ASTM F2832-11(2021)
(Guide)Standard Guide for Accelerated Corrosion Testing for Mechanical Fasteners
Standard Guide for Accelerated Corrosion Testing for Mechanical Fasteners
ABSTRACT
This guide covers test procedures for performing accelerated tests to evaluate relative corrosion resistance of various coatings applied to mechanical fasteners. Corrosion mechanisms such as general and crevice corrosion may be evaluated with this method. Test duration may be selected to achieve any desired level of corrosion exposure and provides a frame of reference to determine relative coating resistance to corrosion. Fasteners tightened to a desired tension and subjected to this test procedure may be evaluated to simulate a variety of service conditions. Without large amounts of accumulated field results, it is difficult to relate test duration or the number of test cycles to actual service life for a given application.
SCOPE
1.1 This guide covers test procedures for performing accelerated tests to evaluate relative corrosion resistance of various coatings applied to mechanical fasteners. Corrosion mechanisms such as general and crevice corrosion may be evaluated with this method. Test duration may be selected to achieve any desired level of corrosion exposure and provides a frame of reference to determine relative coating resistance to corrosion. Fasteners tightened to a desired tension and subjected to this test procedure may be evaluated to simulate a variety of service conditions. Without large amounts of accumulated field results, it is difficult to relate test duration or the number of test cycles to actual service life for a given application.
1.2 This standard is not intended to cover tests of driven fasteners such as nails, staples, screws and lag bolts.
1.3 Units—The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: F2832 − 11 (Reapproved 2021)
Standard Guide for
Accelerated Corrosion Testing for Mechanical Fasteners
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F2832; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope Flat-Rolled Stainless and Heat-Resisting Steel Plate,
Sheet, and Strip
1.1 This guide covers test procedures for performing accel-
B117 Practice for Operating Salt Spray (Fog) Apparatus
erated tests to evaluate relative corrosion resistance of various
B605 Specification for Electrodeposited Coatings of Tin-
coatings applied to mechanical fasteners. Corrosion mecha-
Nickel Alloy
nisms such as general and crevice corrosion may be evaluated
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
with this method. Test duration may be selected to achieve any
F1470 Practice for Fastener Sampling for Specified Me-
desired level of corrosion exposure and provides a frame of
chanical Properties and Performance Inspection
reference to determine relative coating resistance to corrosion.
F1789 Terminology for F16 Mechanical Fasteners
Fasteners tightened to a desired tension and subjected to this
G1 Practice for Preparing, Cleaning, and Evaluating Corro-
testproceduremaybeevaluatedtosimulateavarietyofservice
sion Test Specimens
conditions.Withoutlargeamountsofaccumulatedfieldresults,
2.2 ASME Standard:
it is difficult to relate test duration or the number of test cycles
ASME B18.12 – Glossary of Terms for Mechanical Fasten-
to actual service life for a given application.
ers
1.2 This standard is not intended to cover tests of driven
2.3 IFI Standards
fasteners such as nails, staples, screws and lag bolts.
IFI-170 –Accelerated CorrosionTest for Mechanical Fasten-
1.3 Units—The values stated in SI units are to be regarded
ers
as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
3. Terminology
standard.
3.1 Definitions for many of the terms used in this standard
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
are included in Terminology F1789 and ASME B18.12.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
3.2.1 cycle—a series of events scheduled over a 24-hour
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
period
1.5 This international standard was developed in accor-
3.2.2 phase—a test period which has elapsed for 8 cycles.
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
3.2.3 test duration—a series of cycles as defined in
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Section 4.
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
4. Test Duration
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
4.1 Test duration is specified as A, B, C, D or E in
accordance with Table 1.
2. Referenced Documents
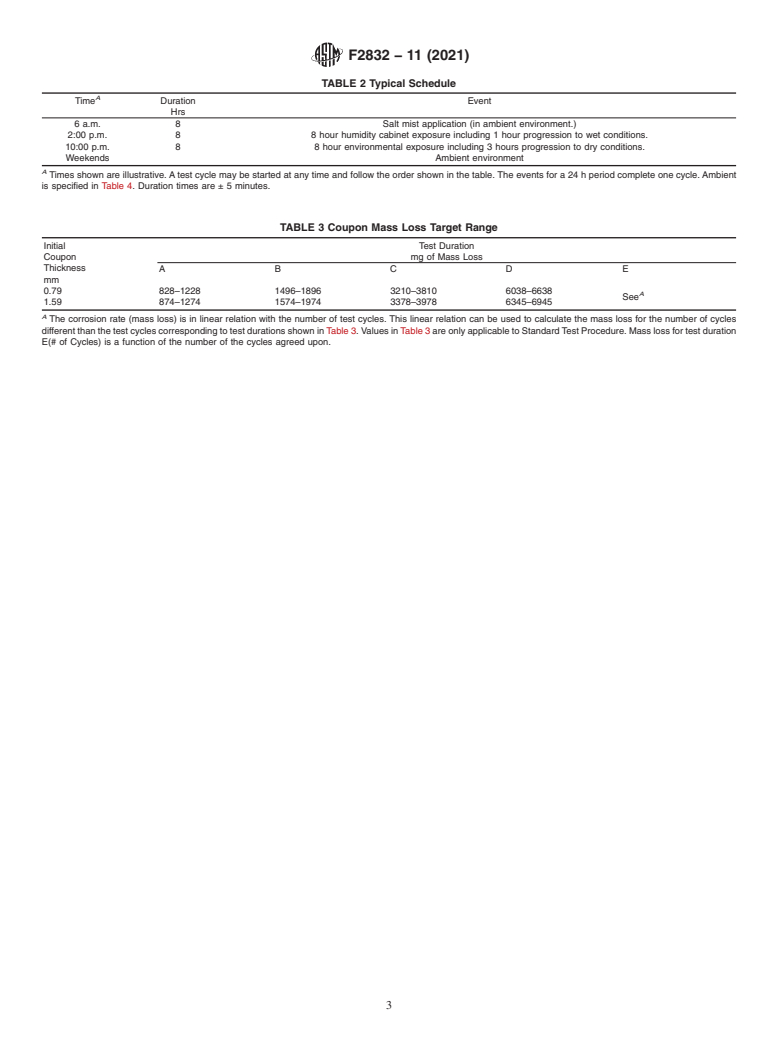
4.2 A typical cycle is shown in Table 2.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
A480/A480M Specification for General Requirements for
5. Apparatus and Materials
5.1 Coupons 25.4 mm wide and 50.8 mm long having a
thickness selected from Table 3 shall be used. Dimensional
This guide is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee F16 on Fasteners and
tolerances of Specification A480/A480M shall apply. Coupons
is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F16.01 on Test Methods.
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2021. Published January 2022. Originally
approved in 2011. Last previous edition approved in 2016 as F2832– 11(2016).
DOI: 10.1520/F2832–11R21 Available from American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), ASME
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or International Headquarters, Two Park Ave., New York, NY 10016-5990, http://
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM www.asme.org.
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available from Industrial Fasteners Institute (IFI), 6363 Oak Tree Blvd.
the ASTM website. Independence, OH 44131 http://www.indfast.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
F2832 − 11 (2021)
TABLE 1 Test Duration
the assembly). If higher loads or proof load tightening is
Test Duration Number of Cycles required then the load level and method of tightening shall be
A8
by agreement between supplier and purchaser.
B16
C40
7.3 Coupons to be tested shall be permanently identified by
D80
numbers stamped onto the surface.
A
E (# of cycles) >80
A 7.4 Coupons to be used shall be cleaned with a methanol or
For special applications as agreed between supplier and purchaser.
acetone solution and weighed prior to use. A coupon’s weight
in 6 0.5-mg shall be recorded for comparison with its weight
after testing in accordance with Table 2.
shall have a plain finish and be manufactured fromAISI–1008
7.5 Coupons as shown in Fig. 1(a) shall be installed by
steel grade. Coupons shall be included with fasteners to be
tested to verify that uniform amounts of corrosion have been drilling a hole to accept a nonmetallic hex fastener. Coupons
shallberaisedabovecouponracksbytwononmetallicwashers
produced by tests. Refer to Fig. 1, Fig. 1 (a) and Fig. 1(b) and
Table 3. Inclusion of a metal loss coupon assists in making to expose both sides of coupons to the test environment. A
minimum of 5 mm shall be provided for spacing between
comparisons from one test to another and allows one to
coupons and test rack surfaces. Fixtures shall be modified as
quantify a repeatable test.
necessary to maintain isolation from rack materials while
5.2 A fog humidity cabinet shall be used in which salt mist
creating and maintaining the required fastener tensions.
applications are coupled with high humidity and moderately
7.6 Dry off shall consist of exposure to high temperature,
high temperature. Water fog or visible water droplets on parts
low humidity air in accordance with Table 4 for three hours.
being tested shall be continuous after equilibrium is reached.
Dry-off may be sequenced manually or automatically.
7.7 Test coupon(s) shall be removed and analyzed after
dry-off in each phase. Each coupon shall be cleaned in
5.3 Racks suitable for supporting bolt or screw assemblies
accordance with the procedures described in Practice G1.
shall be agreed upon between supplier and purchaser. Test
results shall always state materials used for racks during
7.8 For corrosio
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.