ASTM E294-72(1999)
(Test Method)Test Method for Effective Pumping Speed of Vacuum Chamber Systems (Withdrawn 2000)
Test Method for Effective Pumping Speed of Vacuum Chamber Systems (Withdrawn 2000)
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the measurement of effective pumping speed of complete vacuum-chamber systems. The test method is suitable for all types of vacuum systems operating at pressures below 1 X 10 torr and for chambers larger than approximately 10 ft (0.3 m ).
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Standards Content (Sample)
STD-ASTM E294-ENGL 1972 - 0759530 Ob74223 442
Designation: E 294 - 72 (Reapproved 1999)
Nb
Standard Test Method for
Effective Pumping Speed of Vacuum Chamber Systems‘
niis standard is issued under the ked designatio0 E 294; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
Onpinai adoption or, ia the case. of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscripî epsïion (e) indicates an editorial change sinCe the last revision or reapproval.
suring devices. The chamber is pumped to a pressure (Po), then
1. scope
gas is admitted at a measured ñow rate (Q) to a point near the
1.1 This test method covers the measurement of effective
center of the test zone. The chamber pressure (P) is allowed to
pumping speed of complete vacuum-chamber systems. The test
stabilize. This establishes the effective pumping speed (&) by
method is suitable for all types of vacuum systems operating at
the equation:
pressures below 1 X lo4 torr and for chambers larger than
approximately 10 ft3 (0.3 m3).
S, = Q/(P - Po) (1)
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
4.2 The flow of gas is increased in increments for each
as the standard.
pressure decade above the ultimate pressure to 1 X lo4 torr.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
4.3 Two separate test runs are conducted Nitrogen is the gas
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
for the first test, followed by a similar run using atmospheric
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appm-
air.
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to we. 5. Significance and Use
5.1 This test method is suitable for specification acceptance,
2. Referenced Documents
service evaluation, and for comparative evaluation between
2.1 ASTM Standards:
vacuum-chamber systems.
E296 Practice for ionization Gage Application to Space
5.2 The effects of system leakage, materials out-gassing,
Simulators*
flow impedance, pump operating deficiencies, and physical
E297 Methods for Calibrating Ionization Vacuum Gage
arrangement of the chamber and pump system components are
Tubes3
integrated by this test method. The effective pumping speed
measured is the basic vacuum performance of the overall
3. symbols
faciiity.
3.1 decade = one logarithmic cycle of pressure.
3.2 PGl = test-zone pressure, torr, as read on Bayard-Alpert
6. Apparatus
gage No. 1.
6.1 The arrangement of test apparatus is shown schemati-
3.3 P, = test-zone pressure, torr, as read on Bayard-Alpert
cally in Fig. 1. A detailed arrangement of the gas-discharge
gage No. 2.
assembly is shown in Fig. 2.
3.4 P = (PGl + Pa)/2 = average test-zone pressure, torr.
6.2 The gas-discharge assembly shall include a 3-in. (76-
3.5 Po = background pressure, torr. The chamber pressure
mm) diameter spherical gas diffuser, as shown by Fig. 2. The
(P) at the end of any 4-h period during which the pressure
gas diffuser shall be welded to the end of a 3/4-in. (19-mm)
0.2 decade with the gas shut-off valve
change is less than
diameter gas-inlet tube of sufficient length to extend from the
closed (that is, from 2 to 4 X 10” torr or 7 to 5 X lo-’ torr).
center of the test zone to a point at least 12 in. (305 mm)
3.6 Q = measured flow rate of test gas, torr Us.
outside the test chamber sheil. The %-in. gas-inlet tube shall be
3.7 Se, = e/(P - Po) = effective pumping speed, Us.
vacuum sealed at the chamber-vacuum shell by a device that
3.8 torr = ln60 standard atm = 1 mm Hg.
will permit no in-leakage of atmospheric gas to the test zone at
static conditions.
4. Summary of Test Method
6.3 Calibrated gas-flow measuring devices, with ranges
4.1 The chamber under test is fitted with nude Bayard-
suitable for the capacity and range of the system under test,
Alpert pressure gages, a gas-inlet system, and gas-flow mea-
shall be provided.
5 X lo4 torr Ws may be deter-
6.3.1 How rates less than
’ This test method is & the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E-21 on Space
mined by a conductance method in which the test gas at a
Simulation aod Applications of Space Technology and is the direa responsibility of
known pressure is admitted through a known conductance.
SubComini= E 21.04 on Space Simulation Test Methods.
Curreni edition approved Sept 29,1972. Published November 1972. origioally 6.3.2 FLOWS greater than 5 X lo4 torr Us but less than
pblished as E 294 - 67 T. Last previous edition E 294 - 67 T.
about 5 torr Us may be measured with some type of constant-
’ Annuni Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 15.03.
pressure displacement tube, using low-vapor pressure fluids.
Discontinued see 1984 Annual Book of ASTM Stadz&, Vol 15.03.
CowngM O ASTM, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, West Conshohocken, PA 194282959. Unbd States.
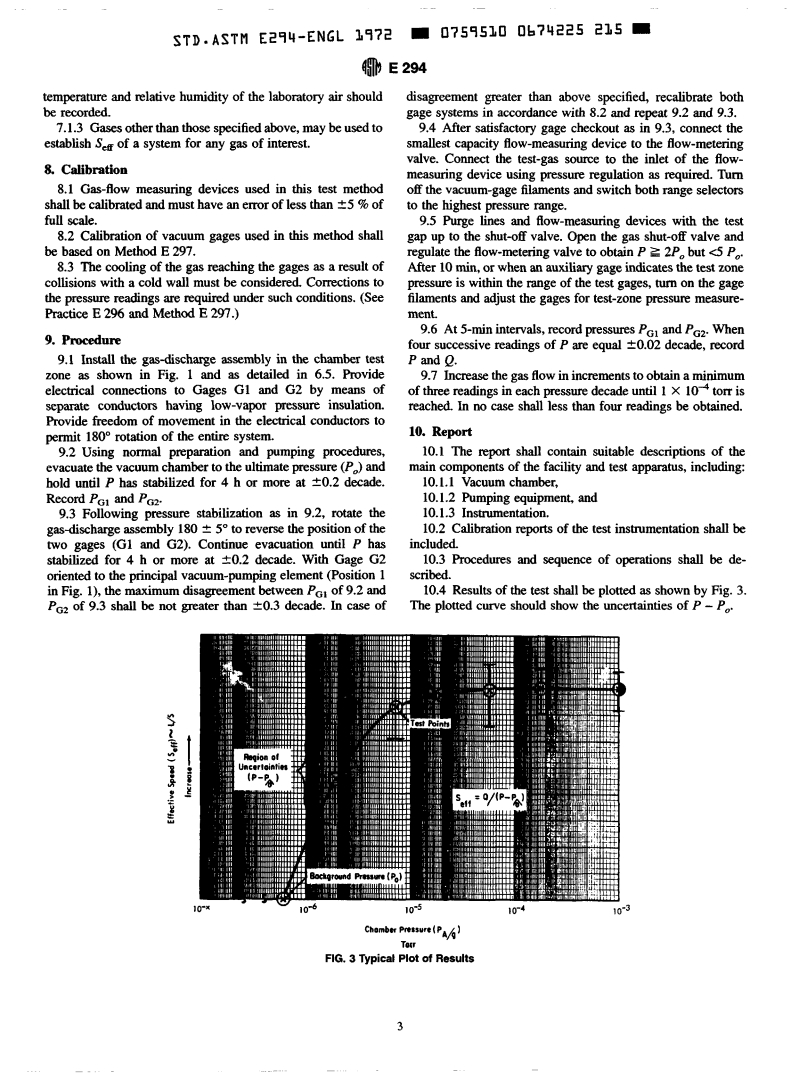
I
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
STD-ASTM E29Y-ENGL 3972 W O
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.