ASTM F1809-02
(Guide)Standard Guide for Selection and Use of Etching Solutions to Delineate Structural Defects in Silicon (Withdrawn 2003)
Standard Guide for Selection and Use of Etching Solutions to Delineate Structural Defects in Silicon (Withdrawn 2003)
SCOPE
This standard was transferred to SEMI (www.semi.org) May 2003
1.1 This guide covers the formulation, selection, and use of chemical solutions developed to reveal structural defects in silicon wafers. Etching solutions identify crystal defects that adversely affect the circuit performance and yield of silicon devices. Sample preparation, temperature control, etching technique, and choice of etchant are all key factors in the successful use of an etching method. This guide provides information for several etching solutions and allows the user to select according to the need. For further information see Appendix X1 and Figs. 1-32. For a test method for counting preferentially etched or decorated surface defects in silicon wafers see Test Method F 1810.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: F 1809 – 02
Standard Guide for
Selection and Use of Etching Solutions to Delineate
1
Structural Defects in Silicon
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F 1809; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This guide covers the formulation, selection, and use of
chemical solutions developed to reveal structural defects in
silicon wafers. Etching solutions identify crystal defects that
adversely affect the circuit performance and yield of silicon
devices. Sample preparation, temperature control, etching tech-
nique, and choice of etchant are all key factors in the successful
use of an etching method. This guide provides information for
several etching solution and allows the user to select according
to the need. For further information see Appendix X1and Figs.
1-32 . For a test method for counting preferentially etched or
decorated surface defects in silicon wafers see Test Method
F 1810.
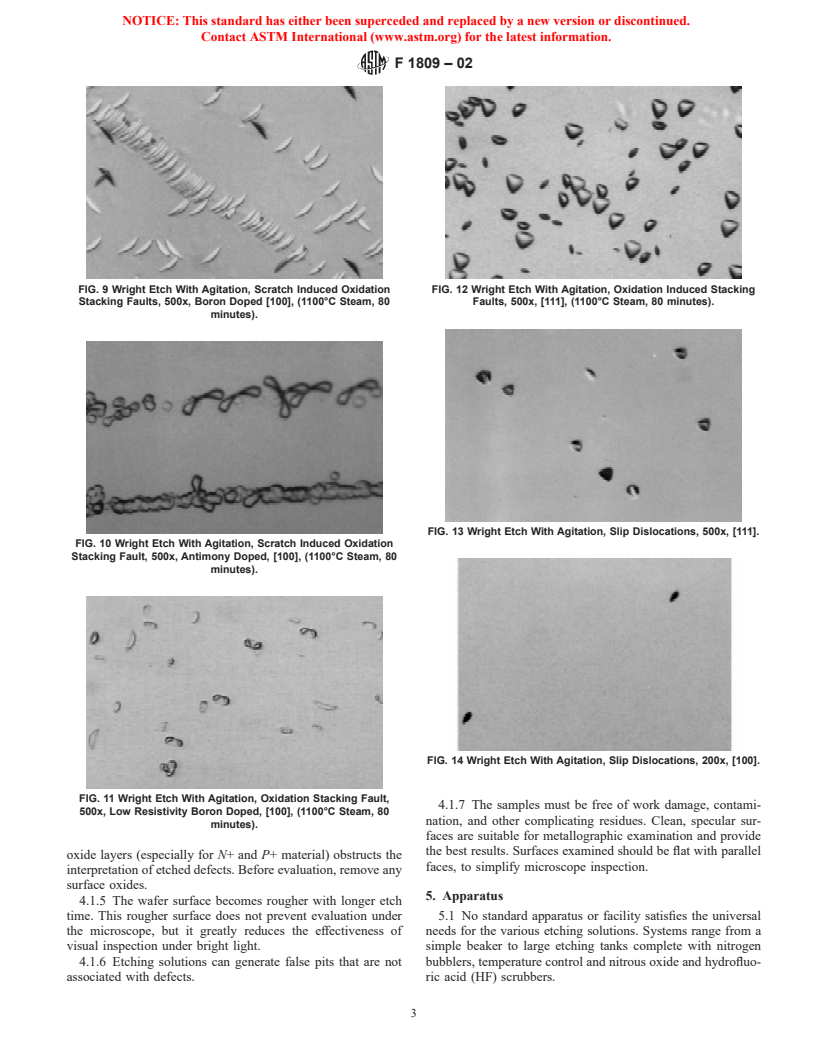
FIG. 1 Secco Etch With Agitation, Oxidation Stacking Fault,
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the
1000x, [100], (1100°C Steam, 80 minutes), ;4 μm removal.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
4
C35 Specifications and Guidelines for Nitric Acid
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
3. Significance and Use
3.1 Structural defects formed in the bulk of a silicon wafer
2. Referenced Documents
during its growth or induced by electronic device processing
2.1 ASTM Standards:
can affect the performance of the circuitry fabricated on that
D 5127 Guide for Ultra Pure Water Used in the Electronics
wafer. These defects take the form of dislocations, slip,
2
and Semiconductor Industry
stacking faults, shallow pits, or precipitates.
F 1725 Guide for Analysis of Crystallographic Perfection in
3.2 The exposure of the various defects found on or in a
3
Silicon Ingots
silicon wafer is often the first critical step in evaluating wafer
F 1726 Guide for Analysis of Crystallographic Perfection in
quality or initiating failure analysis of an errant device struc-
3
Silicon Wafers
ture. Etching often accomplishes this task.
F 1727 Practice for Detection of Oxidation Induced Defects
3
in Polished Silicon Wafers
F 1810 Method for Counting Preferentially Etched or Deco-
3
rated Surface Defects in Silicon Wafers
2.2 SEMI Standards:
4
C18 Specification for Acetic Acid
4
C28 Specifications and Guidelines for Hydrofluoric Acid
1
This guide is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F01 on Electronics
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F01.06 on Silicon Materials and
Process Control.
Current edition approved Dec. 10, 2002. Published February 2003. Originally
published as F 1809 – 97. Last previous edition F 1809 – 97.
2
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, 11.01
3
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 10.05.
4
Available from Semiconductor Equipment and Materials International, 3081 FIG. 2 Secco Etch With Agitation, Oxidation Stacking Fault, 400x,
Zanker Road, San Jose, CA 95134 (www.semi.org). [100], (1100°C Steam, 80 minutes), ;4 μm removal.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
F1809–02
FIG. 3 Secco Etch Without Agitation, Flow Pattern Defect 200x, FIG. 6 Secco Etch With Agitation, Scratch Induced Oxidation
[100], ;8 μm removal. Stacking Faults, 100x, [100], (1100°C Steam, 80 minutes), ;15 μm
removal.
FIG. 4 Secco Etch With Agitation, Expitaxial Stacking Fault, 150x,
[100], ;4 μm removal. FIG. 7 Wright Etch With Agitation, Damaged Induced Oxidation
Stacking Fault, 1000x, [100], (1100°C Steam, 80 minutes).
FIG. 5 Secco Etch With Agitation, Bulk Oxidation Stacking Fault,
200x, [100], (1100°C Steam, 80 minutes), ;15 μm removal. FIG. 8 Wright Etch With Agitation, Bulk Oxidation Stacking Fault,
500x, [100], (1100°C Steam, 80 minutes).
4. Interferences
4.1 Complicating factors are different for each etchant.
Research the choice of etchants in advance to ensure the 4.1.3 Insufficient agitation, bubble formation or particles in
method and solution are compatible with the sample and the etching solution can generate artifacts on the silicon surface
objectives. Commonly encountered problems are: that mimic actual defects. Insufficien
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.