metallic valves-Part 1: Pressure test, test procedures and acceptance criteria
Mandatory RequirementsGlobal Technical Regulation on Hydrogen and Fuel Cell Vehicles
2.8 APINIST Standard:
API 598Handbook 44 Valve Inspection and TestingSpecifications, Tolerances, and Other Technical Requirements for Weighing
and Measuring Devices
3. Terminology
3.1 Acronyms:
3.1.1 FCV—Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicle.
3.1.2 HQSA—Hydrogen quality sampling assembly for sampling gaseous hydrogen fuel.
3.1.3 PEM—Polymer Electrolyte Membrane or Proton Exchange Membrane
3.1.4 PSA-H70—Particulate sampling adapter for sampling particulate in hydrogen fuel up to pressures of 70 MPa.
3.1.5 SAE International—Society of Automotive Engineering
3.1 Definitions—For definitions of general terms used in D03 Gaseous Fuels standards, refer to Terminology D4150.
3.2 Definitions:Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.2.1 maximum allowable working pressure (MAWP), n—the maximum gauge pressure of the working fluid (gas or liquid) to
which a piece of process equipment or system is rated with consideration for initiating fault management above normal operation.
3.2.2 nominal working pressure (service pressure, working pressure), n—the gauge pressure that characterizes typical operation
of a pressure vessel, container, or system.
3.2.2.1 Discussion—
For compressed hydrogen gas containers, NWP is the container pressure, as specified by the manufacturer, at a uniform gas
temperature of 15 °C (59 °F) and full gas content.
Available from Canadian Standards Association (CSA), 178 Rexdale Blvd., Toronto, ON M9W 1R3, Canada, http://www.csagroup.org.
Available from American National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St., 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
Available from SAE International (SAE), 400 Commonwealth Dr., Warrendale, PA 15096-0001, http://www.sae.org.
Available from International Organization for Standardization (ISO), 1, ch. de la Voie-Creuse, CP 56, CH-1211 Geneva 20, Switzerland, http://www.iso.org.
Available from European Committee for Standardization (CEN), Avenue Marnix 17, B-1000, Brussels, Belgium, http://www.cen.eu.American Society of Mechanical
Engineers (ASME), ASME International Headquarters, Two Park Ave., New York, NY 10016-5990, http://www.asme.org.
Available from Deutsches Institut fur Normung e.V.(DIN), Burggrafenstrasse 6, 10787 Berlin, Germany, http://www.din.de.
Available from American Petroleum Institute (API), 1220 L. St., NW, Washington, DC 20005-4070, http://www.api.org.
HEPA is a trademark of the HEPA Corporation, 3071 East Coronado Street Anaheim, CA 92806.
The mention of trade names in this test method does not constitute endorsement or recommendation. Other manufacturers of equipment or equipment models can be
used.Available from UNECE, https://unece.org/.
Microsoft Excel is a trademark of the Microsoft Corporation, One Microsoft Way Redmond, WA 98052-6399.Available from National Institute of Standards and
Technology (NIST), 100 Bureau Dr., Stop 1070, Gaithersburg, MD 20899-1070, http://www.nist.gov.
D7650 − 21
3.2.3 pinhole—pinhole, n—a small hole generated during sampling of particulate in hydrogen particulates that can be identified
by microscope.
3.3 SAE J2719 Hydrogen Fuel Quality for Fuel Cell Vehicles—Abbreviations:
This MAWP document specifies allowable levels of constituents in the hydrogen fuel at the vehicle/station interface.—Maximum
Allowable Working Pressure
PM—Particulate Matter
NWP—Nominal Working Pressure
PPE—Personal Protective Equipment
PRD—Pressure Relief Device
3.4 SAE J2600–Compressed Hydrogen Surface Vehicle Refueling Connection Devices—This document specifies the design
requirements for nozzles and receptacles used in high pressure hydrogen applications such as delivery from a fueling station to a
FCV.
4. Summary of Test MethodPractice
4.1 This test method practice provides a procedure for the sampling of particulate matter (PM) contained in hydrogen used as a
FCV fuel. gaseous fuels primarily used in motor vehicles. It is designed to collect all particulates 0.2 μm 0.2 μm or larger contained
in a known amount of hydrogenfuel at a station dispenser nozzle in a way that simulates a FCV or a gaseous hydrogen powered
internal combustion vehicle engine fueling event. The adapter used for sampling particulates in hydrogen fuel is called a Particulate
Sampling Adapter for pressures up to 70 MPa (PSA-H70) and is described in Section vehicle fueling event. 7. Great care should
be taken to avoid contamination and exposure of the PSA-H70, filters, and other equipment with particles sized 10 μm or larger
prior to use.
4.1.1 The practice has two different approaches:
(1) The Tank Approach emulates a typical fueling by collecting the gas, which passes across the filter, into a tank.
(2) The Atmosphere Approach allows the gas to escape to atmosphere but sets a constant back pressure typically found during
a fueling.
5. Significance and Use
5.1 Fuel cells such as proton exchange membrane fuel cells require high purity hydrogen for maximum material performance and
lifetime. Collection and measurement of particulate matter 0.2 μm or larger is necessary for assuring a feed gas of sufficient quality
to satisfy fuel cell system needs. In addition, internal combustion engines using high pressure hydrogen fuel also require low
particulate levels. Specifically, particulate matter has been implicated in the premature failure of pneumatic control components,
such as valves within vehicles. This sampling procedure is used to collect and measure samples containing particles 0.2 μm a
particulate filter sample containing particulates 0.2 μm or larger in size.size to be used to measure the size and concentration of
particulates in a gaseous fuel stream.
5.2 Although not intended for application to gases other than hydrogen and related fuel cell supply gases, the techniques within
this sampling procedure can be applied to other high pressure gaseous samples requiring particulate collection and measurement.
6. Interferences
6.1 Dust and other environmental particulate matter PM 10 μm or larger will interfere with the accurate measurement of
particulates contained in FCV quality hydrogen; particulates; therefore, every measure should be taken according to Section 1413
to avoidprevent contamination of the apparatus and all equipment, supplies, and gases used in these procedures.
7. Apparatus Design
NOTE 1—The use of trade names in this section are not intended as an endorsement for use.
7.1 Fig. 1 and Fig. 2 below show a recommended piping and instrumentation design of the two different sampling approaches.
Both apparatuses have the following:
(1) Receptacle to attach to dispenser nozzle,
D7650 − 21
FIG. 1 Piping and Instrumentation Diagram Sampling Using the Tank Approach
FIG. 12 PSA-H70 ComponentsPiping and Instrumentation Diagram Sampling Using the Atmosphere Approach
(2) Filter and filter holder,
(3) Pressure relief valve to protect against over-pressurization,
(4) Control valves to regulate the gas,
(5) Pressure gauge to monitor the pressure of the apparatus, and
(6) Check valves to prevent back flow of the gas from the vent stack. If the apparatus has a tank, check valves should be placed
upstream of the tank to prevent any gas from the tank from flowing backwards across the filter.
7.1.1 The requirements for these components and for components specific to sampling are discussed below. The design of the
apparatus can vary if the requirements below are met.
7.2 General Apparatus Requirements—See CSA HGV 4.1 for general information on hydrogen and NGV 4.1 for general
information on natural gas.
7.2.1 All equipment shall be designed to the maximum allowable working pressure (MAWP) of the dispenser.
7.2.2 All equipment shall be designed to the maximum peak flow rate of the dispenser. The peak flow rate for most dispensers
for passenger cars is typically 60 g/s.
7.2.3 All apparatus components shall be constructed with materials compatible with the gaseous fuel being tested. High pressure
hydrogen may alter the mechanical properties of common structural metal alloys. These effects are similar for all relevant structural
metals and alloys in that hydrogen reduces the resistance to crack initiation and crack growth and reduces ductility. The reduction
is dependent on several variables based on the material, the environment, and the mechanical loading conditions. This can lead
to failure or hydrogen leaks. The sampling apparatus and all equipment used according to this test method must be closely
inspected for signs of cracks or any other combination of signs of wear and damage.
7.2.4 The apparatus shall be built to withstand gaseous fuel temperatures ranging from −40 °C to 50 °C, except the tank which
should have a temperature range of −40 °C to 85 °C.
7.2.5 The equipment shall be designed to operate in ambient conditions.
7.2.6 Refer to Section 10 (Hazards) for more information regarding safety requirements. A hazard analysis shall be performed on
the apparatus. This shall be available to share with dispenser manufacturers/operators.
D7650 − 21
7.2.7 The flow path from the nozzle to the filter shall be designed to minimize trapping particulates on any surface.
7.2.8 All hose assemblies shall have an anti-whip that is attached to a suitable anchor point during sampling to prevent the hose
from whipping should the connection become uncoupled.
7.3 Receptacle—The receptacles shall be designed in accordance with SAE J2600 or ISO 17268 for hydrogen or NGV1 for natural
gas. Most receptacles have an integrated particulate filter installed in them. Receptacles for testing purposes shall not contain a
filter.
7.4 Filter Holder Requirements—The PSA-H70 has a design pressure of 800 Bar (11600 psi) and is certified after 97/23/EC and
API 598 (conform to DIN EN 12266-1) up to 1200 bar (17400 psi) shell test pressures with appropriate safety factors built in. It
is designed for a flow rate of 60 g per second of hydrogen without d
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.