ASTM A485-14
(Specification)Standard Specification for High Hardenability Antifriction Bearing Steel
Standard Specification for High Hardenability Antifriction Bearing Steel
ABSTRACT
This specification covers high hardenability modifications of high-carbon bearing quality steel to be used in the manufacture of antifriction bearings. The grades of steels covered here are: Grade 1, Grade 2, Grade 3, Grade 4, Grade B2, Grade B3, Grade B4, Grade B5, Grade B6, Grade B7, and Grade B8. Heat and product analyses shall be performed wherein specimens shall conform to required chemical composition of carbon, manganese, phosphorus, sulfur, silicon, chromium, nickel, titanium, copper, molybdenum, oxygen, and aluminum. The steels shall undergo normalizing followed by spheroidize annealing before heating for end quenching. Test for hardenability shall be performed wherein specimens shall conform to required Brinell and Rockwell hardness.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers high hardenability modifications of high-carbon bearing quality steel to be used in the manufacture of antifriction bearings.
1.2 Supplementary requirements of an optional nature are provided and when desired shall be so stated in the order.
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
General Information
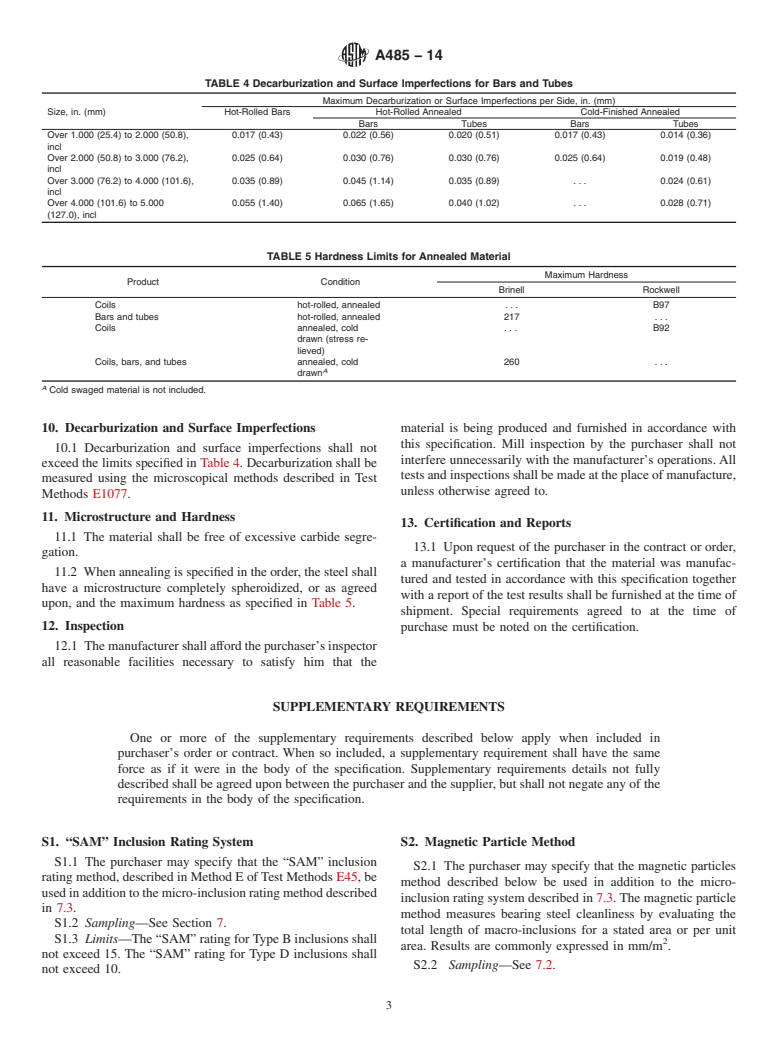
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:A485 −14
Standard Specification for
High Hardenability Antifriction Bearing Steel
This standard is issued under the fixed designation A485; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope* 2.2 Other Standards:
SAE J148a Grain Size Determination of Steel
1.1 This specification covers high hardenability modifica-
ISO 683 Part 17: Ball and Roller Bearing Steels
tions of high-carbon bearing quality steel to be used in the
manufacture of antifriction bearings.
3. Ordering Information
1.2 Supplementary requirements of an optional nature are 3.1 Orders for material under this specification should
provided and when desired shall be so stated in the order. include the following information:
3.1.1 Quantity (weight or number of pieces),
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
3.1.2 Grade identification,
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
3.1.3 ASTM designation and year of issue,
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
3.1.4 Dimensions,
and are not considered standard.
3.1.5 Supplementary requirements, if included.
2. Referenced Documents
4. Process
2.1 ASTM Standards: 4.1 The steel shall be made by a process that is capable of
A29/A29M SpecificationforGeneralRequirementsforSteel providing a high quality product meeting the requirements of
Bars, Carbon and Alloy, Hot-Wrought this specification.
A255 Test Methods for Determining Hardenability of Steel
5. Chemical Composition and Analysis
A751 Test Methods, Practices, and Terminology for Chemi-
5.1 Typical examples of chemical compositions are shown
cal Analysis of Steel Products
in Table 1. Other compositions may be specified.
E45 Test Methods for Determining the Inclusion Content of
Steel
5.2 An analysis of each heat of steel shall be made by the
E381 Method of Macroetch Testing Steel Bars, Billets, steel manufacturer in accordance withTest Methods, Practices,
Blooms, and Forgings
and Terminology A751. The chemical composition thus deter-
E1019 Test Methods for Determination of Carbon, Sulfur, mined shall conform to the requirements specified in Table 1
Nitrogen, and Oxygen in Steel, Iron, Nickel, and Cobalt
for the ordered grade or to other requirements agreed upon
Alloys by Various Combustion and Fusion Techniques between manufacturer and purchaser.
E1077 Test Methods for Estimating the Depth of Decarbur-
5.3 Product analysis may be made by the purchaser in
ization of Steel Specimens
accordance with Test Methods, Practices, and Terminology
A751. Permissible variations in product analysis shall be in
accordance with Specification A29/A29M.
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee A01 on Steel,
6. Sizes, Shapes, and Dimensional Tolerances
Stainless Steel and RelatedAlloys, and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
A01.28 on Bearing Steels.
6.1 The physical size and shape of the material shall be
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2014. Published November 2014. Originally
agreed upon between manufacturer and purchaser.
approved in 1963. Last previous edition approved in 2009 as A485 – 09. DOI:
10.1520/A0485-14.
2 3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or Available from SAE International (SAE), 400 Commonwealth Dr.,Warrendale,
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM PA 15096-0001, http://www.sae.org.
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available from International Organization for Standardization (ISO), 1, ch. de
the ASTM website. la Voie-Creuse, CP 56, CH-1211 Geneva 20, Switzerland, http://www.iso.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
A485−14
A,B
TABLE 1 Chemical Composition
C D
Number Name C Mn P (max) S (max) Si Cr Ni (max) Ti (max) Cu (max) Mo O (max) Al (max)
1 Grade 1 0.90–1.05 0.90–1.20 0.025 0.015 0.45–0.75 0.90–1.20 0.25 0.0050 0.30 0.10 (max) 0.0015 0.050
2 Grade 2 0.85–1.00 1.40–1.70 0.025 0.015 0.50–0.80 1.40–1.80 0.25 0.0050 0.30 0.10 (max) 0.0015 0.050
3 Grade 3 0.95–1.10 0.65–0.90 0.025 0.015 0.15–0.35 1.10–1.50 0.25 0.0050 0.30 0.20–0.30 0.0015 0.050
4 Grade 4 0.95–1.10 1.05–1.35 0.025 0.015 0.15–0.35 1.10–1.50 0.25 0.0050 0.30 0.45–0.60 0.0015 0.050
E
B2 100CrMnSi4–4 0.93–1.05 0.90–1.20 0.025 0.015 0.45–0.75 0.90–1.20 . . . 0.30 0.10 (max) 0.0015 0.050
E
B3 100CrMnSi6–4 0.93–1.05 1.00–1.20 0.025 0.015 0.45–0.75 1.40–1.65 . . . 0.30 0.10 (max) 0.0015 0.050
E
B4 100CrMnSi6–6 0.93–1.05 1.40–1.70 0.025 0.015 0.45–0.75 1.40–1.65 . . . 0.30 0.10 (max) 0.0015 0.050
E
B5 100CrMo7 0.93–1.05 0.25–0.45 0.025 0.015 0.15–0.35 1.65–1.95 . . . 0.30 0.15–0.30 0.0015 0.050
E
B6 100CrMo7–3 0.93–1.05 0.60–0.80 0.025 0.015 0.15–0.35 1.65–1.95 . . . 0.30 0.20–0.35 0.0015 0.050
E
B7 100CrMo7–4 0.93–1.05 0.60–0.80 0.025 0.015 0.15–0.35 1.65–1.95 . . . 0.30 0.40–0.50 0.0015 0.050
E
B8 100CrMnMoSi8–4–6 0.93–1.05 0.80–1.10 0.025 0.015 0.40–0.60 1.80–2.05 . . . 0.30 0.50–0.60 0.0015 0.050
A
Elements not quoted shall not be intentionally added to the steel without the agreement of the purchaser.
B
Intentional additions of calcium or calcium alloys for deoxidation or inclusion shape control are not permitted unless specifically approved by the purchaser.
C
Steels B2 through B8 meet the requirements of ISO 683, Part 17, Second Edition, Table 3.
D
Oxygen content applies to product analysis and shall be determined in accordance with Test Methods E1019.
E
A maximum titanium content may be agreed upon at the time of inquiry and order.
TABLE 2 Inclusion Rating
betakenatrandomfromthefirstusableplatepoured,oneingot
Rating Units atrandomfromtheusableplatepourednearesttothemiddleof
Thin Series Heavy Series the heat, and one ingot at random from the last usable plate
A—2.5 A—1.5 poured.When a heat is constituted by two usable plates, two of
B—2.0 B—1.0
thesampleingotsshallbeselectedfromthesecondusableplate
C—0.5 C—0.5
poured.When a heat consists of a single usable plate, any three
D—1.0 D—1.0
random ingots may be selected. Other methods of sampling
shall be as agreed upon between manufacturer and purchaser.
TABLE 3 Hardenability Values
7.2.3 For strand cast products, a minimum of six samples
Rockwell C representing the first, middle, and last portion of the heat cast
Minimum Rockwell C Values at Sixteenth of Inch
shall be examined. At least one sample shall be taken from
Grade 10 20 28
each strand.
1 46 . .
3 3
2 . . . 52 32
7.3 InclusionRating—Specimensapproximately ⁄8by ⁄4in.
3 46 . .
(9.5 by 19.1 mm) shall be taken from an area halfway between
4 . . . 52 35
the center and outside of the billet. The polished face shall be
longitudinaltothedirectionofrolling.Thescaleusedforrating
the specimens shall be the chart described in Test Methods
6.2 Dimensional tolerances for hot-rolled or hot-rolled and
E45, Method A, Plate I-A. Inclusion fields with sizes or
annealed bars, in straight lengths or coils, and cold-finished
numbers intermediate between configurations shown on the
bars furnished under this specification shall conform to the
chart shall be classified as the lesser of the rating number. The
requirements specified in the latest edition of Specification
worst field of each inclusion type from each specimen shall be
A29/A29M.
recorded as the rating for the specimen. Two thirds of all
specimens and at least one from each ingot tested, or from the
7. Quality Tests
first, middle and last portion of the strands tested as well as the
7.1 The supplier shall be held responsible for the quality of
average of all specimens, shall not exceed the rating specified
the material furnished and shall make the necessary tests to
in Table 2.
ensure this quality. The supplier shall be required to report on
the results of the micro-inclusion rating tests detailed below.
8. Grain Size
Quality tests shown in 7.1 through 7.3 are based upon
8.1 The steels covered by this specification shall have the
procedures established in Test Methods E45.
capability of showing fine fracture grain size (approximately
7.2 Sampling—Samples taken in accordance with the fol-
ASTM No. 8) (SAE J418a) when quenched from normal
lowing paragraphs shall be obtained from 4 by 4 in. (102 by
austenizing temperatures not exceeding 1550°F (843°C).
102 mm) rolled bill
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: A485 − 09 A485 − 14
Standard Specification for
High Hardenability Antifriction Bearing Steel
This standard is issued under the fixed designation A485; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope*
1.1 This specification covers high hardenability modifications of high-carbon bearing quality steel to be used in the manufacture
of antifriction bearings.
1.2 Supplementary requirements of an optional nature are provided and when desired shall be so stated in the order.
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
A29/A29M Specification for General Requirements for Steel Bars, Carbon and Alloy, Hot-Wrought
A255 Test Methods for Determining Hardenability of Steel
A751 Test Methods, Practices, and Terminology for Chemical Analysis of Steel Products
E45 Test Methods for Determining the Inclusion Content of Steel
E381 Method of Macroetch Testing Steel Bars, Billets, Blooms, and Forgings
E1019 Test Methods for Determination of Carbon, Sulfur, Nitrogen, and Oxygen in Steel, Iron, Nickel, and Cobalt Alloys by
Various Combustion and Fusion Techniques
E1077 Test Methods for Estimating the Depth of Decarburization of Steel Specimens
2.2 Other Standards:
SAE J148a Grain Size Determination of Steel
ISO 683 Part 17: Ball and Roller Bearing Steels
3. Ordering Information
3.1 Orders for material under this specification should include the following information:
3.1.1 Quantity (weight or number of pieces),
3.1.2 Grade identification,
3.1.3 ASTM designation and year of issue,
3.1.4 Dimensions,
3.1.5 Supplementary requirements, if included.
4. Process
4.1 The steel shall be made by a process that is capable of providing a high quality product meeting the requirements of this
specification.
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee A01 on Steel, Stainless Steel and Related Alloys, and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee A01.28
on Bearing Steels.
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2009Oct. 1, 2014. Published November 2009November 2014. Originally approved in 1963. Last previous edition approved in 20032009
as A485 – 03.A485 – 09. DOI: 10.1520/A0485-09.10.1520/A0485-14.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Available from The Engineering Society for Advanced Mobility of Land, Sea, Air and Space, 400 Commonwealth Drive, Warrendale, PA 15096-001.SAE International
(SAE), 400 Commonwealth Dr., Warrendale, PA 15096-0001, http://www.sae.org.
Available from the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), 1, rue de Varembé, Case postale 56, CH-1211, Genève 20, Switzerland. ch. de la Voie-Creuse,
CP 56, CH-1211 Geneva 20, Switzerland, http://www.iso.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
A485 − 14
5. Chemical Composition and Analysis
5.1 Typical examples of chemical compositions are shown in Table 1. Other compositions may be specified.
5.2 An analysis of each heat of steel shall be made by the steel manufacturer in accordance with Test Methods, Practices, and
Terminology A751. The chemical composition thus determined shall conform to the requirements specified in Table 1 for the
ordered grade or to other requirements agreed upon between manufacturer and purchaser.
5.3 Product analysis may be made by the purchaser in accordance with Test Methods, Practices, and Terminology A751.
Permissible variations in product analysis shall be in accordance with Specification A29/A29M.
6. Sizes, Shapes, and Dimensional Tolerances
6.1 The physical size and shape of the material shall be agreed upon between manufacturer and purchaser.
6.2 Dimensional tolerances for hot-rolled or hot-rolled and annealed bars, in straight lengths or coils, and cold-finished bars
furnished under this specification shall conform to the requirements specified in the latest edition of Specification A29/A29M.
7. Quality Tests
7.1 The supplier shall be held responsible for the quality of the material furnished and shall make the necessary tests to ensure
this quality. The supplier shall be required to report on the results of the micro-inclusion rating tests detailed below. Quality tests
shown in 7.1 through 7.3 are based upon procedures established in Test Methods E45.
7.2 Sampling—Samples taken in accordance with the following paragraphs shall be obtained from 4 by 4 in. (102 by 102 mm)
rolled billets or forged sections. Tests may be made on smaller or larger sections by agreement with the purchaser. A minimum
of 3 to 1 reduction of rolled billets or forged sections is required for strand cast products.
7.2.1 For top poured products, a minimum of six samples representing the top and bottom of the first, middle and last usable
ingots shall be examined.
7.2.2 For bottom poured products, a minimum of six samples shall be taken from semi-finished or finished product representing
the top and bottom of three ingots. One ingot shall be taken at random from the first usable plate poured, one ingot at random from
the usable plate poured nearest to the middle of the heat, and one ingot at random from the last usable plate poured. When a heat
is constituted by two usable plates, two of the sample ingots shall be selected from the second usable plate poured. When a heat
consists of a single usable plate, any three random ingots may be selected. Other methods of sampling shall be as agreed upon
between manufacturer and purchaser.
7.2.3 For strand cast products, a minimum of six samples representing the first, middle, and last portion of the heat cast shall
be examined. At least one sample shall be taken from each strand.
3 3
7.3 Inclusion Rating—Specimens approximately ⁄8 by ⁄4 in. (9.5 by 19.1 mm) shall be taken from an area halfway between the
center and outside of the billet. The polished face shall be longitudinal to the direction of rolling. The scale used for rating the
specimens shall be the chart described in Test Methods E45, Method A, Plate I-r.I-A. Inclusion fields with sizes or numbers
intermediate between configurations shown on the chart shall be classified as the lesser of the rating number. The worst field of
each inclusion type from each specimen shall be recorded as the rating for the specimen. Two thirds of all specimens and at least
one from each ingot tested, or from the first, middle and last portion of the strands tested as well as the average of all specimens,
shall not exceed the rating specified in Table 2.
8. Grain Size
8.1 The steels covered by this specification shall have the capability of showing fine fracture grain size (approximately ASTM
No. 8) (SAE J418a) when quenched from normal austenizing temperatures not exceeding 1550°F (843°C).
A,B
TABLE 1 Chemical Composition
C D
Number Name C Mn P (max) S (max) Si Cr Ni (max) Ti (max) Cu (max) Mo O (max) Al (max)
1 Grade 1 0.90–1.05 0.90–1.20 0.025 0.015 0.45–0.75 0.90–1.20 0.25 0.0050 0.30 0.10 (max) 0.0015 0.050
2 Grade 2 0.85–1.00 1.40–1.70 0.025 0.015 0.50–0.80 1.40–1.80 0.25 0.0050 0.30 0.10 (max) 0.0015 0.050
3 Grade 3 0.95–1.10 0.65–0.90 0.025 0.015 0.15–0.35 1.10–1.50 0.25 0.0050 0.30 0.20–0.30 0.0015 0.050
4 Grade 4 0.95–1.10 1.05–1.35 0.025 0.015 0.15–0.35 1.10–1.50 0.25 0.0050 0.30 0.45–0.60 0.0015 0.050
E
B2 100CrMnSi4–4 0.93–1.05 0.90–1.20 0.025 0.015 0.45–0.75 0.90–1.20 . . . 0.30 0.10 (max) 0.0015 0.050
E
B3 100CrMnSi6–4 0.93–1.05 1.00–1.20 0.025 0.015 0.45–0.75 1.40–1.65 . . . 0.30 0.10 (max) 0.0015 0.050
E
B4 100CrMnSi6–6 0.93–1.05 1.40–1.70 0.025 0.015 0.45–0.75 1.40–1.65 . . . 0.30 0.10 (max) 0.0015 0.050
E
B5 100CrMo7 0.93–1.05 0.25–0.45 0.025 0.015 0.15–0.35 1.65–1.95 . . . 0.30 0.15–0.30 0.0015 0.050
E
B6 100CrMo7–3 0.93–1.05 0.60–0.80 0.025 0.015 0.15–0.35 1.65–1.95 . . . 0.30 0.20–0.35 0.0015 0.050
E
B7 100CrMo7–4 0.93–1.05 0.60–0.80 0.025 0.015 0.15–0.35 1.65–1.95 . . . 0.30 0.40–0.50 0.0015 0.050
E
B8 100CrMnMoSi8–4–6 0.93–1.05 0.80–1.10 0.025 0.015 0.40–0.60 1.80–2.05 . . . 0.30 0.50–0.60 0.0015 0.050
A
Elements not quoted shall not be intentionally added to the steel without the agreement of the purchaser.
B
Intentional additions of calcium or calcium alloys for deoxidation or inclusion shape control are not per
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.