ASTM B883-05
(Specification)Standard Specification for Metal Injection Molding (MIM) Ferrous Materials
Standard Specification for Metal Injection Molding (MIM) Ferrous Materials
ABSTRACT
This specification covers ferrous metal injection molded (MIM) materials fabricated by mixing elemental or pre-alloyed metal powders with binders, injecting into a mold, debinding, and sintering with or without subsequent heat treatment. These materials are: low-alloy steel produced from admixtures of iron powder and other alloying elements such as nickel and molybdenum (MIM-2200 and MIM-2700); low-alloy steel produced from admixtures of iron powder and other alloying elements such as nickel, molybdenum, and carbon (MIM-4605); austenitic stainless steel produced from pre-alloyed powder or an admixture of powders (MIM-316L); precipitation hardening stainless steel produced from pre-alloyed powder or an admixture of powders (MIM-17-4 PH); and ferritic stainless steel produced from pre-alloyed powder or an admixture of powders (MIM-430L). Chemical analysis shall be performed for the elements copper, chromium, molybdenum, and nickel. The materials shall be subjected to tensile test and unnotched Charpy impact energy test.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers ferrous metal injection molded materials fabricated by mixing elemental or pre-alloyed metal powders with binders, injecting into a mold, debinding, and sintering, with or without subsequent heat treatment.
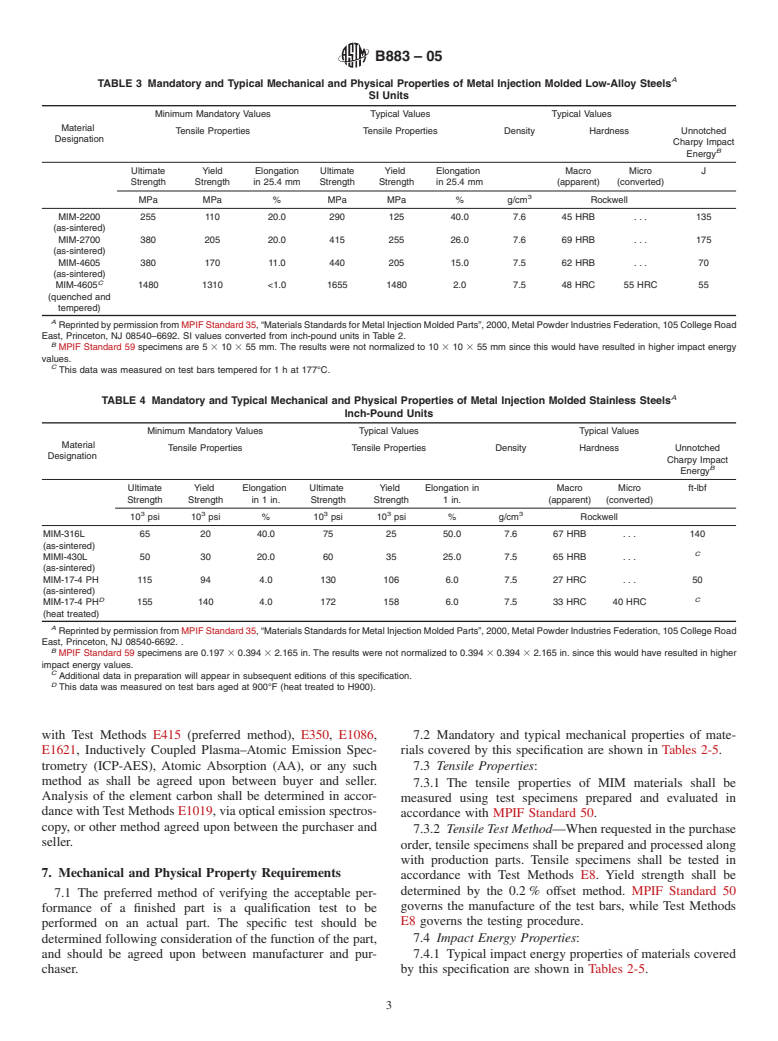
1.2 This specification covers the following injection molded materials.
1.2.1 CompositionsMIM-2200, low-alloy steel produced from admixtures of iron powder and other alloying elements such as nickel and molybdenum.
MIM-2700, low-alloy steel produced from admixtures of iron powder, and other alloying elements such as nickel and molybdenum.
MIM-4605, low-alloy steel produced from admixtures of iron powder and other alloying elements such as nickel, molybdenum, and carbon.
MIM-316L, austenitic stainless steel produced from pre-alloyed powder or an admixture of powders.
MIM-17-4 PH, precipitation hardening stainless steel produced from prealloyed powder or an admixture of powders.
MIM-430L , ferritic stainless steel produced from pre-alloyed powder or an admixture of powders.
1.3 Chemical composition limits are specified in .
1.4 Property values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. Conversions to SI units may be approximate.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: B883 – 05
Standard Specification for
1
Metal Injection Molding (MIM) Ferrous Materials
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B883; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope nected Porosity of Sintered Metal Structural Parts and
3
Oil-Impregnated Bearings
1.1 This specification covers ferrous metal injection molded
B933 Test Method for Microindentation Hardness of Pow-
materials fabricated by mixing elemental or pre-alloyed metal
der Metallurgy (PM) Materials
powders with binders, injecting into a mold, debinding, and
E8 Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials
sintering, with or without subsequent heat treatment.
E18 Test Methods for Rockwell Hardness of Metallic Ma-
1.2 This specification covers the following injection molded
terials
materials.
E350 Test Methods for ChemicalAnalysis of Carbon Steel,
1.2.1 Compositions:
Low-Alloy Steel, Silicon Electrical Steel, Ingot Iron, and
1.2.1.1 MIM-2200, low-alloy steel produced from admix-
Wrought Iron
turesofironpowderandotheralloyingelementssuchasnickel
E415 Test Method for Atomic Emission Vacuum Spectro-
and molybdenum.
metric Analysis of Carbon and Low-Alloy Steel
1.2.1.2 MIM-2700, low-alloy steel produced from admix-
E1019 Test Methods for Determination of Carbon, Sulfur,
tures of iron powder, and other alloying elements such as
Nitrogen, and Oxygen in Steel, Iron, Nickel, and Cobalt
nickel and molybdenum.
Alloys by Various Combustion and Fusion Techniques
1.2.1.3 MIM-4605, low-alloy steel produced from admix-
E1086 Test Method for Atomic Emission Vacuum Spectro-
tures of iron powder and other alloying elements such as
metric Analysis of Stainless Steel by Point-to-Plane Exci-
nickel, molybdenum, and carbon.
tation Technique
1.2.1.4 MIM-316L, austenitic stainless steel produced from
E1621 Guide for X-Ray Emission Spectrometric Analysis
pre-alloyed powder or an admixture of powders.
F1089 Test Method for Corrosion of Surgical Instruments
1.2.1.5 MIM-17-4 PH, precipitation hardening stainless
4
2.2 MPIF Standards:
steel produced from prealloyed powder or an admixture of
MPIF Standard 35, Material Standards for Metal Injection
powders.
Molded Parts
1.2.1.6 MIM-430L , ferritic stainless steel produced from
MPIF Standard 50, Method for Preparing and Evaluating
pre-alloyed powder or an admixture of powders.
Metal Injection Molded Debound and Sintered Tension
1.3 Chemical composition limits are specified in Table 1.
Test Specimens
1.4 Property values stated in inch-pound units are to be
MPIF Standard 51, Determination of Microhardness of
regarded as the standard. Conversions to SI units may be
Powder Metallurgy Materials
approximate.
MPIF Standard59,DeterminationofCharpyImpactEnergy
2. Referenced Documents
of Unnotched Metal Injection Molded Test Specimens
2
MPIF Standard 62, Determination of the Corrosion Resis-
2.1 ASTM Standards:
tance of MIM Grades of Stainless Steel Immersed in 2 %
B243 Terminology of Powder Metallurgy
Sulfuric Acid Solution
B311 Test Method for Density of Powder Metallurgy (PM)
MPIF Standard 63, Density Determination of MIM Com-
Materials Containing Less Than Two Percent Porosity
ponents (Gas Pycnometer)
B328 Test Method for Density, Oil Content, and Intercon-
3. Terminology
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee B09 on Metal
3.1 Definitions:
Powders and Metal Powder Products and is the direct responsibility of Subcom-
3.1.1 Definitions of powder metallurgy terms can be found
mittee B09.11 on Near Full Density Powder Metallurgy Metals.
in Terminology B243. Additional descriptive information is
Current edition approved March 1, 2005. Published March 2005. Originally
approved in 1997. Last previous edition approved in 1997 as B883 – 97. DOI:
10.1520/B0883-05.
2 3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or Withdrawn. The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM on www.astm.org.
4
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available from Metal Powder Industries Federation (MPIF), 105 College Road
the ASTM website. East, Princeton, NJ 08540–6692, USA.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
B883 – 05
TABLE 1 Chemical Composition Requirements For Metal Injection Molded Materials
Material
Fe Ni Cr Co Mo C Cu Si Mn Nb + Ta V Other
Designation
MIM-2200 Min. Bal. 1.5 - - - - - -
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.