ASTM D2502-04
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Estimation of Molecular Weight (Relative Molecular Mass) of Petroleum Oils From Viscosity Measurements
Standard Test Method for Estimation of Molecular Weight (Relative Molecular Mass) of Petroleum Oils From Viscosity Measurements
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
This test method provides a means of calculating the mean relative molecular mass of petroleum oils from another physical measurement.
Mean relative molecular mass is a fundamental physical constant that can be used in conjunction with other physical properties to characterize hydrocarbon mixtures.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the estimation of the mean molecular weight (relative molecular mass) of petroleum oils from kinematic viscosity measurements at 100 and 210°F (37.78 and 98.89°C). It is applicable to samples with molecular weights in the range from 250 to 700 and is intended for use with average petroleum fractions. It should not be applied indiscriminately to oils that represent extremes of composition or possess an exceptionally narrow molecular weight (relative molecular mass) range.
1.2 Values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are provided for information purposes only.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D2502–04
Standard Test Method for
Estimation of Mean Relative Molecular Mass of Petroleum
1
Oils from Viscosity Measurements
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D2502; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope Mean Relative Molecular Mass of Petroleum Oils from
4
Viscosity Measurements (D2502)
1.1 This test method covers the estimation of the mean
relative molecular mass of petroleum oils from kinematic
3. Summary of Test Method
viscosity measurements at 100 and 210°F (37.78 and
2 3.1 The kinematic viscosity of the oil is determined at 100
98.89°C). It is applicable to samples with mean relative
and 210°F (37.78 and 98.89°C). A function “H” of the 100°F
molecular masses in the range from 250 to 700 and is intended
viscosity is established by reference to a tabulation of H
for use with average petroleum fractions. It should not be
function versus 100°F viscosity. The H value and the 210°F
applied indiscriminately to oils that represent extremes of
viscosity are then used to estimate the mean relative molecular
composition or possess an exceptionally narrow mean relative
mass from a correlation chart.
molecular mass range.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
4. Significance and Use
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
4.1 This test method provides a means of calculating the
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
mean relative molecular mass of petroleum oils from another
and are not considered standard.
physical measurement.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
4.2 Mean relative molecular mass is a fundamental physical
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
constant that can be used in conjunction with other physical
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
properties to characterize hydrocarbon mixtures.
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
5. Procedure
5.1 Determine the kinematic viscosity of the oil at 100 and
2. Referenced Documents
210°F (37.78 and 98.89°C) as described in Test Method D445.
3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
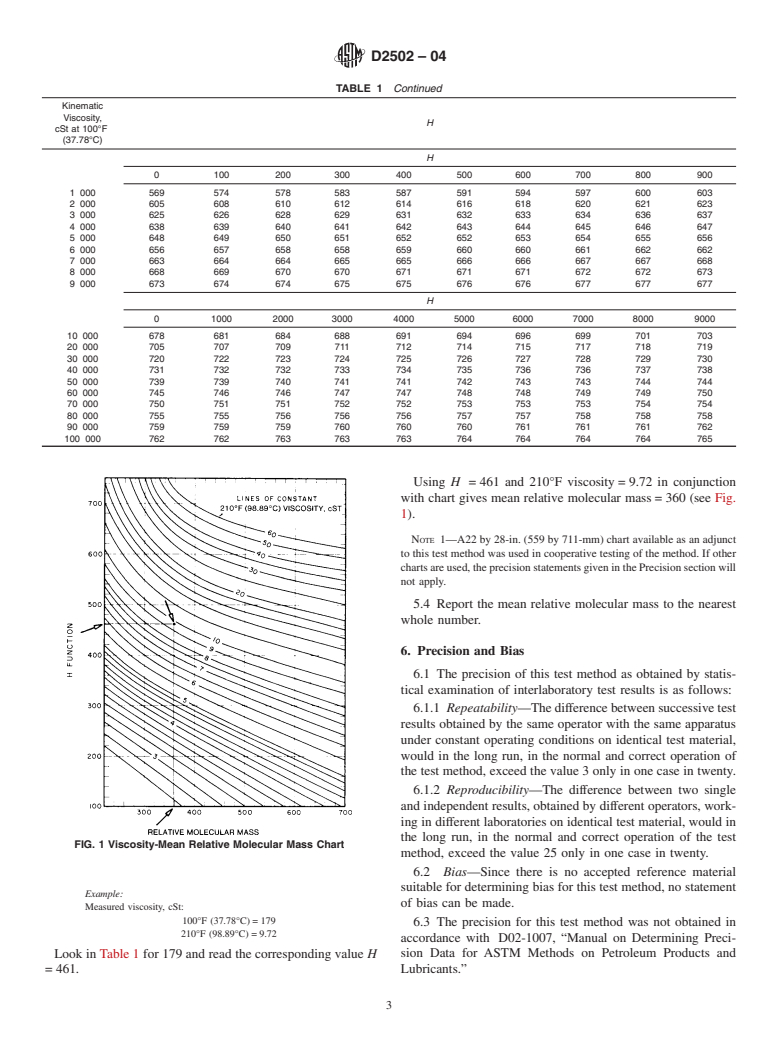
5.2 Look in Table 1 for 100°F (37.78°C) viscosity and read
D445 Test Method for Kinematic Viscosity of Transparent
the value of H that corresponds to the measured viscosity.
and Opaque Liquids (and Calculation of Dynamic Viscos-
Linear interpolation between adjacent columns may be re-
ity)
quired.
2.2 ASTM Adjuncts:
5.3 Read the viscosity–mean relative molecular mass chart
for H and 210°F (98.89°C) viscosity. A simplified version of
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on
thischartisshowninFig.1forillustrationpurposesonly(Note
Petroleum Products and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
1). Interpolate where necessary between adjacent lines of
D02.04 on Hydrocarbon Analysis.
210°F viscosity. After locating the point corresponding to the
Current edition approved April 1, 2004. Published April 2004. Originally
approved in 1966. Last previous edition approved in 2002 as D2502–92(2002). value of H (ordinate) and the 210°F viscosity (superimposed
DOI: 10.1520/D2502-04.
lines), read the mean relative molecular mass along the
2
Hirschler, A. E., Journal of the Institute of Petroleum, JIPEA, Vol 32, 1946, p.
abscissa.
133.
3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
4
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available from ASTM International Headquarters. Order Adjunct No.
the ASTM website. ADJD2502.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D2502–04
TABLE 1 Tabulation ofH Function
Kinematic
Viscosity,
H
cSt at 100°F
(37.78°C)
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8
2 −178 −151 −126 −104 −85
3 −67 −52 −38 −25 −13
4 −1 9 19 28 36
544 52 59 66 73
6 79 85 90 96 101
7 106 111 116 120 124
8 128 132 136 140 144
9 147 151 154 157 160
10 163 166 169 172 175
11 178 180 183 185 188
12 190 192 195 197 199
13 201 203 206 208 210
14 211 213 215 217 219
15 221 222 224 226 227
16 229 231 232 234 235
17 237 238 240 241 243
18 244 245 247 248 249
19 251 252 253 255 256
20 257 258 259 261 262
21 263 264 265 266 267
22 269 270 271 272 273
23 274 275 276 277 278
24 279 280 281 281 282
25 283 284 285 286 287
26 288 289 289 290 291
27 292 293 294 294 295
28 296 297 298
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.